Abstract
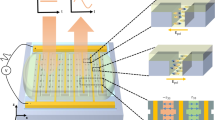
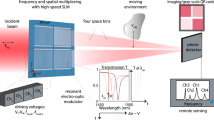
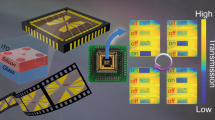
Active metasurfaces incorporating electro-optic materials enable high-speed free-space optical modulators that show great promise for a wide range of applications, including optical communication, sensing and computing. However, the limited light–matter interaction lengths in metasurfaces typically require high driving voltages exceeding tens of volts to achieve satisfactory modulation. Here we present low-voltage, high-speed free-space optical modulators based on silicon-organic-hybrid metasurfaces with dimerized-grating-based nanostructures. By exploiting a high-Q resonant mode, normally incident light is effectively trapped within a submicrometre-scale silicon slot region embedded with organic electro-optic material. Consequently, highly efficient modulation is obtained, enabling data transmission at 50 Mbps and 1.6 Gbps with driving voltages of only 0.2 V and 1 V, respectively. These metasurface modulators can now operate at complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor-compatible voltage levels, allowing energy-efficient high-speed practical applications of active metasurfaces.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All numerical data are available via figshare at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28281509 (ref. 59). Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Yu, N. et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334, 333–337 (2011).
Kuznetsov, A. I. et al. Roadmap for optical metasurfaces. ACS Photon. 11, 816–865 (2024).
Chen, W. T. et al. A broadband achromatic metalens for focusing and imaging in the visible. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 220–226 (2018).
Wang, S. et al. A broadband achromatic metalens in the visible. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 227–232 (2018).
Rubin, N. A. et al. Matrix Fourier optics enables a compact full-Stokes polarization camera. Science 365, eaax1839 (2019).
Miyata, M., Nemoto, N., Shikama, K., Kobayashi, F. & Hashimoto, T. Full-color-sorting metalenses for high-sensitivity image sensors. Optica 8, 1596–1604 (2021).
Balthasar Mueller, J. P., Rubin, N. A., Devlin, R. C., Groever, B. & Capasso, F. Metasurface polarization optics: independent phase control of arbitrary orthogonal states of polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 113901 (2017).
Xiong, B. et al. Breaking the limitation of polarization multiplexing in optical metasurfaces with engineered noise. Science 379, 294–299 (2023).
Gopakumar, M. et al. Full-colour 3D holographic augmented-reality displays with metasurface waveguides. Nature 629, 791–797 (2024).
Oh, J. et al. Adjoint-optimized metasurfaces for compact mode-division multiplexing. ACS Photon. 9, 929–937 (2022).
Soma, G. et al. Compact and scalable polarimetric self-coherent receiver using a dielectric metasurface. Optica 10, 604–611 (2023).
Komatsu, K. et al. Scalable multi-core dual-polarization coherent receiver using a metasurface optical hybrid. J. Light. Technol. 42, 4013–4022 (2024).
Li, S.-Q. et al. Phase-only transmissive spatial light modulator based on tunable dielectric metasurface. Science 364, 1087–1090 (2019).
Holsteen, A. L., Cihan, A. F. & Brongersma, M. L. Temporal color mixing and dynamic beam shaping with silicon metasurfaces. Science 365, 257–260 (2019).
Zhang, Y. et al. Electrically reconfigurable non-volatile metasurface using low-loss optical phase-change material. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 661–666 (2021).
Shaltout, A. M., Shalaev, V. M. & Brongersma, M. L. Spatiotemporal light control with active metasurfaces. Science 364, eaat3100 (2019).
Wu, P. C. et al. Dynamic beam steering with all-dielectric electro-optic III–V multiple-quantum-well metasurfaces. Nat. Commun. 10, 3654 (2019).
Park, J. et al. All-solid-state spatial light modulator with independent phase and amplitude control for three-dimensional LiDAR applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 69–76 (2021).
Panuski, C. L. et al. A full degree-of-freedom spatiotemporal light modulator. Nat. Photon. 16, 834–842 (2022).
Sisler, J. et al. Electrically tunable space-time metasurfaces at optical frequencies. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 1491–1498 (2024).
Ren, F. et al. Surface-normal plasmonic modulator using sub-wavelength metal grating on electro-optic polymer thin film. Opt. Commun. 352, 116–120 (2015).
Zhang, J., Kosugi, Y., Otomo, A., Nakano, Y. & Tanemura, T. Active metasurface modulator with electro-optic polymer using bimodal plasmonic resonance. Opt. Express 25, 30304–30311 (2017).
Miyano, H. et al. Dimerized plasmonic-organic grating for high-speed metasurface modulator. In OptoElectronics and Communications Conference/International Conference on Photonics in Switching and Computing TuD3-2 (IEEE, 2022).
Sun, X. et al. Manipulating dual bound states in the continuum for efficient spatial light modulator. Nano Lett. 22, 9982–9989 (2022).
Zhang, J. et al. High-speed metasurface modulator using perfectly absorptive bimodal plasmonic resonance. APL Photon. 8, 121304 (2023).
Zhang, L. et al. Plasmonic metafibers electro-optic modulators. Light Sci. Appl. 12, 198 (2023).
Benea-Chelmus, I.-C. et al. Electro-optic spatial light modulator from an engineered organic layer. Nat. Commun. 12, 5928 (2021).
Sun, X. et al. Electro-optic polymer and silicon nitride hybrid spatial light modulators based on a metasurface. Opt. Express 29, 25543–25551 (2021).
Sun, X. & Qiu, F. Polarization independent high-speed spatial modulators based on an electro-optic polymer and silicon hybrid metasurface. Photon. Res. 10, 2893 (2022).
Benea-Chelmus, I.-C. et al. Gigahertz free-space electro-optic modulators based on Mie resonances. Nat. Commun. 13, 3170 (2022).
Ogasawara, M. et al. Electro-optic polymer surface-normal modulator using silicon high-contrast grating resonator. In Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics JTh2A.48 (2019).
Zheng, T., Gu, Y., Kwon, H., Roberts, G. & Faraon, A. Dynamic light manipulation via silicon-organic slot metasurfaces. Nat. Commun. 15, 1557 (2024).
Kosugi, Y., Yamada, T., Otomo, A., Nakano, Y. & Tanemura, T. Surface-normal electro-optic-polymer modulator with silicon subwavelength grating. IEICE Electron. Express 13, 20160595–20160595 (2016).
Fukui, T. et al. 17 GHz lossless InP-membrane active metasurface. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2505.07072 (2025).
Damgaard-Carstensen, C., Thomaschewski, M. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Electro-optic metasurface-based free-space modulators. Nanoscale 14, 11407–11414 (2022).
Damgaard-Carstensen, C. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Nonlocal electro-optic metasurfaces for free-space light modulation. Nanophotonics 12, 2953–2962 (2023).
Damgaard-Carstensen, C., Yezekyan, T., Brongersma, M. L. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Highly efficient, tunable, electro-optic, reflective metasurfaces based on quasi-bound states in the continuum. ACS Nano 19, 11999–12006 (2025).
Weigand, H. et al. Enhanced electro-optic modulation in resonant metasurfaces of lithium niobate. ACS Photon. 8, 3004–3009 (2021).
Trajtenberg-Mills, S. et al. LNoS: lithium niobate on silicon spatial light modulator. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.14608 (2024).
Di Francescantonio, A. et al. Efficient GHz electro-optical modulation with a nonlocal lithium niobate metasurface in the linear and nonlinear regime. Nat. Commun. 16, 7000 (2025).
Ju, Y., Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., Deng, X. & Zuo, H. Polarization independent lithium niobate electro-optic modulator based on guided mode resonance. Opt. Mater. 148, 114928 (2024).
Karvounis, A. et al. Electro-optic metasurfaces based on barium titanate nanoparticle films. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 2000623 (2020).
Weigand, H. C. et al. Nanoimprinting solution-derived barium titanate for electro-optic metasurfaces. Nano Lett. 24, 5536–5542 (2024).
Weiss, A. et al. Tunable metasurface using thin-film lithium niobate in the telecom regime. ACS Photon. 9, 605–612 (2022).
Overvig, A. C., Shrestha, S. & Yu, N. Dimerized high contrast gratings. Nanophotonics 7, 1157–1168 (2018).
Jin, W. et al. Benzocyclobutene barrier layer for suppressing conductance in nonlinear optical devices during electric field poling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 243304 (2014).
Kieninger, C. et al. Ultra-high electro-optic activity demonstrated in a silicon-organic hybrid modulator. Optica 5, 739–748 (2018).
Sun, K., Wang, W. & Han, Z. High-Q resonances in periodic photonic structures. Phys. Rev. B 109, 085426 (2024).
Koshelev, K., Lepeshov, S., Liu, M., Bogdanov, A. & Kivshar, Y. Asymmetric metasurfaces with high-Q resonances governed by bound states in the continuum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 193903 (2018).
Joannopoulos, J. D., Johnson, S. G., Winn, J. N. & Meade, R. D. Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light—Second Edition (Princeton Univ. Press, 2008).
Chang, F., Onohara, K. & Mizuochi, T. Forward error correction for 100 G transport networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48, S48–S55 (2010).
Chen, Z. et al. Observation of miniaturized bound states in the continuum with ultra-high quality factors. Sci. Bull. 67, 359–366 (2022).
Dolia, V. et al. Very-large-scale-integrated high quality factor nanoantenna pixels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 1290–1298 (2024).
Ledentsov, N. et al. High speed VCSEL technology and applications. J. Light. Technol. 40, 1749–1763 (2022).
Ren, C., Komatsu, K., Soma, G., Nakano, Y. & Tanemura, T. Metasurface-based functional optical splitter for a spatially parallelized dual-polarization coherent modulator. Opt. Lett. 49, 7238–7241 (2024).
Morita, R. et al. High-speed high-power free-space optical communication via directly modulated watt-class photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers. Optica 11, 971 (2024).
Hammond, S. R., Elder, D. L. & Johnson, L. E. Plasmonic organic hybrid electro-optic modulators as a platform for process optimization towards extraordinary nonlinearity and exceptional stability enabling commercial applications. Proc. SPIE 12418, Organic Photonic Materials and Devices XXV 1241807 (SPIE, 2023).
Xu, H. et al. Ultrahigh electro-optic coefficients, high index of refraction, and long-term stability from Diels–Alder cross-linkable binary molecular glasses. Chem. Mater. 32, 1408–1421 (2020).
Soma, G. et al. Subvolt high-speed free-space modulator with electro-optic metasurface. Figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28281509 (2025).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Y. Nakano and A. Otomo for their support and fruitful discussions. G.S. thanks K. Saito for his help in building the measurement system. T.T. and G.S. thank Z. Han for providing insightful comments. T.T. thanks K. Ueda for fruitful discussions and his encouragement. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI, grant numbers JP23H05444 (T.T.) and JP24KJ0557 (G.S.). The device was fabricated in part at Takeda Cleanroom with help of Nanofabrication Platform Center of School of Engineering, the University of Tokyo, Japan, supported by ‘Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan’ of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), grant number JPMXP1224UT1115 (T.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.S. and T.T. conceived the device concept and experiments. G.S. performed the metasurface design, simulation, fabrication and experiments. K.A. developed the OEO process, constructed the poling set-up and assisted with the poling process. S.K. assisted with numerical simulation. Y.T. assisted with device fabrication. G.S. and T.T. wrote the paper with inputs from all authors. T.T. supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
G.S. and T.T. are listed as inventors in a patent application related to this work, filed by the University of Tokyo, application number 2025-41949. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Nanotechnology thanks Hyounghan Kwon and Cosmin-Constantin Popescu for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Extended Data Fig. 1 Benchmark comparison of this work against previously reported electro-optic metasurface modulators.
The modulation swing ΔR (top panel vertical axis), bandwidth (bottom panel vertical axis), and the required voltage Vreq to shift the resonance wavelength by an amount equal to its linewidth (horizontal axis) of experimentally demonstrated EO metasurface modulators in the literature. Our presented device exhibits the lowest Vreq and the highest modulation efficiency η = ΔR/Vreq. The bandwidth is also the highest among all dielectric resonating devices. The numerical values are listed in Extended Data Table 1.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections 1–4, Figs. 1–10 and Tables 1 and 2.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Source data of Fig. 1.
Source Data Fig. 2
Source data of Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Source data of Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Source data of Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soma, G., Ariu, K., Karakida, S. et al. Subvolt high-speed free-space modulator with electro-optic metasurface. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 1625–1632 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-025-02000-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-025-02000-4