Abstract
GeoCrack is the first large-scale open source annotated dataset of fracture traces from geological outcrops, enabling deep learning-based fracture segmentation, setting a new standard for natural fracture characterization datasets. GeoCrack contains images from photogrammetric surveys of fractured rock exposures across 11 sites in Europe and the Middle East, capturing diverse lithologies and tectonic settings. Each image was cleaned, normalized, and manually segmented, followed by a recursive annotation vetting process to ensure the quality and accuracy of the digitized fracture edges. The processed images and corresponding binary masks were divided into 224 × 224 patches, yielding 12,158 pairs. GeoCrack captures representive real-world challenges in fracture edge annotation, such as contrast variations between fracture traces and the host medium due to geological and geomorphological factors like aperture dilation, host rock composition, outcrop weathering, and groundwater staining. Physical occlusions like shadows and vegetation are also considered to minimize false positives. GeoCrack was validated using a U-Net implementation for fracture segmentation, achieving satisfactory IoU of 85%. GeoCrack holds strong potential to advance deep fracture segmentation in geological applications, effectively tackling the diverse challenges of real-world fracture identification.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background & Summary
The analysis of fracture networks hosted within rock formations represents a key component of many geoscience, geoengineering and geotechnical engineering workflows. For example, natural fracture systems impart petrophysical anisotropy within the upper crust, often playing an integral role in the movement and trapping of mobile geofluids within both porous and crystalline geologic media, and determining the pathways and eventual fates of contaminants released into the shallow subsurface. Consequently, the characterization and modelling of fracture networks represents a first order consideration within numerous subsurface engineering applications, including CO2 sequestration1, hydrocarbon and geothermal reservoir characterization2,3, and nuclear waste geological disposal facility site appraisal4. Furthermore, fracture networks govern rock mass strength, with the relative density of natural and induced fractures forming key inputs into rock mass classification schemes, commonly used to evaluate slope stability and steer the safe implementation of engineering structures, such as bridge footings, dam foundations, and tunnel portals5. Finally, discontinuity networks often formed the locus of strain accommodation during deformation within the brittle crust6, acting as an archive for paleostress fields, aiding the study of ancient plate kinematics7,8.
While fracture systems can be observed in-situ via quasi-1D sampling of wellbore micro-resistivity images and core9, rock exposures at the Earth’s surface are the most common medium used for the study of discontinuity network geometry10,11,12,13,14,15, both directly for rock mass classification and as analogues for subsurface equivalents. The intersection of a quasi-planar discontinuity with the rock exposure is typically expressed as a lineament or trace2,16. Fracture characterization studies seek to interrogate these structural traces to elicit the key properties (e.g., size, intensity, topology) of the underlying fracture network, either through manual surveys2 or digitization of trace maps from remotely sensed imagery (esp. RGB photography11,13). With respect to fracture characterization from outcrop images, considerable effort has been expended over the past several decades to automate trace map digitization. Conventionally, these efforts have focused upon the use of classic edge detection algorithms which leverage discontinuities in pixel intensity (e.g., Hough Transform, Sobel, Canny, Phase Congruency13,17,18,19,20). More recently, deep-learning based edge detection/segmentation has emerged as a powerful tool for the automatic extraction of structural traces21,22,23, potentially overcoming key limitations of classic pixel intensity-based approaches, such as challenging manual parameter selection and the unwanted detection of non-trace objects.
Presently, there is an ostensible lack of comprehensive and standardized datasets focused on fracture edges in outcrop images, which acts as a major bottleneck restricting the development and benchmarking of deep learning-based semantic edge segmentation approaches for the automated extraction of structural traces from rock exposures. Existing research is often fragmented and lacks large-scale, high-precision annotated image edge datasets which are common within other scientific disciplines (i.e., materials science24, civil infrastructure25,26,27, food recognition28, and biomedical imaging29,30,31). To address this gap, we have developed a first-of-a-kind extensive dataset of annotated fracture edges, amenable to the training and testing of diverse deep learning architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs)32,33,34,35,36 and Vision Transformers (ViTs). This dataset includes images of rock outcrops from 11 geologically diverse and extensively characterized study areas, with digital photographs captured using both terrestrial and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) based surveys. A subset of 49 representative high-quality images has been selected from this global database and subjected to filtering, cleaning, and manual annotation. The selected images contain a variety of fracture geometries, as well as non-fracture scene elements (e.g., roots, shadows) which give rise to false positives during edge segmentation, providing a test-bed for automated discontinuity extraction under real-world conditions. Annotation quality was maintained using both peer-to-peer evaluations between operators and consultation with structural geologists, ensuring pixel-level accuracy and objective validity. Vetted annotated images were split into 224 × 224 patches suited for deep learning model training, which were further vetted for image quality and fracture density, resulting in 12158 patches containing 127659 individual fracture edges. To demonstrate the utility of the GeoCrack dataset37 for deep edge segmentation model development, we have implemented a U-Net classifier trained with a subset of 1245 patches. With an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 85% and a pixel accuracy of 92%, this rudimentary model demonstrates the GeoCrack’s utility for deep learning model development for geological fracture edge segmentation tasks. Consequently, we believe that the GeoCrack dataset37 holds substantial potential not only for semantic edge segmentation routines but also as a foundation for future multi-class segmentation efforts that could incorporate additional classes such as vegetation and fractures. This expansion promises to be transformative towards numerous geoscientific, geoengineering, and geotechnical application areas, such as fractured outcrop analog modeling, rock mass classification, and paleotectonic reconstruction.
Methods
Compilation of the GeoCrack dataset37 involved the following stages: (1) photogrammetric survey acquisition and preprocessing, (2) manual annotation of fracture traces, (3) verification and correction of annotated edge masks, (4) extraction and retention of optimal image-mask patches using a smart patch retention algorithm, and (5) final verification and compilation of the complete dataset (see Fig. 1). Detailed descriptions of these steps are provided below to ensure reproducibility and facilitate future expansion of the dataset towards different lithologies and/or structural domains.
Image acquisition, selection, preprocessing
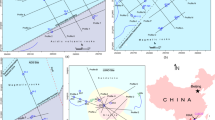
Images were acquired during photogrammetric survey campaigns conducted within Europe (Greece, Malta, and Italy) and the Middle East (Oman and the United Arab Emirates), mapping naturally fractured outcrops. Surveys targeted a range of lithologies (carbonate and clastic sedimentary rocks, crystalline ultramafic igneous rocks), hosting different styles of discontinuities (e.g., joints, faults, shear fractures, styolites) formed a variety of stress regimes (see Table 1). Surveys were conducted using both unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and terrestrial image capture using a range of camera models and lenses (see Table 2). An advantage of photogrammetric surveys in the context of the current dataset is that the high degree of image overlap required for surface reconstruction produces redundancy in outcrop coverage, providing a large database for optimum image selection. Moreover, the photogrammetric post-processing of the photo-survey dataset also facilitates the removal of lens distortion effects via self calibration38. However, terrestrial and aerial surveys were conducted using prime lenses in order to minimize distortion aberrations. Images were collected using photogrammetric survey best practices outlined in Tavani et al.39. For example, surveys were conducted wherever possible under a limited time window with cloud cover and/or the sun behind the camera to ensure homogeneous illumination and to minimize shadowing and lens flare. Moreover, where possible images were captured orthonormally and equidistant to the target exposure surfaces to minimize perspective effects and disparities in ground sampling distance (the distance between two neighboring pixel centroids as measured on the ground: GSD) across individual surveys.
We implemented stringent quality control measures to select a subset of representative images from each site, ensuring that only those with a minimum resolution of 300 DPI and dimensions of 4032 × 3024 pixels were retained post-cropping to remove non-geological scene elements. Survey distances varied from several meters to several tens of meters depending on the scale of the exposure and accessibility. Images were chosen based on fracture density and excluded if they had low exposure or significant non-geological elements, such as sky, foreground, drift, vegetation, or were heavily impacted by optical artifacts, such as lens flare or diffraction spikes. Motion blur was quantified using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), with a threshold set at less than 0.5% deviation in pixel alignment consistency, following empirical studies that indicate this limit minimizes perceptible blur40,41. Aliasing was assessed using Fourier analysis, ensuring high-frequency artifacts did not exceed 2% of the total image spectrum, as supported by literature on spatial accuracy42,43. Our quantitative analysis revealed an average motion blur deviation of 0.3% and a 12% discard rate due to artifacts, demonstrating the robustness of our selection criteria.
For compilation of the present dataset, fracture identification and delineation are performed manually, leveraging the textural expression of discontinuities on the imaged exposure surfaces. When exposed at the earth’s surface, fractures typically appear as linear or curvilinear objects, detectable as a visible discontinuity within the exposed rock mass. In outcrop, fractures can vary significantly in size, from hairline cracks to laterally extensive fissures with broad apertures. It should be noted that the ability to detect a given discontinuity from an image is heavily dependent upon numerous factors. GSD (itself a function of image resolution and distance to the targeted exposure surface) and the apparent fracture aperture (which can be positively correlated to fracture size44,45) arguably offer the primary controls over the detectability of a given fracture. Additionally, the degree of contrast between fracture trace and its host medium depends upon a multitude of geological, geomechanical, and geomorphological factors, such as the occurrence and relative magnitude of displacement across the discontinuity plane (i.e., in the case of faults), host rock composition and color, the degree of outcrop induration and weathering, the presence of fracture cement and/or discoloration/staining related to groundwater seepage, all of which may serve to highlight or obfuscate the target discontinuity. Physical occlusions, such as the presence of shadows, drift, and vegetation/roots may also hamper fracture identification (Fig. 2D). In some cases, scene artifacts such as surficial staining and shadowing may even mimic the appearance of cracks (Fig. 2B,C), potentially resulting in false positives during fracture identification. In addition, not all compositional and/or structural discontinuities within the rock mass constitute fracture traces, which may result in the erroneous annotation of non-fracture objects. Bedding interfaces, sedimentary structures, and stylolites, which form coevally to the deposition of sedimentary rocks and preclude brittle deformation, can represent pronounced lineations within the rock mass. Man-made discontinuities related to excavation and extraction activities, such as blast holes, which mimic the presence of geologic fractures (Fig. 2A), represent additional sources of error during fracture identification. Finally, the geometry and topology of the fracture network itself impact the operator’s ability to identify individual fracture traces, with blind fractures isolated within the rock mass (see Seers et al.13) generally being more readily separable than complex branching or anatomizing discontinuity forms.
It is clear from the above discussion that the ability to detect and delineate a given fracture is highly case-specific, meaning that it is challenging to define unifying rules in terms of optimum image capture parameters, target image spatial resolution with respect to the feature resolution of the discontinuity network, or minimum cut-offs in terms of fracture trace length or aperture (i.e., in pixel units) with respect to fracture detectability. The diverse range of conditions and confounding elements in the selected images that constitute Geocrack37 highlights the real-world nature of the dataset and underlines the need for robust crack segmentation algorithms capable of handling such complexities (see Fig. 3). Rather than omit challenging scene elements, an effort was expended to include images that contain occlusions and scene elements that are potential false positives within an automated fracture detection routine. Indeed, the primary motivation behind the compilation of GeoCrack37 is to develop a standardized structural trace image database that can act as a test bed for deep learning-based fracture segmentation techniques, subject to real-world conditions.
Examples of diverse fracture edges in the dataset, showcasing various annotation challenges. (A) Rock overhang obscuring fracture traces; (B) multiple parallel discontinuities resulting in step-like outcrop topography; (C) roots occluding fractures traces; (D) dilated fissures resulting in shadow occlusions; (E) surficial weathering introducing textural complexity, obfuscating trace identification; (F) fine, (apparent) discontinuous layer-bound fractures; (G) vegetation partially obscuring fracture traces; (H) dilated aperture of a curvilinear fracture introducing ambiguity into trace digitization; (I) surficial-staining and vegetation growth within fracture apertures adds complexity into trace delineation; (J) pervasively fractured carbonate with high fracture densities and non-systematic orientations offering complexity for manual digitization; (K) plants and moss nucleating within fracture apertures occluding traces; (L) complex anatomizing and ladderlike fractures connecting systematic joints introducing complexity into the digitization task.
Preprocessing steps were implemented to further enhance image quality and consistency prior to fracture digitization and annotation. These steps included correcting lens distortion in OpenCV46 using its intrinsic radial distortion coefficients (k1, k2) calculated in Agisoft Metashape47 via self-calibration during photogrammetric reconstruction, ensuring accurate geometric representation of the scene. Color balancing was achieved through the Gray World algorithm48, which adjusted color balance to account for varied lighting conditions present during image capture. Normalization was performed using histogram equalization to maintain uniformity in brightness and contrast across the dataset. Further to this, denoising was applied to the selected images to reduce noise (including Gaussian noise from low-light or overcast conditions, sensor noise from varying camera equipment, compression artifacts, and shadow-induced contrast noise), and enhance image clarity in order to aid fracture identification. Specifically, the Non-Local Means (NLM) filter49 was employed, due to its edge-preserving capabilities (parameters: h = 10, templateWindowSize = 7, searchWindowSize = 21). Further filtering, including the Gaussian filter (sigma = 1.5) and median filter (kernel size = 3 × 3) were utilized to smooth the images while preserving essential edge details. Morphological operations (morphological opening/erosion and dilation: kernel size = 3 × 3) were applied to consolidate edges, cleaning fracture trace objects, aiding in the identification and extraction of discontinuity patterns. This process effectively refined the edges of thin, thread-like fractures, facilitating pixel-accurate identification and annotation. Additional image processing, such as contrast enhancement and edge detection algorithms (Hessian-based edge detection50), further highlighted fracture edges by enhancing the visibility of subtle discontinuities.
Fracture annotation
Binary mask creation
Creating binary masks was an essential step in annotating fractures within the selected outcrop images. Once the fractures were identified, each fracture was manually traced to ensure the mask accurately honored the fracture’s geometry, clearly delineating between fractured and non-fractured regions. Annotations were digitized using Adobe Photoshop, where fracture edges were marked on a second mask layer. A consistent brush size of 3px and hardness of 100 was used for all annotations to maintain uniformity across the dataset. We acknowledge this as a limitation, as it may impact precision for fractures narrower than 3 pixels, which would not be captured at a true pixel level (see Fig. 4).
Mask overlay and patching
To create patches, the binary mask was overlaid on the original image and then segmented (see Fig. 5). This overlay facilitated the verification of mask accuracy and provided a clear understanding of the fractures’ spatial distribution. To make the dataset suitable for computer vision (CV) tasks, the overlaid images were divided into smaller patches of 224 × 224 pixels. This resolution was selected based on its compatibility with widely used convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures, such as ResNet and VGG, which commonly operate on image patches of this size51,52. The choice of 224 × 224 pixels strikes a balance between retaining sufficient contextual information for common CV tasks and ensuring computational efficiency during future model training and inference51.
Smart patch retention algorithm
The patches created from the annotated images vary in quality. Some patches only contain non-fracture scene elements, such as sky, vegetation, or drift cover, while others include edges that are not representative of the targeted geological features (e.g., corner cases, vehicles, or scale references such as pens and measuring tapes). This variability necessitates a rigorous algorithm to selectively retain patches that are optimal for fracture edge extraction.
The primary criterion for patch selection was to retain only square patches (224 × 224 pixels), discarding edge cases where patches did not meet the criteria. The secondary criterion focused on edge density: each patch must contain at least 25% of its area marked by fracture edges. This threshold ensures preserving patches rich in geological fracture data, thereby enhancing the dataset’s signal-to-noise ratio. We empirically determined the 25% threshold by testing various levels of edge density, ranging from 10% to 50%, and evaluating the signal-to-noise ratio and relevance of the resulting patches. This process balanced the inclusion of relevant objects while excluding noisy, low-quality patches.
Additionally, the patches were Min-Max normalized and Z-score standardized to enhance image quality and consistency. Normalization adjusts the pixel intensity values to a common scale, typically between 0 and 1. Standardization ensures consistent lighting conditions and removes artifacts introduced during image acquisition, such as shadows or reflections, which could affect the accuracy of fracture detection. These steps are crucial after the original image processing chain to mitigate residual inconsistencies and artifacts. Normalizing and standardizing ensure uniformly scaled pixel values and minimized lighting variations, which leads to more reliable and robust modeling. Since most deep learning models incorporate these preprocessing steps, their performance and accuracy are significantly enhanced53. Consequently, this improves the accuracy of fracture detection by providing a consistent and artifact-free dataset.
Assembling the data
The high-resolution outcrop image pool comprised 49 annotated images, which were segmented into 12158 224 × 224-pixel patches and compiled into the GeoCrack database37 (see Table 3 for a detailed breakdown of the dataset). The images were stored in two main formats: preserved outcrop images accompanied by a complete annotation mask and patched format amenable to model training and inference. With respect to porting the patch data towards the training of deep architectures, this component of the dataset was split into a 50-25-25 ratio for a segmentation model, which resulted in 6079 images for training, 3039 for validation, and 3040 for testing. Metadata containing the paths to the patches for each category is provided as a.csv file. The chosen number of patches and their split align with established practices in the literature, providing a robust foundation for effective model training54.
Data Records
The dataset titled GeoCrack: A High-Resolution Dataset of Fracture Edges in Geological Outcrops37 is hosted in the Harvard Dataverse (https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/E4OXHQ GeoCrack Dataset) and is structured into three primary folders: Raw Data, Patched Data, and Code (see Fig. 6 for the complete repository structure).
Raw data
This folder encompasses the original outcrop images, which are further categorized into three subfolders:
-
Raw Images: Contains unprocessed images captured directly from the camera. These images are named according to the location and time of capture, providing a comprehensive record of the geological outcrops in their unprocessed form.
-
Cleaned Images: Features images that have undergone noise reduction and sharpening to enhance clarity for subsequent annotation. These images are crucial for precise edge segmentation and are identified by the suffix _cleaned.png.
-
Edge Mask: This subfolder includes the fully annotated edge masks corresponding to the cleaned images. These masks highlight fracture edges and are named with the suffix _mask.png.
Additionally, the Raw Data folder contains a text file named metadata.txt. This file holds extensive metadata for each image, detailing geographic and geological information, such as location in Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinates, elevation, and geological context. It also includes comprehensive camera details, such as the make and model of the camera, lens specifications, exposure settings, and environmental conditions at the time of capture. This metadata is critical for researchers aiming to correlate image data with geological and environmental parameters.
The Patched Data folder contains merged patches derived from the high-resolution images. The patches are named systematically to indicate their source and type. For instance, an edge patch is labeled as image_name_patch_number_mask.png, where image_name refers to the original outcrop image, patch_number identifies the specific patch, and mask denotes it as an edge mask.
The Code folder consists of three python scripts:
-
make_patches.py: This script generates image-mask pairs by implementing a smart patch retention algorithm. It processes an input image and its annotation mask to create high-resolution patches.
-
make_dataset.py: This script creates datasets for deep learning model training. It accepts the directory path containing the patches and outputs three.csv files: train.csv, test.csv, and validation.csv.Each.csv file lists paths to image-mask pairs, ensuring a structured and balanced dataset split for training, testing, and validation.
-
unet.py: This script implements a U-Net for demonstrating the dataset’s utility for training deep learning models in edge segmentation tasks.
This structure ensures that the dataset is highly organized and functional for researchers and practitioners in the field of geoscience, subsurface/geotechnical engineering, and deep learning. The inclusion of raw, cleaned, and annotated data, along with scripts for data preparation and model training makes this dataset a robust resource for advancing the study and analysis of geological fracture edges using state-of-the art artificial intelligence-based methodologies.
Technical Validation
Creating an accurately annotated fracture dataset through manual digitization is a resource-intensive task. To ensure the integrity and cost-efficiency of our annotated fracture edges on geological outcrop images, we adopted a robust validation methodology, originally proposed by55. This validation framework effectively mitigates three major sources of error: (1) overlooked fracture edges, (2) inaccurately delineated fracture edges, and (3) misclassified edges. Such a method is crucial for maintaining the precision and reliability of our dataset annotations.
Error categories and mitigation strategies
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the fracture-annotated image dataset, we identified potential error categories and implemented corresponding mitigation strategies:
-
1.
Overlooked Fracture Edges: As discussed above, identifying every fracture edge is inherently challenging due to varying image resolutions, lighting conditions, and geological characteristics of the host rock and fracture network. To mitigate this, we conducted multiple review rounds involving experienced annotators and an expert geoscientist to ensure thorough labeling.
-
2.
Inaccurate Delineation of Fracture Edges: Accurate edge delineation is critical. Overly broad edges may incorporate extraneous pixels, while excessively narrow edges might exclude essential parts of the fractures. Annotation workshops were conducted to standardize the annotation process among all team members, ensuring consistency and precision.
-
3.
Incorrectly Classified Edges: Misclassification can occur when annotators mistake other features for fracture edges, or when shadows obscure the edges. Feedback mechanisms, including regular peer reviews and having an expert geologist available constantly to validate, supervise, and facilitate annotation, were established to ensure continuous improvement during the annotation process.
By implementing these quality assurance measures, we aimed to enhance the accuracy and reliability of the fracture annotations, ensuring a high-quality dataset for future research.
Recruitment and training of annotators
To implement these error mitigation measures, we recognized that annotator compensation could significantly impact data quality56. To balance cost and quality, we employed annotators who were motivated by both fair compensation and the valuable experience offered by the project.
Training protocol
The research assistants (RAs) underwent rigorous training by the expert geologist to familiarize themselves with the project objectives, annotation tools, and the criteria for accurate fracture edge annotation. They were trained to label all visible fracture edges, including partially visible traces, and to classify ambiguous fractures as undefined for later review.
Validation process
Each annotated image was reviewed in two stages. The first stage involved review by two RAs following a structured workflow. The first RA ensured comprehensive fracture edge annotation, focusing on small and boundary-proximal fractures. The second RA verified the precision of the annotations, making necessary adjustments. Both RAs then confirmed the correct identification of fractures and re-evaluated any undefined edges. The second stage of review involved validation by expert geoscientists. They evaluated the correctness of the RAs’ reviews and resolved any doubts or differing opinions on the annotations.
Assessment of validation efficacy
Consistency across annotators is crucial for dataset reliability. We employed multiple metrics to assess the effectiveness of our validation process. Coverage validation involved calculating the number of annotations added and removed during validation (see Fig. 7). Pre-validation, the dataset contained 12,158 image patches, with an average of 7 edges per image, totaling approximately 85,104 fracture edges. Post-validation, the dataset was updated to reflect the addition and removal of edges. During validation, specific percentages of annotations were classified into different categories based on their quality and completeness. Post-validation, the dataset showed significant updates. The total number of edges increased to approximately 127,659 edges, with detailed classifications as follows: 33.3% (42,553 annotations) were identified as incomplete and required completion (orange), 25.0% (31,866 annotations) were previously identified (green), 42.2% (53,240 annotations) required drawing (orange), and 25.0% (31,866 annotations) were found to be misclassified (red) (Table 4). To evaluate annotation quality, we compared agreement and exact matches between pre- and post-validation annotations. Post-validation, a significant percentage of annotations agreed with pre-validation annotations, indicating consistency and reliability in our validation process. Post-validation, the dataset demonstrated a marked improvement in annotation quality and completeness. The discrepancy between pre- and post-validation annotations underscores the necessity for rigorous validation to ensure the dataset’s reliability. The detailed breakdown of post-validation annotations provided insights into the image regions that required completion, identification, or correction. Overall, the validation process ensured that our dataset not only grew in terms of the number of annotations over the course of the vetting process but also improved in quality, providing a more robust and reliable resource for subsequent analysis and research in geological fracture edge segmentation.
Dataset validation for deep learning segmentation tasks
To ensure the suitability of our fracture-annotated image dataset for deep learning segmentation tasks57,58, we conducted a thorough evaluation to verify its effectiveness for model training. The results demonstrated the dataset’s robustness in training deep learning models, ensuring precise fracture segmentation on validation and test sets.
For this evaluation, a U-Net model was trained on a subset of 1,245 images, each with dimensions of 224 × 224 pixels. The model achieved satisfactory results in pixel-level classification, successfully detecting narrow cracks, as illustrated in Fig. 8. The model achieved an Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 85%, a pixel accuracy of 92%, a recall (true positive rate) of 88%, and a precision of 90%. This test confirms the dataset’s potential to develop robust deep learning models for segmentation tasks, highlighting its reliability and value for future research and applications.
Usage Notes
For processing the dataset of rock edges, researchers may utilize software such as interpreted languages such as MATLAB or Python, or image processing software such as ImageJ, which are well-suited for image analysis tasks. We used OpenCV for preprocessing (functions: cvtColor, fastNlMeansDenoising, HessianEdgeDetection), and Adobe Photoshop for fracture annotation. Other annotation tools like LabelImg or VIA can also be used. Python was employed for image processing operations but proved slow (note that anecdotally, MATLAB may offer improved performance for patching and preprocessing). Custom scripts and workflows are provided on our GitHub repository to facilitate reproducibility and ease of use.
Data availability
The code used for dataset generation and processing is hosted on GitHub and can be accessed at: https://github.com/YaqoobAnsari/GeoCrack-A-High-Resolution-Dataset-of-Fracture-Edges-in-Geological-OutcropsGeoCrack Repo. The repository includes detailed documentation on the versions of software used, as well as specific variables and parameters applied in the generation, testing, and processing of the dataset. Access to the code is unrestricted and open to the public.
References
Huo, D. & Gong, B. Discrete modeling and simulation on potential leakage through fractures in co2 sequestration. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition?, SPE–135507 (SPE, 2010).
Seers, T. D. & Hodgetts, D. Comparison of digital outcrop and conventional data collection approaches for the characterization of naturally fractured reservoir analogues. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 374, 51–77 (2014).
Watanabe, K. & Takahashi, H. Fractal geometry characterization of geothermal reservoir fracture networks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 100, 521–528 (1995).
Yoshida, H., Nagatomo, A., Oshima, A. & Metcalfe, R. Geological characterisation of the active atera fault in central japan: Implications for defining fault exclusion criteria in crystalline rocks around radioactive waste repositories. Engineering geology 177, 93–103 (2014).
Singh, B. & Goel, R. Engineering rock mass classification (Elsevier, 2011).
King, G. The accommodation of large strains in the upper lithosphere of the earth and other solids by self-similar fault systems: the geometrical origin of b-value. Pure and Applied Geophysics 121, 761–815 (1983).
Hancock, P. Brittle microtectonics: principles and practice. Journal of structural geology 7, 437–457 (1985).
Engelder, T. Stress regimes in the lithosphere, 151 (Princeton University Press, 2014).
Mazdarani, A., Kadkhodaie, A., Wood, D. A. & Soluki, Z. Natural fractures characterization by integration of fmi logs, well logs and core data: a case study from the sarvak formation (iran). Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology 13, 1247–1263 (2023).
Baecher, G. B. Statistical analysis of rock mass fracturing. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology 15, 329–348 (1983).
Bonnet, E. et al. Scaling of fracture systems in geological media. Reviews of geophysics 39, 347–383 (2001).
Seers, T. D. & Hodgetts, D. Probabilistic constraints on structural lineament best fit plane precision obtained through numerical analysis. Journal of Structural Geology 82, 37–47 (2016).
Seers, T. D. & Hodgetts, D. Extraction of three-dimensional fracture trace maps from calibrated image sequences. Geosphere 12, 1323–1340 (2016).
Bisdom, K., Nick, H. M. & Bertotti, G. An integrated workflow for stress and flow modelling using outcrop-derived discrete fracture networks. Computers & Geosciences 103, 21–35 (2017).
Tavani, S. et al. Transverse jointing in foreland fold-and-thrust belts: a remote sensing analysis in the eastern pyrenees. Solid Earth 11, 1643–1651 (2020).
Odling, N. E. Scaling and connectivity of joint systems in sandstones from western norway. Journal of Structural Geology 19, 1257–1271 (1997).
Wang, J. & Howarth, P. J. Use of the hough transform in automated lineament. IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 28, 561–567 (1990).
Wu, T.-D. & Lee, M.-T. Geological lineament and shoreline detection in sar images. In 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 520–523 (IEEE, 2007).
Lemy, F. & Hadjigeorgiou, J. Discontinuity trace map construction using photographs of rock exposures. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 40, 903–917 (2003).
Vasuki, Y., Holden, E.-J., Kovesi, P. & Micklethwaite, S. Semi-automatic mapping of geological structures using uav-based photogrammetric data: An image analysis approach. Computers & Geosciences 69, 22–32 (2014).
Marques, A. et al. Deep learning application for fracture segmentation over outcrop images from uav-based digital photogrammetry. In 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, 4692–4695 (IEEE, 2021).
Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., Bai, L., Yang, Y. & Ma, Q. Application of an improved u-net neural network on fracture segmentation from outcrop images. In IGARSS 2022-2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 3512–3515 (IEEE, 2022).
Chudasama, B. et al. Automated mapping of bedrock-fracture traces from uav-acquired images using u-net convolutional neural networks. Computers & Geosciences 182, 105463 (2024).
Zhang, L., Yang, F., Zhang, Y. D. & Zhu, Y. J. Road crack detection using deep convolutional neural network. In Image Processing (ICIP), 2016 IEEE International Conference on, 3708–3712 (IEEE, 2016).
Zou, Q., Cao, Y., Li, Q., Mao, Q. & Wang, S. Cracktree: Automatic crack detection from pavement images. Pattern Recognition Letters 33, 227–238 (2012).
Goo, J. M., Milidonis, X., Artusi, A., Boehm, J. & Ciliberto, C. Hybrid-segmentor: A hybrid approach to automated fine-grained crack segmentation in civil infrastructure. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.02866 (2024).
Bai, Y., Sezen, H. & Yilmaz, A. End-to-end deep learning methods for automated damage detection in extreme events at various scales. In 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 6640–6647 (IEEE, 2021).
Ansari, M. Y. & Qaraqe, M. Mefood: A large-scale representative benchmark of quotidian foods for the middle east. IEEE Access 11, 4589–4601 (2023).
Löffler, M. T. et al. A vertebral segmentation dataset with fracture grading. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2, e190138 (2020).
Ansari, M. Y. et al. Advancements in deep learning for b-mode ultrasound segmentation: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence (2024).
Tomaszkiewicz, K. & Owerko, T. A pre-failure narrow concrete cracks dataset for engineering structures damage classification and segmentation. Scientific Data 10, 925 (2023).
Ansari, M. Y., Mangalote, I. A. C., Masri, D. & Dakua, S. P. Neural network-based fast liver ultrasound image segmentation. In 2023 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), 1–8 (IEEE, 2023).
Ansari, M. Y., Qaraqe, M., Righetti, R., Serpedin, E. & Qaraqe, K. Enhancing ecg-based heart age: impact of acquisition parameters and generalization strategies for varying signal morphologies and corruptions. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 11, 1424585 (2024).
Yaqoob, M. et al. Microcrystalnet: An efficient convolutional neural network for microcrystal classification using scanning electron microscope petrography (2024).
Alzubaidi, F. et al. Automatic fracture detection and characterization from unwrapped drill-core images using mask r–cnn. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 208, 109471 (2022).
Ansari, Y., Tiyal, N., Flushing, E. F. & Razak, S. Prediction of indoor wireless coverage from 3 d floor plans using deep convolutional neural networks. In LCN, 435–438 (2021).
Yaqoob, M. et al. Geocrack: A high-resolution dataset for segmentation of fracture edges in geological outcrops, https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/E4OXHQ (2024).
Zhang, Z. & Tang, Q. Camera self-calibration based on multiple view images. In 2016 Nicograph International (NicoInt), 88–91 (IEEE, 2016).
Tavani, S., Corradetti, A., Mercuri, M. & Seers, T. Virtual outcrop models of geological structures. ArTS Archivio della ricerca di Trieste (2024).
Zhang, Y. & Hirakawa, K. Blur processing using double discrete wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1091–1098 (2013).
Kumar, S. & Jain, Y. K. Performance evaluation and analysis of image restoration technique using dwt. International Journal of Computer Applications 72, 11–20 (2013).
Stone, H. S., Tao, B. & McGuire, M. Analysis of image registration noise due to rotationally dependent aliasing. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 14, 114–135 (2003).
Young, S. S. Alias-free image subsampling using fourier-based windowing methods. Optical Engineering 43, 843–855 (2004).
Vermilye, J. M. & Scholz, C. H. Relation between vein length and aperture. Journal of structural geology 17, 423–434 (1995).
Neuman, S. P. Multiscale relationships between fracture length, aperture, density and permeability. Geophysical Research Letters 35 (2008).
Bradski, G. & Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV: Computer vision with the OpenCV library (O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2008).
Over, J.-S. R. et al. Processing coastal imagery with agisoft metashape professional edition, version 1.6–structure from motion workflow documentation. Tech. Rep., US Geological Survey (2021).
Rizzi, A., Gatta, C. & Marini, D. Color correction between gray world and white patch. In Human Vision and Electronic Imaging VII, 4662, 367–375 (SPIE, 2002).
Buades, A., Coll, B. & Morel, J.-M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In 2005 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'05), 2, 60–65 (Ieee, 2005).
Ghanta, S., Shamsabadi, S. S., Dy, J., Wang, M. & Birken, R. A hessian-based methodology for automatic surface crack detection and classification from pavement images. In Structural Health Monitoring and Inspection of Advanced Materials, Aerospace, and Civil Infrastructure 2015, 9437, 524–534 (SPIE, 2015).
Rukundo, O. Effects of image size on deep learning. Electronics 12, 985 (2023).
Sudeep, S., Sangram, S., Shivaprasad, S., Prasad, S. & Nayaka, R. Deep learning based image classification using small vggnet architecture. In AIP Conference Proceedings, 2742 (AIP Publishing, 2024).
Huang, L. et al. Normalization techniques in training dnns: Methodology, analysis and application. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 45, 10173–10196 (2023).
Shahinfar, S., Meek, P. & Falzon, G. “how many images do i need?” understanding how sample size per class affects deep learning model performance metrics for balanced designs in autonomous wildlife monitoring. Ecological Informatics 57, 101085 (2020).
Su, H., Deng, J. & Fei-Fei, L. Crowdsourcing annotations for visual object detection. In Workshops at the twenty-sixth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (2012).
Sorokin, A. & Forsyth, D. Utility data annotation with amazon mechanical turk. In 2008 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, 1–8 (IEEE, 2008).
Ansari, M. Y. et al. Towards developing a lightweight neural network for liver ct segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 27–35 (Springer, 2022).
Rai, P. et al. Efficacy of fusion imaging for immediate post-ablation assessment of malignant liver neoplasms: A systematic review. Cancer Medicine 12, 14225–14251 (2023).
Consorti, L. et al. Biostratigraphic investigations assisted by virtual outcrop modeling: a case study from an eocene shallow-water carbonate succession (val rosandra gorge, trieste, ne italy). Italian Journal of Geosciences 143, 60–74 (2024).
Jurkovšek, B. et al. Geology of the classical karst region (sw slovenia–ne italy). Journal of Maps 12, 352–362 (2016).
Quick, J. E., Sinigoi, S. & Mayer, A. Emplacement dynamics of a large mafic intrusion in the lower crust, ivrea-verbano zone, northern italy. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 99, 21559–21573 (1994).
Souquière, F. & Fabbri, O. Pseudotachylytes in the balmuccia peridotite (ivrea zone) as markers of the exhumation of the southern alpine continental crust. Terra Nova 22, 70–77 (2010).
Menegoni, N. et al. Fracture network characterisation of the balmuccia peridotite using drone-based photogrammetry, implications for active-seismic site survey for scientific drilling. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (2024).
Dart, C., Bosence, D. & McClay, K. Stratigraphy and structure of the maltese graben system. Journal of the Geological Society 150, 1153–1166 (1993).
Bonson, C. G., Childs, C., Walsh, J. J., Schöpfer, M. P. & Carboni, V. Geometric and kinematic controls on the internal structure of a large normal fault in massive limestones: the maghlaq fault, malta. Journal of Structural Geology 29, 336–354 (2007).
Martinelli, M., Bistacchi, A., Balsamo, F. & Meda, M. Late oligocene to pliocene extension in the maltese islands and implications for geodynamics of the pantelleria rift and pelagian platform. Tectonics 38, 3394–3415 (2019).
Tavani, S. et al. Early-orogenic deformation in the ionian zone of the hellenides: Effects of slab retreat and arching on syn-orogenic stress evolution. Journal of Structural Geology 124, 168–181 (2019).
Mattern, F., Pracejus, B., Scharf, A., Frijia, G. & Al-Salmani, M. Microfacies and composition of ferruginous beds at the platform-foreland basin transition (late albian to turonian natih formation, oman mountains): Forebulge dynamics and regional to global tectono-geochemical framework. Sedimentary geology 429, 106074 (2022).
Searle, M. P., Cherry, A. G., Ali, M. Y. & Cooper, D. J. Tectonics of the musandam peninsula and northern oman mountains: From ophiolite obduction to continental collision. GeoArabia 19, 135–174 (2014).
Maurer, F., Rettori, R. & Martini, R. Triassic stratigraphy, facies and evolution of the arabian shelf in the northern united arab emirates. International Journal of Earth Sciences 97, 765–784 (2008).
Acknowledgements
Student research assistants performed the manual annotation of fracture edges on the outcrop images using the Adobe Photoshop GUI. In particular, we thank the diligent efforts of Rehaan Hussain and Rohit Duvvuri who served for months as manual annotators and/or validators for this work. This work was supported in part by the Qatar National Research Fund (QNRF) National Priorities Research Program (Project: NPRP10-0104-170104-491140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y. and M.Y.A.; Data collection: T.D.S., S.T. and A.C.; Data labeling, M.Y.., V.R.S.K. and T.A.T.; Formal analysis, M.I.; Methodology, M.Y. and M.I.; Supervision, T.D.S.; Validation, M.Y. and M.I.; Visualization M.Y.; Writing–original draft, M.Y., T.D.S. and M.Y.A.; Writing–review & editing, M.Y.A., T.D.S., S.T. and M.I.; All the authors revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yaqoob, M., Ishaq, M., Ansari, M.Y. et al. GeoCrack: A High-Resolution Dataset For Segmentation of Fracture Edges in Geological Outcrops. Sci Data 11, 1318 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-04107-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-04107-0
This article is cited by
-
Deep Learning Approaches to Evaluating ADHD Using EEG Data: RNN, GRU, and LSTM Models
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering (2026)
-
A survey of transformers and large language models for ECG diagnosis: advances, challenges, and future directions
Artificial Intelligence Review (2025)