Abstract
Recently, it has been great efforts to synthesize an efficient water-oxidizing catalyst. However, to find the true catalyst in the harsh conditions of the water-oxidation reaction is an open area in science. Herein, we showed that corrosion of some simple manganese salts, MnCO3, MnWO4, Mn3(PO4)2 · 3H2O, and Mn(VO3)2 · xH2O, under the water-electrolysis conditions at pH = 6.3, gives an amorphous manganese oxide. This conversion was studied with X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), as well as, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDXS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), spectroelectrochemistry and electrochemistry methods. When using as a water-oxidizing catalyst, such results are important to display that long-term water oxidation can change the nature of the manganese salts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Electrochemical water splitting to hydrogen and oxygen is a promising way to generate hydrogen fuel1. According to thermodynamic and kinetic barriers, the oxygen-evolution reaction (OER) is the most challenging half-reaction in the water splitting2. Hence, developing efficient water-oxidizing catalysts with lowering the overpotential of the oxidation half-reaction and thus expedite the reaction is an active area in science2,3,4,5,6,7. Due to the great amount of the current needs to energy sources, design and synthesis of inexpensive water-oxidizing catalysts based on earth-abundant materials are essential. Therefore, first-row transition metals and their derivatives are among the most promising water-oxidizing catalysts for future3.
Among different transition-metal ions, manganese compounds have attracted tremendous attention. Because a Mn4CaO5 cluster in photosystem II (PSII) is the only natural system that demonstrates water oxidation8, manganese-based compounds from solid-state materials to molecular complexes have been potentially interesting materials for water oxidation in the past few decades2,9,10,11,12,13. Manganese is also an earth-abundant, environmentally friendly and low-cost element. Interesting properties of manganese oxides have made them attractive materials in various catalytic applications and energy storages, as well14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22.
There have been considerable efforts to find efficient manganese complexes as homogenous or heterogeneous water-oxidizing catalysts12,13, it has been established that in most cases these compounds are unstable upon operation under harsh conditions of chemical or electrochemical water oxidation and are converted to manganese oxides23,24,25,26,27,28. Not only the conversion of manganese complexes to oxide phases but also surface amorphization of crystalline calcium manganese oxides or manganese oxides in the chemical or electrochemical water oxidation reaction has been reported29,30,31. These converted materials showed exceed catalytic activity29,30,31. This process is also the reason for the instability of mixed oxide systems such as Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ and La0.65Sr0.35MnO3 during the OER32,33. Comparably, an amorphous phase has been reported as the active phase in the water-oxidizing activity of a series of cobalt-substituted crystalline zinc oxide precatalysts34. Additionally, it was found that in the water-oxidizing activity of cobalt selenide particles, an amorphous cobalt oxide was the true catalyst35. Reports from Hu’s lab displayed an in situ formation of a core-shell Ni2P/NiOx assembly during the water-oxidation performance of Ni2P catalyst36. Likewise, reorganization of the material to an active amorphous phase under catalytic condition was responsible for water-oxidizing activity of CoP precatalysts37.
All above-mentioned cases highlight the importance of studying the long-term stability of the water-oxidizing catalysts. Especially finding the true catalysts, is a key step in the commercial application of a water-oxidizing catalyst. Finding the reason for the instability of a catalyst and identifying the true catalyst in the applied condition is also helpful to design and synthesize efficient water-oxidizing catalysts with higher activity, and better stability. Recently, we showed that a series of non-oxide manganese salts are converted to an amorphous manganese oxide phase, in the presence of Ce(IV) solution as an oxidant38. Herein, we studied the long-term stability of a series of manganese salts (MnCO3, MnWO4, Mn(VO3)2 · xH2O and Mn3(PO4)2 · 3H2O), under the electrochemical water-oxidation conditions. This question may rise why studying the stability of these materials is important under both chemical and electrochemical water oxidation condition. Under chemical water-oxidation conditions in the presence of an oxidant, the high oxidizing ability of the oxidant, as well as, pH of the solution might be effective in the instability of a catalyst (the pH of a Ce(IV) solution is around 1). However, in this work, we have applied an electrochemical condition in a neutral electrolyte to eliminate the pH effect. On the other hand, despite chemical methods, the applied potential is tunable in the electrochemical method; therefore, one can investigate the effect of applied overpotential on the stability of the utilized catalyst. We could detect the transformation of the mentioned manganese salts to an amorphous manganese oxide phase using various techniques such as XRD, SEM, EDXS, HRTEM, XANES and EXAFS, XPS, spectroelectrochemistry, and electrochemistry. From now on, the freshly prepared salts and the converted materials are denoted according to Table 1.
Results
Manganese salts were synthesized using a simple precipitation method. Then, the synthesized salts were used under electrochemical water-oxidation conditions at a pH around 6.3. Therefore, manganese salts were introduced to the anodic half-cell of a convective-suspension-collision system39.
In this system, a half-cell consisted of a platinum plate as an electrode in a 1 M KCl solution that was used as a reference half-cell. On the other hand, a platinum plate, which was immersed in a suspension of mother salts in a 0.1 M LiClO4 solution acted as a working half-cell. Finally, an inverted glass U-tube filled with a mixture of 5% agar in 1 M KCl had connected two half-cells as a salt bridge. A 2.0 V potential was applied between two electrodes. The suspension in the working half-cell was stirred by using a magnetic stirrer, and the synthesized salts collided with the anode continuously. Since in this method no binder or polymer (such as Nafion) has been utilized to attach the material on the conductive electrode, we could provide a large amount of the post operando material without any contamination of the binder polymer. It should be noted that as the post operando material might be an amorphous phase, any amorphous species could influence the characterization accuracy. Therefore, to have a precise detection on the post catalytic species, avoiding such amorphous contamination was very important.
After the conversion of the mother salt under the convective-suspension-collision condition for 24 h, a brown solid was precipitated on the surface of the anode. The brown compound was scratched and was analyzed with different methods. In the case of MPB, the conversion happened slowly. Thus, we collected the brown precipitate after 5 days.
The characterization of the post operando materials showed that the investigated salts were converted to an amorphous manganese oxide phase with different morphology and an unlike chemical structure to mother compounds.
The morphologies of the different fresh manganese salts and the samples after the conversion were studied using SEM (Fig. 1). While MPB, MWB, MVB, and MCB samples showed various morphologies, all the converted materials exhibited no distinguishable morphology in SEM imaging, which suggested the low crystalline structure of them.
Since the oxygen evolution reaction occurs on the surface of a catalyst rather than the bulk of the sample, the samples were studied with EDXS analysis, as well. EDXS results of the original salts and the converted materials have been presented in Table 2.
Interestingly, vanadium content in the EDX results for MVA is zero, which confirms, at least in the interaction volume of the analysis; whole manganese vanadate was converted to manganese oxide in the electrocatalytic reaction. Pourbaix diagram displays that vanadium ions could form soluble species under this condition40.
Figure 2 shows XRD patterns of all samples, before and after the electrocatalytic reaction. Full interpretations of XRD data have been presented in Figs S1–S5. The XRD pattern of MCB sample (Fig. 2a right panel), demonstrated the crystalline structure of this sample and the pattern completely match to MnCO3 structure. The MVB sample had two crystalline phases: MnV2O6 · 2H2O and MnV2O6 · 4H2O. No other impurities were observable in the XRD pattern of this sample. In the XRD pattern of the MWB sample in Fig. 2c (right panel), the main peaks at ~8.24°, 11.01 and 16.94° are well consistent with the manganese tungstate phase. The sharp peak at ~4.96°, which corresponds to the main peak of Na6W7O24 · 14H2O phase, shows the co-existence of this phase in the MWB sample. The XRD pattern of MPB sample contains main diffraction peaks at 2θ = 12.15, 13.53, and 15.68° which could be assigned to crystalline Mn3(PO4)2 · 3H2O phase with 3.35, 3.01 and 2.6 Å d-spacing, respectively.
Left panel: XRD patterns of MCB (a) MVB (b) MWB (c) MPB (d). Right panel: XRD patterns of MCA (a) MVA (b) MWA (c) MPA (d). Well-defined crystalline structures are observed for all original salts. However, no recognizable diffraction peaks for the converted materials confirm the amorphous phase of these samples.
As it is clear in Fig. 2, well-defined crystalline structures were observed for all original salts. However, no recognizable diffraction peaks for the converted materials corroborate amorphous phase of these samples. In the case of MCA sample, despite to the amorphous background, a few broad peaks were visible at 2θ = 5.59, 11.05, 16.73, 29.27° with 7.2, 3.6, 2.4 and 1.4 Å d-spacing which were related to a manganese oxide phase with a layered structure.
The microstructure and crystallinity of the material were further examined with TEM and electron diffraction (ED) (Fig. 3). All mother salts showed clear borders on the edge of the particles. However, in the case of MCB sample, an amorphous compound has covered the crystalline core of the particle (Fig. 3a). According to the chemical instability of the manganese carbonate phase, this phase has the potential to be converted to oxide. Therefore, this amorphous shell can be attributed to an amorphous oxide phase, which has covered the crystalline manganese carbonate core. An amorphous background in the XRD pattern of this material validates this hypothesis.
HRTEM images of converted materials combined with an ED analysis revealed that upon water electrolysis, all investigated salts converted to assembled amorphous phases, which were appeared as amorphous rings in the ED images.
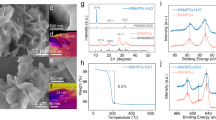
In the next step, we used XPS to investigate the probable oxidation of the original salts to manganese oxide (Fig. 4). Therefore, we utilized Mn 3 s peak to distinguish the oxidation state of Mn41. Coupling of the non-ionized 3 s electron with 3d valence band electrons in Mn species leads to a splitting which its magnitude can be used to find the oxidation state of it. According to Fig. 4, the ΔE 3 s for all samples after the operation in the water electrolysis is around 4.7, 5.7, 5.7 eV for MCA, MPA, and MWA, respectively. To further investigation of oxidation state and chemical environment of Mn species, we examined the MnWO4 sample before and after the conversion with XAS method, as well.
XANES and its first derivative show presence of Mn ions in higher oxidation state for MWA compared to MWB (Fig. 5). A linear combination fitting shows that MnO2, MWB, and layered Mn oxide exist almost 72, 28 and 0% in MWA
XANES (a) and first derivative spectra of MWA and MWB along with references. (b) Linear combination fitting of MWA while considering MWB, layered Mn oxide and MnO2 as components. (c) k-weight EXAFS spectra of various materials. (d) In comparison to MWB, the white-edge of MWA has shifted to higher energies, which confirms higher oxidation states of manganese sites in this material. A linear combination fitting showed that MWA consists of 72% MnO2 and 28% MWB.
An inspection of χ(k) spectra envisaged that local coordination of Mn ions in MWB is similar to MnO; however, MWA exhibit similarity with MnO2 (Fig. 6).
Further, simulation envisaged that Mn-O shell is different in MWB and MWA as clear from the Fourier Transform of EXAFS spectra. Co-ordination number and bond lengths have been shown in Table 3.
Furthermore, the catalytic stability of these manganese salts was tested through continuous cyclic voltammetry (CV). Consequently, a suspension of the compounds was dispersed on the surface of a bare FTO/glass substrate and was fixed with an ethanolic solution of Nafion. The electrodes were subjected to continuous CV (Fig. 7a). After 5 cycles, an oxidation peak was observed at voltages >1.2 V, for all samples (Figs S6–S9). This peak could be related to the oxidation of manganese ions. CVs of the fresh and the converted compounds are displayed in Fig. 7b,c. Figure 7a, shows that after continuous CV within −0.3–1.9 V, the samples electrochemically behave very similar to amorphous manganese oxides rather than the other phases of manganese oxides, in the same experiment condition42. The CV of the original salts in the 100th cycle showed a broad peak within 0.7–0.9 V which was centered at around 0.85 V. This broad peak is attributed to Mn(III) to Mn(IV) oxidation in amorphous manganese oxide42. The extreme broadening of signals due to electronic interactions of Mn sites in the amorphous phase manganese oxide led to this broadening42. We attributed the difference in the voltammograms to the different rate of conversion of the samples. Moreover, we also observed that cyclic voltammograms of the converted materials in the convective-suspension-collision system were close to amorphous manganese oxides (Fig. 7c).
Continuous CV of MCB (a) and 100th CV of all original salts. (b) CV of the converted materials in the water electrolysis condition. (c) A three-electrode system including an FTO slide, Pt foil as a counter electrode and Ag|AgCl|KClsat as a reference electrode was applied for investigation of the electrochemical properties of the catalyst (room temperature, LiClO4 (0.25 M), pH = 6.3, scan rate = 50 mV · s−1). Continuous CV of the mother salts confirmed their instability under electrochemical water oxidation conditions. A progressive manganese leakage into solution in the form of [Mn(H2O)6]2+ and its re-oxidation to manganese oxide, under the water oxidation conditions, might provoke a continuous change of surface composition in these materials.
To have a deep understanding of surface change during the CV, we used in-situ spectro-cyclic voltammetry and spectro-amperometry as a probe to characterize the surfaces of the electrodes during cycling (Fig. 8a–f). Upon application of a CV within −0.3–1.8 V, a broad peak at 380–600 nm appeared due to the oxidation of Mn(II) ions in the manganese carbonate phase (Fig. 8a,b). This new peak is similar to those observed previously for manganese oxide films in an aqueous electrolyte42. With taking the shape of this peak, the color of the electrode changed from yellowish-white to dark-brown. The peak could be related to the transition between the valence and conduction bands attributed to excitation from an O2p to Mn3d state but with some Mn3d to the Mn3d character43. Manganese carbonate with Mn(III) or Mn(IV) sites has not been reported, so the newly formed phase on the surface of the electrode could have a manganese-oxide based structure. We observed similar spectro-electrochemical behavior for the MCB material during continues CV in a 0.7–1.8 V potential window for 20 min (Fig. 8c,d). The water oxidation at 2.0 V indicated such spectrum as well (Fig. 8e,f).
Spectro-electrochemical analysis of MCB under water oxidation using CV (each spectrum after one minute) (a–d) and amperometry (2.0 vs. NHE). MnCO3 was placed on the FTO by Nafion. 1.0 mg of MnCO3 was dispersed in 50 μL water. Then, the suspension (30 μL) of this mixture was dripped onto the FTO electrode surface and dried at room temperature. Eventually, 10 μL of 0.5 wt % Nafion solution was deposited onto the center of the modified electrode. A spectro-electrochemical study on a manganese carbonate-coated electrode showed that upon applying a potential to the electrode, the material was not stable and was converted to a manganese oxide phase. With conversion of carbonate, the color of the electrode changed from yellowish-white to dark-brown and a peak at around 400 nm became to view in the visible spectrum.
Discussions
According to Fig. 1, SEM results showed that while the mother salts presented different morphologies, all the converted materials had a very similar view without especial morphology. Therefore, this observation confirmed morphologically instability of the mother salts under water oxidation condition. EDXS results showed that, especially in the case of Mn(VO3)2 · xH2O, the original salts were completely unstable under the harsh condition of water electrolysis, and they were converted to a manganese oxide phase without high-range order. Furthermore, the transformation of the original salts to an amorphous phase was confirmed with XRD method. As it is clear in Fig. 2, well-defined crystalline structures are observed for all original salts. However, unrecognizable diffraction peaks for the converted materials corroborate amorphous phase of these samples. Only in the case of MCA, some broad peaks related to a layered manganese oxide phase are observable in its XRD pattern. More crystallinity of this sample might be linked to the high tendency of the related original salt to degradation. It is hypothesized that in the most beginning of the water- electrolysis reaction the manganese carbonate was converted to completely amorphous manganese oxide and during the reaction the crystallinity of the oxide structure raised.
Additionally, conversion of these manganese salts to an amorphous phase was confirmed with HRTEM combined with ED. Sharp borders of particles in the HRTEM images of all original salts suggested their ordered structure, however, in the case of converted materials, the amorphous nature of the materials was clear using HRTEM and ED studies. Some bright spots were visible in the ED image of the MCA sample, which suggests a partially ordered crystal structure for this sample. However, according to dispersed rings, most of the sample is amorphous. The results by TEM is consistent with the XRD results of the MCA sample in Fig. 1, which a few broad peaks were clear on an amorphous background.
To get more details on the possible oxidation of the investigated salts after water -oxidation reaction, we used XPS method. For all samples, the value of ΔE3s is lower than ΔE3s for MnO (the ΔE for Mn(II) in MnO is >6.0 eV)44 which indicates oxidation of Mn(II) sites toward higher oxidation states in the converted materials. We further investigated the MWB and MWA samples with XAS method. XANES revealed the main edge of MWA close to MnO2 (Fig. 5a) which is further confirmed by the first derivative of XANES spectra (Fig. 5b). Linear combination fitting of the XANES spectra of MWA revealed the contribution of MnO2 in the sample (Fig. 5c). k-weight EXAFS spectra envisaged that co-ordination of manganese in these two materials is different from each other (Fig. 5d). Mn-O distance is also smaller for MWA (1.94 Å) compared to MWB (2.11 Å). Mn-O distance in MnO2 is around 1.89 Å, which is close to MWA sample. These results show that under water-oxidation conditions the sample was not stable and was converted to manganese oxide species.
According to Fig. 7, our results suggest that the mother salts are not stable during continuous CV studies, as well. A progressive manganese leakage into solution in the form of [Mn(H2O)6]2+ and its re-oxidation to manganese oxide, under the water oxidation conditions, might provoke a continuous change of surface composition in these materials33. Such effect has also been observed in structure transformation of La0.65Sr0.35MnO3 or crystalline manganese oxides into amorphous manganese oxide, as well33. These results suggested that the manganese salts were not stable as the system evolved in time. The applied potential window (−0.3–1.8) was chosen by purpose. The conversion of the original salts in this potential slot showed that decomposition of the initial materials to manganese oxide occurred even in the potentials lower than 2.0 V (the applied potential in the convective-suspension-collision system). On the other hand, irreversible conversion of the original salts to manganese oxide even after sweeping the potential to mines potentials confirmed that the newly formed manganese oxide is a stable phase.
In the light of all the presented data, we suggest that the investigated salts are not stable during the electrochemical water oxidation reaction and they oxidize to a manganese oxide phase. The instability of many manganese salts, manganese complexes, and manganese oxides in the water-electrolysis conditions established that stability of a manganese-based water-oxidizing catalyst is as important as its efficiency and should be carefully considered in the design and synthesize a manganese-based water-oxidizing catalyst (Fig. 9). Such extensive instability for manganese-based Mn compounds is related to the leaking/re-oxidation Mn(II), the decomposition of ligands for Mn complexes, and high stability of amorphous Mn oxide under water oxidation. It seems that, at least, at the end of water oxidation, amorphous manganese oxide is responsible for the catalytic activity of the applied precursors.
Conversion of different manganese-based materials to amorphous manganese oxide under the chemical or electrochemical conditions. *In the case of Oxone, the molecular-based mechanism was also reported13. In the presence of oxidant or under electrochemical conditions, different Mn-based compounds such as Mn-oxides, Mn-complexes and non-oxide Mn-salts are converted to amorphous manganese oxides.
Conclusions
In summary, we studied the conversion of a series of non-oxide Mn-based salts in the electrochemical water oxidation condition, and we observed that all investigated salts were converted to an amorphous manganese oxide phase. This conversion was identified with different methods such as XANES, EXAFS, SEM, EDXS, XPS, HRTEM, spectroelectrochemistry, and electrochemistry. The XRD and SEM results confirmed that although the starting mother salts were crystalline materials with well-defined morphologies, in electrochemical water oxidation condition, they were converted to a manganese oxide phase with very low crystallinity and without any especial morphology. The amorphous phase of the samples was established with ED coupled HRTEM, as well. Furthermore, a CV or amperometry experiment coupled with visible spectroscopy displayed that the salts were instable through the electrochemical water oxidation condition, and a new manganese oxide phase formed during catalytic operation. The visible spectra of the newly formed phase showed a broad peak at 380–600 nm. This peak was related to the transition between the valence and conduction bands attributed to excitation from an O2p to Mn3d state with some Mn3d to the Mn3d character. The oxidation and conversion of the mother salts to a manganese oxide phase was confirmed by XPS and XAS methods, as well. Based on our results and some recent literature reports, we could observe, different Mn-based materials were converted to an amorphous manganese oxide phase. The instability of most Mn-based materials in the water splitting conditions and their conversion to an amorphous manganese oxide phase is a critical point, which should be considered in the design and synthesis of water- oxidizing catalysts and their future applications in scale-up hydrogen production devices.
Experimental
Materials and methods
The manganese salts were prepared by a simple method. Firstly, an aqueous solution of MnCl2.4H2O was added to a prepared solution containing the stoichiometric amount of Na2WO4 or Na2CO3 or NH4VO3 or Na2HPO4 precursors, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. After completing the precipitation, the compound was filtered. Then the sample was washed repeatedly with distilled water for removal of free ions. The product was dried at 60 °C for 10 h in air atmosphere. Previous reports on MnCO3 show that this material is not stable at elevated temperatures45. Therefore, to avoid the manganese oxide impurities in the mother salt, this sample was dried at room temperature.
According to the low solubility of NH4VO3 in water, when this material was utilized as the precursor, the solution was stirred at 70 °C until a clear yellow solution was obtained. Then the aqueous solution of MnCl2.4H2O was added to it. Afterward, the remaining steps were repeated as mentioned before. In the next step, the stability of the final samples was studied in a convective-suspension-collision system39, which is described with detail in the following section.
Convective-suspension-collision system
A three-electrode system containing two platinum plates was used to study the stability of the compounds in the water electrolysis condition at near neutral pH. Electrodes were dipped into LiClO4 (0.1 M) and KCl (1.0 M) solutions as anodic and cathodic electrolytes, respectively. As a convective-suspension-collision technique, 250 mg of the manganese salts were suspended in 10 mL electrolyte (LiClO4) under continuous stirring. A constant potential of 2.0 V across the electrodes was applied for 24 h. After 24 h a dark brown solid, which was precipitated on the surface of the anode, was collected. Then, the compound was washed several times with distilled water and was dried at room temperature. In the case of manganese phosphate salt, the reaction was continued for 5 days. The remaining steps were repeated as same as the mentioned details.
Electrochemical experiments
Electrochemical experiments were performed using an EmStat3+ from PalmSens Company (Netherlands). To fabricate the manganese salts modified electrodes, 2.0 mg of the manganese salts or converted materials, which were emerged from the convective-suspension-collision system, were dispreaded in 100 μL of distilled water. Then 40 μL of the resulting suspension was cast onto the surface of an FTO/glass substrate and was allowed to dry with evaporation. In the next step, 10 μL of an ethanolic solution of Nafion was dropped on the surface of the mentioned electrode to attach the compounds to the electrode. For electrochemical characterization, a three-electrode setup was composed of the fabricated electrode, an Ag|AgCl|KClsat electrode, and a platinum rod, which served as working, reference, and auxiliary electrodes, respectively.
Characterization
SEM and TEM images were taken using SEM - Zeiss Supra 50 VP and FEI Tecnai G2 F20 transmission electron microscope (TF20 200 kV), respectively. The XRD patterns were recorded with an STOE STADI diffractometer (Mo-Kα radiation). The high-resolution visible spectra were recorded by a mini spectrophotometer (Pooyesh Tadbir Karaneh (Phystec), Iran). XPS measurements were done by an X-Ray BesTec XPS system (Germany) with an Al Kα X-ray source (hν = 1,486.6 eV). EXAFS measurements for the MWB and MWA along with references were performed at 1D XAS KIST (Korea Institute of Science and Technology) beamline, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Pohang, South Korea. EXAFS spectra were processed using ATHENA, these spectra were simulated by ARTEMIS using quick first shell fit.
References
Walter, M. G. et al. Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 110, 6446–6473, https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1002326 (2010).
Najafpour, M. M. et al. Manganese compounds as water-oxidizing catalysts. From the natural water-oxidizing complex to nanosized manganese oxide structures. Chem. Rev. 116, 2886–2936, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00340 (2016).
Singh, A. & Spiccia, L. Water oxidation catalysts based on abundant 1st row transition metals. Coordin Chem Rev 257, 2607–2622, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.027 (2013).
Kanan, M. W. & Nocera, D. G. In situ formation of an oxygen-evolving catalyst in neutral water containing phosphate and Co2+. Science (New York, N.Y.) 321, 1072–1075, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1162018 (2008).
Jung, S., McCrory, C. C. L., Ferrer, I. M., Peters, J. C. & Jaramillo, T. F. Benchmarking nanoparticulate metal oxide electrocatalysts for the alkaline water oxidation reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 3068–3076, https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA07586F (2016).
Jiao, F. & Frei, H. Nanostructured cobalt and manganese oxide clusters as efficient water oxidation catalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 3, 1018, https://doi.org/10.1039/c002074e (2010).
Wang, F. et al. Morphology-controlled synthesis of CoMoO4 nanoarchitectures anchored on carbon cloth for high-efficiency oxygen oxidation reaction. RSC Adv. 9, 1562–1569, https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09484E (2019).
Umena, Y., Kawakami, K., Shen, J.-R. & Kamiya, N. Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Nature 473, 55–60, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09913 (2011).
Harriman, A., Richoux, M.-C., Christensen, P. A., Mosseri, S. & Neta, P. Redox reactions with colloidal metal oxides. Comparison of radiation-generated and chemically generated RuO2 · 2H2O. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 83, 3001, https://doi.org/10.1039/f19878303001 (1987).
Joliot, P. & Johnson, G. N. Regulation of cyclic and linear electron flow in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 13317–13322, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110189108 (2011).
Morita, M., Iwakura, C. & Tamura, H. The anodic characteristics of manganese dioxide electrodes prepared by thermal decomposition of manganese nitrate. Electrochimica Acta 22, 325–328, https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(77)85081-0 (1977).
Rumberger, E. M. W., Ahn, H. S., Bell, A. T. & Tilley, T. D. Water oxidation catalysis via immobilization of the dimanganese complex Mn2(μ-O)2Cl(μ-O2CCH3)(bpy)2(H2O)(NO3)2 onto silica. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 42, 12238–12247, https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt51472b (2013).
Young, K. J., Brennan, B. J., Tagore, R. & Brudvig, G. W. Photosynthetic water oxidation. Insights from manganese model chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 48, 567–574, https://doi.org/10.1021/ar5004175 (2015).
Zhu, S. et al. Low-Charge-Carrier-Scattering Three-Dimensional α-MnO2/β-MnO2 Networks for Ultra-High-Rate Asymmetrical Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 1051–1059, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01592 (2019).
Zhu, S. J., Zhang, J., Ma, J. J., Zhang, Y. X. & Yao, K. X. Rational design of coaxial mesoporous birnessite manganese dioxide/amorphous-carbon nanotubes arrays for advanced asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 278, 555–561, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.054 (2015).
Zhu, S. J. et al. Rational design of octahedron and nanowire CeO2@MnO2 core-shell heterostructures with outstanding rate capability for asymmetric supercapacitors. Chemcomm (Cambridge, England) 51, 14840–14843, https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc03976b (2015).
Guo, X. et al. Quasi-parallel arrays with a 2D-on-2D structure for electrochemical supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 24717–24727, https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA07869F (2018).
Zhu, S. et al. Structural Directed Growth of Ultrathin Parallel Birnessite on β-MnO2 for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 12, 1033–1042, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b03431 (2018).
Lv, X. et al. Controllable synthesis of MnO2 nanostructures anchored on graphite foam with different morphologies for a high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor. CrystEngComm 20, 1690–1697, https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE02108A (2018).
Liu, X. Y. et al. Engineering hydrogenated manganese dioxide nanostructures for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 537, 661–670, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.11.075 (2019).
Huang, M. et al. Self-assembly of mesoporous nanotubes assembled from interwoven ultrathin birnessite-type MnO2 nanosheets for asymmetric supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 4, 3878, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03878 (2014).
He, Y., Jiang, D. B., Chen, J., Jiang, D. Y. & Zhang, Y. X. Synthesis of MnO2 nanosheets on montmorillonite for oxidative degradation and adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 510, 207–220, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.066 (2018).
Hocking, R. K. et al. Water-oxidation catalysis by manganese in a geochemical-like cycle. Nature chem. 3, 461–466, https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1049 (2011).
Najafpour, M. M., Moghaddam, A. N., Dau, H. & Zaharieva, I. Fragments of layered manganese oxide are the real water oxidation catalyst after transformation of molecular precursor on clay. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 7245–7248, https://doi.org/10.1021/ja5028716 (2014).
Najafpour, M. M. et al. The role of nano-sized manganese oxides in the oxygen-evolution reactions by manganese complexes. Towards a complete picture. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 43, 13122–13135, https://doi.org/10.1039/c4dt01367k (2014).
Najafpour, M. M. & Moghaddam, A. N. Nano-sized manganese oxide. A proposed catalyst for water oxidation in the reaction of some manganese complexes and cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 41, 10292–10297, https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt30965c (2012).
Singh, A. et al. Water oxidation catalysis by nanoparticulate manganese oxide thin films. Probing the effect of the manganese precursors. Chem. Mater. 25, 1098–1108, https://doi.org/10.1021/cm3041345 (2013).
Walter, C. et al. A molecular approach to manganese nitride acting as a high performance electrocatalyst in the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. 130, 706–710, https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201710460 (2018).
Indra, A., Menezes, P. W. & Driess, M. Uncovering structure-activity relationships in manganese-oxide-based heterogeneous catalysts for efficient water oxidation. Chem Sus Chem 8, 776–785, https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402812 (2015).
Najafpour, M. M., Haghighi, B., Sedigh, D. J. & Ghobadi, M. Z. Conversions of Mn oxides to nanolayered Mn oxide in electrochemical water oxidation at near neutral pH, all to a better catalyst. Catalyst evolution. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 42, 16683–16686, https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt52304g (2013).
Najafpour, M. M. & Sedigh, D. J. Water oxidation by manganese oxides, a new step towards a complete picture. Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 42, 12173–12178, https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt51345a (2013).
May, K. J. et al. Influence of oxygen evolution during water oxidation on the surface of perovskite oxide catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 3264–3270, https://doi.org/10.1021/jz301414z (2012).
Najafpour, M. M. et al. Transformation of La0.65Sr0.35MnO3 in electrochemical water oxidation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 8560–8568, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.016 (2017).
Pfrommer, J. et al. A molecular approach to self-supported cobalt-substituted ZnO materials as remarkably stable electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Angew. Chem. 126, 5283–5287, https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201400243 (2014).
Najafpour, M. M., Hosseini, S. M., Tavahodi, M. & Ghobadi, M. Z. The conversion of CoSe2 to Co oxide under the electrochemical water oxidation condition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 13469–13475, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.288 (2016).
Stern, L.-A., Feng, L., Song, F. & Hu, X. Ni2P as a Janus catalyst for water splitting. The oxygen evolution activity of Ni2P nanoparticles. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 2347–2351, https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EE01155H (2015).
Wang, P., Song, F., Amal, R., Ng, Y. H. & Hu, X. Efficient water splitting catalyzed by cobalt phosphide-based nanoneedle arrays supported on carbon cloth. Chem Sus Chem 9, 472–477, https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201501599 (2016).
Heidari, S. et al. Water oxidation by simple manganese salts in the presence of cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate. Towards a complete picture. Dalton trans (Cambridge, England: 2003) 47, 1557–1565, https://doi.org/10.1039/c7dt04143h (2018).
Xiao, X. & Bard, A. J. Observing single nanoparticle collisions at an ultramicroelectrode by electrocatalytic amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 9610–9612, https://doi.org/10.1021/ja072344w (2007).
Post, K. & Robins, R. G. Thermodynamic diagrams for the vanadium-water system at 298·15 K. Electrochim Acta 21, 401–405, https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(76)85115-8 (1976).
Ilton, E. S., Post, J. E., Heaney, P. J., Ling, F. T. & Kerisit, S. N. XPS determination of Mn oxidation states in Mn (hydr)oxides. Appl Surf Sci. 366, 475–485, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.159 (2016).
Najafpour, M. M. et al. Nanolayered manganese oxides. Insights from inorganic electrochemistry. Catal. Sci. Technol. 7, 3499–3510, https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY00215G (2017).
Kwon, K. D., Refson, K. & Sposito, G. On the role of Mn(IV) vacancies in the photoreductive dissolution of hexagonal birnessite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 4142–4150, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.04.031 (2009).
Allen, G. C., Harris, S. J., Jutson, J. A. & Dyke, J. M. A study of a number of mixed transition metal oxide spinels using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl Surf Sci. 37, 111–134, https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-4332(89)90977-X (1989).
Saputra, E. et al. Manganese oxides at different oxidation states for heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate for phenol degradation in aqueous solutions. Appl Catal B: Environmental 142–143, 729–735, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.06.004 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences and the National Elite Foundation for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.M.N. proposed the concept. All authors designed, performed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Heidari, S., Singh, J.P., Feizi, H. et al. Electrochemical water oxidation by simple manganese salts. Sci Rep 9, 7749 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44001-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44001-z