Abstract
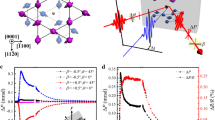
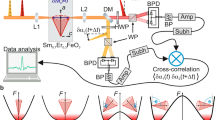
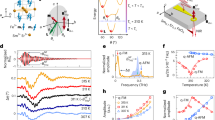
Antiferromagnets have gained a growing interest for next-generation spintronic applications. Among them, the antiferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Mn3Sn stands out because of its electrical and magnetic properties driven by its non-collinear spin structure at room temperature. Despite research progress on the current-induced switching of the magnetic octupole in Mn3Sn, the ultrafast switching inherent to the antiferromagnet remains to be resolved, and the underlying mechanism is yet elusive. Here we measure the spatiotemporally resolved current-induced switching dynamics in polycrystalline Mn3Sn films using ultrafast magneto-optical Kerr effect imaging, with current pulses as short as 140 ps. Our results directly reveal two distinct switching regimes depending on the intensity and duration of the current pulse: a non-thermal process that does not require the transient melting of antiferromagnetic order, and a temperature-assisted process that relies on heating above the magnetic ordering temperature. Our work highlights the potential of Mn3Sn towards ultrafast magnetic recording devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data that support the findings of this work are available in the Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Satoh, T. et al. Spin oscillations in antiferromagnetic NiO triggered by circularly polarized light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 077402 (2010).
Bossini, D. et al. Macrospin dynamics in antiferromagnets triggered by sub-20 femtosecond injection of nanomagnons. Nat. Commun. 7, 10645 (2016).
Jungwirth, T., Marti, X., Wadley, P. & Wunderlich, J. Antiferromagnetic spintronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 231–241 (2016).
Baltz, V. et al. Antiferromagnetic spintronics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 90, 015005 (2018).
Li, J. et al. Spin current from sub-terahertz-generated antiferromagnetic magnons. Nature 578, 70–74 (2020).
Vaidya, P. et al. Subterahertz spin pumping from an insulating antiferromagnet. Science 368, 160–165 (2020).
Bai, H. et al. Functional antiferromagnets for potential applications on high-density storage and high frequency. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 210901 (2020).
Miwa, S. et al. Giant effective damping of octupole oscillation in an antiferromagnetic Weyl semimetal. Small Sci. 1, 2000062 (2021).
Jhuria, K. et al. Spin–orbit torque switching of a ferromagnet with picosecond electrical pulses. Nat. Electron. 3, 680–686 (2020).
Garello, K. et al. Ultrafast magnetization switching by spin-orbit torques. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 212402 (2014).
Polley, D. et al. Picosecond spin-orbit torque–induced coherent magnetization switching in a ferromagnet. Sci. Adv. 9, eadh5562 (2023).
Díaz, E. et al. Energy-efficient picosecond spin–orbit torque magnetization switching in ferro- and ferrimagnetic films. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 36–42 (2025).
Yang, Y. et al. Ultrafast magnetization reversal by picosecond electrical pulses. Sci. Adv. 3, e1603117 (2017).
Nakatsuji, S., Kiyohara, N. & Higo, T. Large anomalous Hall effect in a non-collinear antiferromagnet at room temperature. Nature 527, 212–215 (2015).
Higo, T. et al. Anomalous Hall effect in thin films of the Weyl antiferromagnet Mn3Sn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 202402 (2018).
Ikeda, T. et al. Anomalous Hall effect in polycrystalline Mn3Sn thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 222405 (2018).
Ikhlas, M. et al. Large anomalous Nernst effect at room temperature in a chiral antiferromagnet. Nat. Phys. 13, 1085–1090 (2017).
Li, X. et al. Anomalous Nernst and Righi-Leduc effects in Mn3Sn: Berry curvature and entropy flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 056601 (2017).
Higo, T. et al. Large magneto-optical Kerr effect and imaging of magnetic octupole domains in an antiferromagnetic metal. Nat. Photon. 12, 73–78 (2018).
Kuroda, K. et al. Evidence for magnetic Weyl fermions in a correlated metal. Nat. Mater. 16, 1090–1095 (2017).
Nakatsuji, S. & Arita, R. Topological magnets: functions based on Berry phase and multipoles. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 13, 119–142 (2022).
Suzuki, M.-T., Koretsune, T., Ochi, M. & Arita, R. Cluster multipole theory for anomalous Hall effect in antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 95, 094406 (2017).
Nomoto, T. & Arita, R. Cluster multipole dynamics in noncollinear antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 012045 (2020).
Železný, J., Zhang, Y., Felser, C. & Yan, B. Spin-polarized current in noncollinear antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 187204 (2017).
Kimata, M. et al. Magnetic and magnetic inverse spin Hall effects in a non-collinear antiferromagnet. Nature 565, 627–630 (2019).
Rout, P. K., Madduri, P. V. P., Manna, S. K. & Nayak, A. K. Field-induced topological Hall effect in the noncoplanar triangular antiferromagnetic geometry of Mn3Sn. Phys. Rev. B 99, 094430 (2019).
Wang, X. et al. Topological Hall effect in thin films of an antiferromagnetic Weyl semimetal integrated on Si. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 7572–7577 (2023).
Li, X. et al. Chiral domain walls of Mn3Sn and their memory. Nat. Commun. 10, 3021 (2019).
Chen, X. et al. Octupole-driven magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnetic tunnel junction. Nature 613, 490–495 (2023).
Tsai, H. et al. Electrical manipulation of a topological antiferromagnetic state. Nature 580, 608–613 (2020).
Higo, T. et al. Perpendicular full switching of chiral antiferromagnetic order by current. Nature 607, 474–479 (2022).
Xie, H. et al. Magnetization switching in polycrystalline Mn3Sn thin film induced by self-generated spin-polarized current. Nat. Commun. 13, 5744 (2022).
Zheng, Z. et al. Effective electrical manipulation of a topological antiferromagnet by orbital torques. Nat. Commun. 15, 745 (2024).
Sugimoto, S. et al. Electrical nucleation, displacement, and detection of antiferromagnetic domain walls in the chiral antiferromagnet Mn3Sn. Commun. Phys. 3, 111 (2020).
Wu, M. et al. Current-driven fast magnetic octupole domain-wall motion in noncollinear antiferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 15, 4305 (2024).
Sakamoto, S. et al. Antiferromagnetic spin-torque diode effect in a kagome Weyl semimetal. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 216–221 (2025).
Yamada, S. et al. Observation of electrical fast switching in the antiferromagnet Mn3Sn. Meeting Abstracts Phys. Soc. Jpn 16aSK314-8, 1288 (2025).
Krishnaswamy, G. K. et al. Time-dependent multistate switching of topological antiferromagnetic order in Mn3Sn. Phys. Rev. Appl. 18, 024064 (2022).
Takeuchi, Y. et al. Chiral-spin rotation of non-collinear antiferromagnet by spin–orbit torque. Nat. Mater. 20, 1364–1370 (2021).
Yan, G. Q. et al. Quantum sensing and imaging of spin–orbit-torque-driven spin dynamics in the non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn. Adv. Mater. 34, 2200327 (2022).
Yoon, J.-Y. et al. Handedness anomaly in a non-collinear antiferromagnet under spin–orbit torque. Nat. Mater. 22, 1106–1113 (2023).
Shukla, A., Qian, S. & Rakheja, S. Order parameter dynamics in Mn3Sn driven by d.c. and pulsed spin–orbit torques. APL Mater. 11, 091110 (2023).
Xu, Z. et al. Deterministic spin-orbit torque switching including the interplay between spin polarization and kagome plane in Mn3Sn. Phys. Rev. B 109, 134433 (2024).
Pal, B. et al. Setting of the magnetic structure of chiral kagome antiferromagnets by a seeded spin-orbit torque. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo5930 (2022).
Kobayashi, Y., Shiota, Y., Narita, H., Ono, T. & Moriyama, T. Pulse-width dependence of spin–orbit torque switching in Mn3Sn/Pt thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 122, 122405 (2023).
Yoo, M.-W., Lorenz, V. O., Hoffmann, A. & Cahill, D. G. Thermal contribution to current-driven antiferromagnetic-order switching. APL Mater. 12, 081107 (2024).
Ogawa, K. et al. Ultrafast stroboscopic time-resolved magneto-optical imaging of domain wall motion in Pt/GdFeCo wires induced by a current pulse. Phys. Rev. Res. 5, 033151 (2023).
Schlauderer, S. et al. Temporal and spectral fingerprints of ultrafast all-coherent spin switching. Nature 569, 383–387 (2019).
Baumgartner, M. et al. Spatially and time-resolved magnetization dynamics driven by spin–orbit torques. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 980–986 (2017).
Cai, K. et al. Ultrafast and energy-efficient spin–orbit torque switching in compensated ferrimagnets. Nat. Electron. 3, 37–42 (2020).
Matsuo, T. et al. Crossover between intrinsic and temperature-assisted regimes in spin-orbit torque switching of antiferromagnetic order. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.27138 (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a JST-MIRAI program (JPMJMI20A1). K.O. acknowledges financial support from JSPS KAKENHI (grant number JP24KJ0653). We are grateful to K. Kondo for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.O. carried out the optical experiments and analysed the data. K.O. and N.Y. developed the ultrafast TR-MOKE measurement system under the supervision of R.S. H.T. and T. Matsuda optimized the device structure for the TR-MOKE measurements with feedback from K.O., S.N. and R.S. T. Matsuo, Y.T., M.A., H.P. and T.H. grew and characterized the thin films. H.T. fabricated the Hall-bar devices and conducted the transport measurements of current-induced switching phenomena under the supervision of S.N. S.N. and R.S. conceived the project of this study. K.O. and R.S. wrote the manuscript with feedback from all co-authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks Davide Bossini, Zhiqi Liu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections 1–15 and Figs. 1–15.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ogawa, K., Tsai, H., Yoshikawa, N. et al. Ultrafast time-resolved observation of non-thermal current-induced switching in an antiferromagnetic Weyl semimetal. Nat. Mater. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02402-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02402-8
This article is cited by
-
Speeding up antiferromagnetic switching
Nature Materials (2025)