Abstract
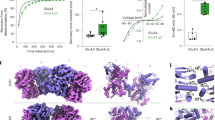
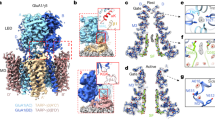
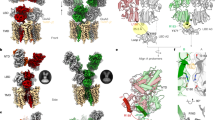
AMPA-subtype glutamate receptors (AMPARs) mediate excitatory synaptic transmission. AMPAR ion channels exhibit multiple subconductance states that tune neuronal responses to glutamate. GluA4 is the rarest subunit in the brain but is enriched in interneurons and the cerebellum. Rising evidence points to GluA4 AMPARs in the development of neurological diseases, but the structural mechanisms of GluA4 function remain enigmatic. Here, we show the distinct features of GluA4 that tune AMPAR function. We find that GluA4 AMPARs have a canonical “Y” shaped architecture where local dimer pairs are domain-swapped between the amino terminal domain (NTD) and ligand binding domain (LBD), both of which comprise the extracellular domain. All four LBDs are glutamate bound yet open the GluA4 ion channel by asymmetric hinging in all four channel helices. We observe that the glutamate-saturated LBD has conformational plasticity, which tunes the ion channel gate below. These data provide a framework for understanding channel subconductance, outline the distinct properties of GluA4, expand our understanding of conformational plasticity in AMPARs, and will inform therapeutic design.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The protein data bank (PDB) and electron microscopy data bank (EMD) accession codes for the GluA4 consensus and substates 1–5 are 9P9B and EMD-71405, 9P9C and EMD-71406, 9P9D and EMD-71407, 9P9E and EMD-71408, 9P9F and EMD-71409, 9P9G and EMD-71410, respectively. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Hansen, K. B. et al. Structure, function, and pharmacology of glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 73, 1469–1658 (2021).
Twomey, E. C. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Structural mechanisms of gating in ionotropic glutamate receptors. Biochemistry 57, 267–276 (2018).
Keinänen, K. et al. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science 249, 556–560 (1990).
Diering, G. H. & Huganir, R. L. The AMPA receptor code of synaptic plasticity. Neuron 100, 314–329 (2018).
Zhao, Y., Chen, S., Swensen, A. C., Qian, W.-J. & Gouaux, E. Architecture and subunit arrangement of native AMPA receptors elucidated by cryo-EM. Science 364, 355–362 (2019).
Cull-Candy, S. G. & Farrant, M. Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors and their auxiliary subunits in synaptic plasticity and disease. J. Physiol. 599, 2655–2671 (2021).
Miguez-Cabello, F. et al. GluA2-containing AMPA receptors form a continuum of Ca2+-permeable channels. Nature 641, 537–544 (2025).
Nakagawa, T., Wang, X., Miguez-Cabello, F. J. & Bowie, D. The open gate of the AMPA receptor forms a Ca2+ binding site critical in regulating ion transport. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 31, 688–700 (2024).
Hong, I. et al. Calcium-permeable AMPA receptors govern PV neuron feature selectivity. Nature 635, 398–405 (2024).
Kwok, K. H. H., Tse, Y. C., Wong, R. N. S. & Yung, K. K. L. Cellular localization of GluR1, GluR2/3 and GluR4 glutamate receptor subunits in neurons of the rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 778, 43–55 (1997).
Mosbacher, J. et al. A molecular determinant for submillisecond desensitization in glutamate receptors. Science 266, 1059–1062 (1994).
Geiger, J. R. P. et al. Relative abundance of subunit mRNAs determines gating and Ca2+ permeability of AMPA receptors in principal neurons and interneurons in rat CNS. Neuron 15, 193–204 (1995).
Swanson, G. T., Kamboj, S. K. & Cull-Candy, S. G. Single-channel properties of recombinant AMPA receptors depend on RNA editing, splice variation, and subunit composition. J. Neurosci. 17, 58–69 (1997).
Yang, Y.-M. et al. GluA4 is indispensable for driving fast neurotransmission across a high-fidelity central synapse. J. Physiol. 589, 4209–4227 (2011).
Chang, M. C. et al. Narp regulates homeostatic scaling of excitatory synapses on parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 1090–1097 (2010).
Pelkey, K. A. et al. Pentraxins Coordinate Excitatory Synapse Maturation and Circuit Integration of Parvalbumin Interneurons. Neuron 85, 1257–1272 (2015).
XiangWei, W. et al. Clinical and functional consequences of GRIA variants in patients with neurological diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 80, 345 (2023).
Beyer, B. et al. Absence seizures in C3H/HeJ and knockout mice caused by mutation of the AMPA receptor subunit Gria4. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 1738–1749 (2008).
Paz, J. T. et al. A new mode of corticothalamic transmission revealed in the Gria4−/− model of absence epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 1167–1173 (2011).
Wang, Y.-X., Wenthold, R. J., Ottersen, O. P. & Petralia, R. S. Endbulb Synapses in the Anteroventral Cochlear Nucleus Express a Specific Subset of AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptor Subunits. J. Neurosci. 18, 1148–1160 (1998).
Gardner, S. M., Trussell, L. O. & Oertel, D. Time course and permeation of synaptic AMPA receptors in cochlear nuclear neurons correlate with input. J. Neurosci. 19, 8721–8729 (1999).
Rubio, M. E. & Wenthold, R. J. Glutamate receptors are selectively targeted to postsynaptic sites in neurons. Neuron 18, 939–950 (1997).
Hunter, C., Petralia, R. S., Vu, T. & Wenthold, R. J. Expression of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits in morphologically defined neurons of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. J. Neurosci. 13, 1932–1946 (1993).
Schmid, S., Guthmann, A., Ruppersberg, J. P. & Herbert, H. Expression of AMPA receptor subunit flip/flop splice variants in the rat auditory brainstem and inferior colliculus. J. Comp. Neurol. 430, 160–171 (2001).
Rubio, M. E. et al. The number and distribution of AMPA receptor channels containing fast kinetic GluA3 and GluA4 subunits at auditory nerve synapses depend on the target cells. Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 3375–3393 (2017).
Schwenk, J. et al. Regional diversity and developmental dynamics of the ampa-receptor proteome in the mammalian brain. Neuron 84, 41–54 (2014).
Gonzalez-Lozano, M. A. et al. Stitching the synapse: Cross-linking mass spectrometry into resolving synaptic protein interactions. Sci. Adv. 6, eaax5783 (2020).
Kita, K. et al. GluA4 facilitates cerebellar expansion coding and enables associative memory formation. eLife https://elifesciences.org/articles/65152, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.65152 (2021).
García-Hernández, S. & Rubio, M. E. Role of GluA4 in the acoustic and tactile startle responses. Hear. Res. 414, 108410 (2022).
Huupponen, J., Atanasova, T., Taira, T. & Lauri, S. E. GluA4 subunit of AMPA receptors mediates the early synaptic response to altered network activity in the developing hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 115, 2989–2996 (2016).
Zhu, J. J., Esteban, J. A., Hayashi, Y. & Malinow, R. Postnatal synaptic potentiation: Delivery of GluR4-containing AMPA receptors by spontaneous activity. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1098–1106 (2000).
Taylor, K. R. et al. Glioma synapses recruit mechanisms of adaptive plasticity. Nature 623, 366–374 (2023).
Stepulak, A. et al. Expression of glutamate receptor subunits in human cancers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 132, 435–445 (2009).
Brocke, K. S. et al. Glutamate receptors in pediatric tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer Biol. Ther. 9, 455–468 (2010).
Tao, Y. et al. Erbin interacts with TARP γ−2 for surface expression of AMPA receptors in cortical interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 290–299 (2013).
Tomita, S. et al. Functional studies and distribution define a family of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins. J. Cell Biol. 161, 805–816 (2003).
Zhang, W., Devi, S. P. S., Tomita, S. & Howe, J. R. Auxiliary proteins promote modal gating of AMPA- and kainate-type glutamate receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 39, 1138–1147 (2014).
Chen, L., Bao, S., Qiao, X. & Thompson, R. F. Impaired cerebellar synapse maturation in waggler, a mutant mouse with a disrupted neuronal calcium channel γ subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 12132–12137 (1999).
Chen, L. et al. Stargazin regulates synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors by two distinct mechanisms. Nature 408, 936–943 (2000).
Hashimoto, K. et al. Impairment of AMPA Receptor Function in Cerebellar Granule Cells of Ataxic Mutant Mouse Stargazer. J. Neurosci. 19, 6027–6036 (1999).
Yelshanskaya, M. V., Patel, D. S., Kottke, C. M., Kurnikova, M. G. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Opening of glutamate receptor channel to subconductance levels. Nature 605, 172–178 (2022).
Zhang, D. et al. Structural mobility tunes signalling of the GluA1 AMPA glutamate receptor. Nature 621, 877–882 (2023).
Rossmann, M. et al. Subunit-selective N-terminal domain associations organize the formation of AMPA receptor heteromers. EMBO J. 30, 959–971 (2011).
Dutta, A., Shrivastava, I. H., Sukumaran, M., Greger, I. H. & Bahar, I. Comparative Dynamics of NMDA- and AMPA-Glutamate Receptor N-Terminal Domains. Structure 20, 1838–1849 (2012).
Nakagawa, T. Structures of the AMPA receptor in complex with its auxiliary subunit cornichon. Science 366, 1259–1263 (2019).
Dürr, K. L. et al. Structure and dynamics of AMPA receptor GluA2 in resting, pre-open, and desensitized states. Cell 158, 778–792 (2014).
Hale, W. D. et al. Allosteric competition and inhibition in AMPA receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-024-01328-0 (2024).
Hale, W. D. et al. Structure of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein subunit γ2. Nat. Commun. 16, 671 (2025).
Kumar Mondal, A., Carrillo, E., Jayaraman, V. & Twomey, E. C. Glutamate gating of AMPA-subtype iGluRs at physiological temperatures. Nature 641, 788–796 (2025).
Vega-Gutiérrez, C. et al. GluA4 AMPA receptor gating mechanisms and modulation by auxiliary proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-025-01666-7 (2025).
Birdsey-Benson, A., Gill, A., Henderson, L. P. & Madden, D. R. Enhanced Efficacy without Further Cleft Closure: Reevaluating Twist as a Source of Agonist Efficacy in AMPA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 30, 1463–1470 (2010).
Smart, O. S., Neduvelil, J. G., Wang, X., Wallace, B. A. & Sansom, M. S. P. HOLE: A program for the analysis of the pore dimensions of ion channel structural models. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 354–360 (1996).
Twomey, E. C., Yelshanskaya, M. V., Grassucci, R. A., Frank, J. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Channel opening and gating mechanism in AMPA-subtype glutamate receptors. Nature 549, 60–65 (2017).
Fang, C. et al. Gating and noelin clustering of native Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. Nature 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09289-0 (2025).
Smith, T. C., Wang, L.-Y. & Howe, J. R. Heterogeneous Conductance Levels of Native AMPA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 20, 2073–2085 (2000).
Prieto, M. L. & Wollmuth, L. P. Gating modes in AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. J. Soc. Neurosci. 30, 4449–4459 (2010).
Smith, T. C. & Howe, J. R. Concentration-dependent substate behavior of native AMPA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 992–997 (2000).
Rosenmund, C., Stern-Bach, Y. & Stevens, C. F. The tetrameric structure of a glutamate receptor channel. Science 280, 1596–1599 (1998).
Poon, K., Nowak, L. M. & Oswald, R. E. Characterizing single-channel behavior of GluA3 receptors. Biophys. J. 99, 1437–1446 (2010).
Shi, E. Y. et al. Noncompetitive antagonists induce cooperative AMPA receptor channel gating. J. Gen. Physiol. 151, 156–173 (2019).
Yuan, C. L. et al. Modulation of AMPA receptor gating by the anticonvulsant drug, perampanel. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 10, 237–242 (2019).
Robert, A. & Howe, J. R. How AMPA receptor desensitization depends on receptor occupancy. J. Neurosci. 23, 847–858 (2003).
Zhang, W., Cho, Y., Lolis, E. & Howe, J. R. Structural and Single-Channel Results Indicate That the Rates of Ligand Binding Domain Closing and Opening Directly Impact AMPA Receptor Gating. J. Neurosci. 28, 932–943 (2008).
Pokharna, A. et al. Architecture, dynamics and biogenesis of GluA3 AMPA glutamate receptors. Nature 645, 535–543 (2025).
Wang, H., Ahmed, F., Khau, J., Mondal, A. K. & Twomey, E. C. Delta-type glutamate receptors are ligand-gated ion channels. Nature 647, 1063–1071 (2025).
Soto, D. et al. Selective regulation of long-form calcium-permeable AMPA receptors by an atypical TARP, γ-5. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 277–285 (2009).
Klykov, O., Gangwar, S. P., Yelshanskaya, M. V., Yen, L. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Structure and desensitization of AMPA receptor complexes with type II TARP γ5 and GSG1L. Mol. Cell 81, 4771–4783.e7 (2021).
Gangwar, S. P. et al. Modulation of GluA2–γ5 synaptic complex desensitization, polyamine block and antiepileptic perampanel inhibition by auxiliary subunit cornichon−2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 30, 1481–1494 (2023).
Shelley, C., Farrant, M. & Cull-Candy, S. G. TARP-associated AMPA receptors display an increased maximum channel conductance and multiple kinetically distinct open states. J. Physiol. 590, 5723–5738 (2012).
Twomey, E. C., Yelshanskaya, M. V., Grassucci, R. A., Frank, J. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Elucidation of AMPA receptor-stargazin complexes by cryo-electron microscopy. Science 353, 83–86 (2016).
Twomey, E. C., Yelshanskaya, M. V., Grassucci, R. A., Frank, J. & Sobolevsky, A. I. Structural bases of desensitization in AMPA receptor-auxiliary subunit complexes. Neuron 94, 569–580.e5 (2017).
Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).
Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 30, 70–82 (2021).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Croll, T. I. ISOLDE: a physically realistic environment for model building into low-resolution electron-density maps. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Struct. Biol. 74, 519–530 (2018).
Liebschner, D. et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Struct. Biol. 75, 861–877 (2019).
Morin, A. et al. Collaboration gets the most out of software. eLife 2, e01456 (2013).
Williams, C. J. et al. MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 27, 293–315 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank R. Johnson and C. Warrick for their assistance with developing the GluA4 expression system. We also thank members of the Huganir and Twomey labs for comments and helpful discussion. All cryo-EM data were collected at the Beckman Center for Cryo-EM at Johns Hopkins with assistance from D. Sousa, D. Ding and K. Cai. W.D.H. is supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant K99 MH132811. R.L.H. is supported by NIH grant R37 NS036715. E.C.T. is supported by NIH grant R35GM154904, the Searle Scholars Program (Kinship Foundation 22098168) and the Diana Helis Henry Medical Research Foundation (142548).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.D.H., R.L.H., and E.C.T. designed the study. W.D.H. and H.W. carried out the experiments. W.D.H., H.W., R.L.H., and E.C.T. analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
R.L.H. is a scientific cofounder and scientific advisory board (SAB) member of Neumora Therapeutics and an SAB member of MAZE Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Dylan Hale, W., Wang, H., Huganir, R.L. et al. Structural basis for activation and conformational plasticity of the GluA4 AMPA receptor. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68953-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68953-9