Abstract
As a basic building block of graphene-based materials, graphene oxide (GO) plays an important role in scientific research and industrial applications. At present, numerous methods have been employed to synthesize GO, there are still some issues that need to be solved, thus it is of importance to develop a green, safe and low-cost GO preparation method. Herein, a green, safe and fast method was designed to prepare GO, namely, graphite powder was firstly oxidized in a dilute sulfuric acid solution (H2SO4, 6 mol/L) with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30 wt%) as oxidant, and then exfoliated to GO by ultrasonic treatment in water. In this process, H2O2 was the only oxidant, and no other oxidants were used, thus the explosive nature of GO preparation reaction in the conventional methods could be completely eliminated. This method has other advantages such as green, fast, low-cost and no Mn-based residues. The experimental results confirm that obtained GO with oxygen-containing groups has better adsorption property compared to the graphite powder. As adsorbent, GO can remove methylene blue (50 mg/L) and Cd2+ (56.2 mg/L) from water with removal capacity of 23.8 mg/g and 24.7 mg/g, respectively. It provides a green, fast and low-cost method to prepare GO for some applications such as adsorbent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Graphene was firstly prepared by the mechanical exfoliation of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite in 20041. Up to now, graphene is widely considered as one of the most important novel 2D nanomaterials2,3,4. As a derivative of graphene5,6, GO has its unique property due to several oxygen-containing groups covalently bonded to its basal planes and edges7,8. More importantly, GO acts as a basic building block, various graphene-based materials can be synthesized through the interactions between GO and other materials9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. Therefore, a green, safe, fast and low-cost preparation of GO is very critical, and lots of attentions have been attracted to this issue.
On the basis of the oxidation-exfoliation process, wet chemical route20 is generally recognized as large-scale preparation method. Since the preparation of GO was firstly reported in 1859 based on the Brodie’s method21, and a mixture of potassium chlorate (KClO3) in fuming nitric acid (HNO3) was used to oxidize graphite. Nearly forty years later, Staudenmaier optimally oxidized graphite by slowly adding KClO3 into a mixture of fuming HNO3 and concentrated H2SO422. In 1958, graphite was usually oxidized by the Hummers’ method23 with a mixture of KMnO4 and NaNO3 in concentrated H2SO4. In 2010, the Hummers’ method was further optimized and called as Tour’s method by replacing NaNO3 and adding proportionate phosphoric acid (H3PO4) as the stabilizer for the mixed system24. Moreover, Jin et al.25 used concentrated H2SO4 as intercalated molecules in the oxidation of graphite to GO and catalyst to the dehydration exfoliation of oxygenic and hydric groups from GO based on the Hummers’ method.
Although researchers have made great efforts to improve the Hummers’ method, there are some practical issues to be resolved, such as long reaction time, security risks, difficult quality control and a large amount of waste acid liquid26. Thus, numerous alternative methods have been explored to synthesize GO. For example, Gao et al.27 reported an iron-based method with potassium ferrate Fe (VI) (K2FeO4) as oxidant, in this process, the impurities of Mn-based metals were effectively avoided, and concentrated H2SO4 was effectively recycled. Yu et al.28 reported a facile and green method to synthesize GO with K2FeO4 and H2O2 as oxidants in water with pH of 3 at 50 °C. As combined catalyst, the mixture of Fe(VI) solution and H2O2 is a substitute of KMnO4 and strongly corrosive acids. However, these iron-based methods have some issues such as the pollution of Fe-based metals and complex post-processing.
With the environmental-friendliness and low cost, the electrochemical processes have been widely developed to prepare GO29,30. For example, Pei et al.31 used concentrated H2SO4 (98 wt%) as intercalation agent of graphite with a direct current of 1.6 V, then employed dilute H2SO4 (50 wt%) as acidic medium to oxidize the intercalated graphite with a direct current of 5 V, and finally hired ultrasonic to exfoliate the intercalated oxidized graphite. In this process, H2SO4 was primarily used as a control agent to tune the oxygen evolution reaction of water for the oxidation of graphitic lattice, thus H2SO4 was recycled, and no other oxidant was needed. Unfortunately, the accompanied water/solvent electrolysis process aggravates the expansion and delamination of graphitic materials, which lead to ineffective current supply or broken circuit29,30. Moreover, the structure and property of obtained products are very different from that of GO prepared by the improved Hummers’ methods5,6,7,8,9,10, maybe due to the low oxidation and exfoliation degree32,33,34,35.
At the same time, great efforts have been paid to uncover the formation mechanism of GO36. For example, Lee et al.37 exfoliated and dispersed 2D materials in pure water due to the presence of surface charges as a result of edge functionalization or intrinsic polarity, which can induce the oxygen attacking. Li et al.38 exfoliated large graphite crystals to small graphene flakes due to the sonication leading to the rupture and kink band striations on the flake surfaces, subsequent oxidative attack and intercalation of solvent. More recently, Zhu et al. exquisitely prepared GO sheets by the microfluidic oxidation of graphite with KMnO4 in concentrated H2SO4 in a sealed screw-top bottle due to the enhanced mass transfer and extremely quick energy exchange39.
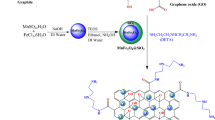
On the basis of the development of GO preparation methods and the exploration of GO formation mechanism above mentioned, we are trying to find a green, safe and low-cost way to prepare GO. In this paper, a green, safe and low-cost method was designed to synthesize GO by oxidizing graphite powder in a dilute H2SO4 solution with H2O2 as oxidant, and subsequent ultrasonic treatment in water. The experimental results prove that GO can be prepared by this method. Interestingly, the obtained GO with oxygen-containing groups can be used as adsorbent to remove methylene blue and Cd2+ from water.
Experimental section
Materials
Graphite powder (99.8 wt% purity, 200 mesh), H2SO4 (18 mol/L) and H2O2 (30 wt% in water) were purchased from National Pharmaceutical Reagent Company. All chemicals were used without further purification. Deionized water (a resistance of 18 MΩ) made from a Milli-Q solvent system was used through all the experiments.
Preparation of GO
As a typical process, the graphite powder was firstly oxidized in a mixture of H2SO4 and H2O2, and then exfoliated to GO in water.
Firstly, 2.0 g of graphite powder was added into a beaker with 50 mL of dilute H2SO4 solution (6 mol/L), and 20 mL of H2O2 (30 wt%) was slowly added into the mixed dispersion under electromagnetic stirring condition. Then, the mixed dispersion was heated to 40 ℃ through a temperature control water bath for 3 h. As control experiments, another beaker was added with 2.0 g of graphite powder and 50 mL of H2SO4 solution without adding H2O2, following the same experimental operation as that of the first beaker.
Secondly, after cooling naturally to room temperature, the resulting dispersion was filtered and cleaned with deionized water several times to pH of 7. The dilute H2SO4 solution was collected and stored for reuse.
Thirdly, a portion of sample was treated with ultrasound in deionized water for 30 min, after filtering, the obtained GO was dried in vacuum at 60 °C for characterizations.
In this process, only H2O2 was oxidizer, and no other oxidant was used. Dilute H2SO4 solution was primarily used as an acidic medium28,31 and control agent to tune the oxygen radical reaction, thus H2SO4 was recycled. The preparation process takes less than 4 h, including 3 h of water bath at 40 °C for oxidation reaction and 30 min of ultrasonic stripping at room temperature.
Characterizations
The microstructures of graphite powder, intermediate and obtained GO were detected by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4800), transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100), and atomic force microscopy (AFM, Nanoscope V, Bruker Instruments). The X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8 diffractometer), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Nicolet5700), Raman spectrometer (LabRAM HR800) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, K-alpha1063) were used to analyze the structural composition of GO.
Results and discussion
Structure analysis
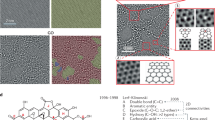
The microstructures of graphite powder, oxidized graphite (marked as intermediate) and GO are shown in Fig. 1. The graphite powder has irregular and tightly stacked structure (Fig. 1b), while the structure of intermediate is loose (Fig. 1c), very different from that of graphite powder, and it can be easily scattered in the deionized water (the inset of Fig. 1c). After ultrasound treatment in deionized water, the intermediate can be exfoliated to GO (Fig. 1d), and the color of GO solution is light yellow (the inset of Fig. 1d).
Figure 2a further reveals that graphite powder has irregular and stacked structure with sizes in a range of dozens of microns. In contrast, the intermediate has a loose structure with smaller sizes, as shown in Fig. 2b. Moreover, the cross-section SEM images of graphite powder and intermediate show their difference more clearly. Compared to graphite powder (Fig. 2c), the intermediate (Fig. 2d) has wider layer spacing. After ultrasonic process, the graphite powder can be separated into large sheets with a size of several microns (Fig. 2e), while the intermediate can be stripped into GO nanosheets (Fig. 2f).
TEM images reveal that obtained GO with folded structure is single-layer or multilayer, as shown in Fig. 3. Thus, it can be confirmed that GO nanosheets can be prepared from graphite powder by this method.
After the intermediate was exfoliated to an aqueous solution of GO (0.5 mg/mL) by ultrasonic treatment, and then GO solution was dripped onto freshly cleaned Si substrate after vacuum drying for AFM characterization. Figure 4 shows that GO with a wrinkled structure has a few-layer thickness40.
An aqueous GO solution (1.0 mg/mL) has a clear Tyndall effect (Fig. 5a). UV–Vis spectrum of this GO solution has a main peak at 231 nm and a broad shoulder at around 300 nm (Fig. 5b), suggesting that some oxygen-containing functional groups are bonded to the basal planes and edges of GO24.
XRD, FTIR and Raman spectra of graphite powder and obtained GO nanosheets were analyzed to reveal their structural difference. As shown in Fig. 6a, the XRD peak of graphite powder locates at 2θ = 26.4°, while the peak of GO nanosheets locates at 2θ = 10.0°, and their peaks are consistent with previous reports41,42, indicating a larger spacing between GO layers compared with graphite powder.
Based on the FTIR spectra analyses, the obtained GO nanosheets have some functional groups41,42 such as O–H stretching vibration (3430 cm−1), C=O stretching vibration (1720 cm−1), C=C vibration (1620 cm−1), C–O vibrations (1400 cm−1, 1050 cm−1) and C–OH vibration (1240 cm−1), while the FTIR spectra of graphite powder are different from that of obtained GO (Fig. 6b).
Raman analyses were also used to prove their structural change (Fig. 6c). It can be seen that both of them have D peak (∼ 1320 cm−1), G peak (∼ 1580 cm−1) and 2D band (∼ 2650 cm−1). Moreover, the intensity ratio of the D band (∼ 1320 cm−1) to the G band (∼ 1580 cm−1) (ID/IG) slightly increases from 0.38 for graphite powder to 0.45 for the obtained GO nanosheets, indicating that the crystal defects and disorder are increased in the obtained GO nanosheets41,42. Moreover, their 2D Raman peak fittings have clear difference, as shown in Fig. 6d.
The XPS spectra of graphite powder and GO nanosheets were performed to analyze their composition. As shown in Fig. 7, both XPS survey spectra have two clear peaks of carbon (C1s) and oxygen (O1s), while the intensity of the O1s peak in GO increases significantly, compared with graphite powder (Fig. 7a). The high-resolution C1s spectra reveal that both of them have C=C/C–C (284.7 eV), C–O (285.8 eV) and C=O (286.7 eV) groups41,42, respectively. Their high-resolution O1s XPS spectra have two major peaks located at 531.8 eV (C–O) and 533.0 eV (C=O), respectively. Moreover, the peak intensity of C=O for graphite powder (Fig. 7b,c) is lower than that of GO nanosheets (Fig. 7e,f), maybe due to the oxidation intercalation of H2O2.
Mechanism analysis
To analyze the preparation process of GO by this method, some important factors should be taken into account as follows.
-
(1)
In the system of H2SO4/H2O2, only H2O2 acts as a strong green oxidizer, and a dilute H2SO4 solution (6 mol/L) is an acidic medium. In this process, some oxygen radicals (such as ·OH and ·OH2) can be produced from H2O2 under acidic conditions, and then the creases and defects on the graphite surface are selectively attacked by oxygen radicals37,38. As a result, the selective attacking endowed GO with some oxygen-containing groups, which are confirmed by the FTIR and XPS spectra of graphite powder and GO nanosheets. Dilute H2SO4 solution is primarily used as an acidic medium28,31 and control agent to tune the oxygen radical reaction, thus H2SO4 is recycled.
-
(2)
The oxidant content and the reaction temperature are very critical influencing factors. In this process, if the oxidant content is low, and the desired oxidation effect will not be achieved. On the other hand, if the temperature of the reaction is too high, and the acceleration of the decomposition reaction of H2O2 results in insufficient reaction time. After optimization, the mixed dispersion (including 2.0 g of graphite powder, 50 mL of 6 mol/L H2SO4 solution, and 20 mL of 30 wt% H2O2) was in a beaker and heated to 40 °C for 3 h, thus the graphite surface was attacked by enough oxygen radicals derived from the decomposition of H2O2 for enough time.
-
(3)
The GO was prepared by this method involving two main processes: the oxidation intercalation and ultrasonic delamination. The oxidation intercalation was accomplished by the selective attacking of oxygen radicals in a dilute H2SO4 solution, which causes GO surface with lots of oxygen-containing functional groups. The delamination was completed by ultrasonic treatment in deionized water, and no other intercalation agent was required in this process.
According to the above analysis, only H2O2 was used as oxidant without harmful byproducts, the dilute H2SO4 solution was used as acidic medium and recycled. The dispersion containing intermediate was not viscous, and the intermediate was easily filtered and cleaned for delamination, thus the preparation process was green, safe and low-cost.
The microstructure of the intermediate was analyzed to confirm the feasibility of this method. As shown in Fig. 8a, the intermediate shows a loose structure, compared with graphite powder (Fig. 1b). The magnified parts of its selected area clearly display some traces after selective attacking (Fig. 8b–d). Moreover, the spacing between layers was markedly widened in the intermediate (Fig. 8e), and lots of traces were left at the edges after selective attacking (Fig. 8f), thus GO nanosheets were successfully prepared from graphite powder to intermediate after the oxidation intercalation of H2O2 and ultrasonic treatment in deionized water.
Adsorptive property
The obtained GO nanosheets with abundant functional groups can be used as adsorbent to remove methylene blue (MB) and Cd2+ from water. In general, MB was used as the model compound to verify the adsorption property of adsorbent. The general experimental process was described as follows: 110 mg of adsorbent was added to 50 mL of MB solution (50 mg/L), followed by stirring at 200 rpm at room temperature. At time intervals of 10 min, the adsorbent was separated by filtration and the concentration of residual MB in the filtrate was calculated by Beer’s law based on the absorption peak at 662 nm with a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-2450)43,44.
On the other hand, an aqueous solution of Cd2+ was prepared by dissolving the corresponding lead nitrate in deionized water to arrive at a concentration of 5.0 × 10–4 mol/L (56.2 mg/L). Adsorption tests were carried out by using 130 mg adsorbent in 50 mL aqueous solution of Cd2+. Batch experiments of adsorption were carried out in conical flasks with stirring under ambient condition. At given time intervals of 10 min, 1 mL of the filtrate was obtained by filtering from the mixed solution. The concentration of Cd2+ in the filtrate was determined by single scan oscillopolarography (JP-303E)45,46.
In contrast, the graphite powder and GO nanosheets adsorbed MB (50 mg/L) at room temperature, their adsorption equilibriums reached at around 50 min (Fig. 9a), their removal efficiency are 75.0% and 95.0%, respectively. Moreover, their adsorption capacity were evaluated as 18.8 mg/g and 23.8 mg/g, respectively.
On the other hand, the graphite powder and GO nanosheets adsorbed Cd2+ (56.2 mg/L) from water at room temperature, their adsorption equilibriums reached at around 50 min (Fig. 9b), their removal efficiency were 46.0% and 88.0%, respectively. As well as their adsorption capacity were evaluated as 12.9 mg/g and 24.7 mg/g, respectively.
From the above comparison of adsorption properties, the graphite powder and GO nanosheets can adsorb MB and Cd2+ from water, especially the adsorption capacity of GO nanosheets is higher than that of graphite powder and some results reported47,48,49,50,51. The adsorption results were also compared with the literature47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55. The adsorption characteristics of MB and Cd2+ onto GO or GO composites were shown in Table 1. In our experiment, GO was directly used as adsorbent, and its adsorption property should be improved. In particular, GO can be hybridized to fabricate composite materials with better adsorption property. For example, the GO/chitosan sponge with chitosan sponge content of 9% has adsorption capacity of 275.5 mg/g for MB56.
Due to abundant functional groups and structure defects on its base planes and edges, GO has unique structure and property (such as novel physicochemical property, large specific surface area, and highly active surface), which plays an important role in the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from water57.
In the case of MB adsorption, negatively charged GO interacts with positive dye of MB, thus the electrostatic attraction and hydrophobic π-π interactions are responsible for this adsorption process58,59. Moreover, the adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of MB onto GO was demonstrated as a mixed physisorption-chemisorption process60.
To remove heavy metal ions from water, GO has various interactions such as coordination, chelation, electrostatic interaction, π–π interaction, acid base interaction with various metal/metal ions, due to its unique chemical structure containing various hydrophilic containing-oxygen groups and tiny sp2 carbon domains surrounded by sp3 domains61,62,63. Bsaed on the literature reported64,65,66, the adsorption process of Cd2+ onto GO was consistent with the pseudo second-order equation and the Langmuir isotherm model. However, the actual adsorption process has various influencing factors67, such as the electronegativity and standard reduction potential of heavy metal ions.
On the other hand, the experimental conditions play an important role in the specific adsorption process. In the cases of MB and Cd2+, some importan influence factors (such as adsorbent dose, solution pH, contact time and temperature) should be taken into account as follows. As shown in Fig. 9, their adsorption equilibriums reach at around 50 min, and the adsorption contact time is considered to be extended to one hour. In order to save operating costs, the adsorption temperature is kept at room temperature.
At the same time, the dosage of adsorbent is gradually increased from 50 to 70, 90, 110, 130, 150 and 170 mg in 50 mL of MB solution (50 mg/L) or Cd2+ solution (56.2 mg/L), and the pH of solution is gradually adjusted from 1 to 12.
Figure 10a shows that adsorption removal of MB reaches equilibrium as the dosage of adsorbent is 110 mg in 50 mL solution, while Fig. 10b reveals that adsorption removal of MB reaches peak at pH of 10. On the other hand, Fig. 10c shows that adsorption removal of Cd2+ reaches equilibrium as the dosage of adsorbent is 130 mg in 50 mL solution, while Fig. 10d reveals that adsorption removal of Cd2+ reaches peak at pH of 7.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we develop a green, safe, fast and low-cost method to prepare GO nanosheets by oxidizing graphite powder in a dilute H2SO4 solution with H2O2 as oxidant and subsequent ultrasonic stripping in deionized water. The formation mechanism can be attributed to strong oxygen radicals attacking to creases and defects on the surface of large graphite sheets, which cause intermediate with oxygen-containing functional groups to be easily exfoliated into nanosheets by ultrasonic treatment. This work provides a green, safe and low-cost method to prepare GO nanosheets for functional applications such as adsorbent.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666–669 (2004).
Geim, A. K. & Novoselov, K. S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 490, 192–200 (2012).
Yang, Y. et al. Large-area graphene-nanomesh/carbon-nanotube hybrid membranes for ionic and molecular manofiltration. Science 364, 1057–1062 (2019).
Park, S. & Ruoff, R. S. Chemical methods for the production of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 217–224 (2009).
Zhu, Y. et al. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 22, 3906–3924 (2010).
Dreyer, D. R., Park, S., Bielawski, C. W. & Ruoff, R. S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 228–240 (2010).
Yu, H. et al. High-efficient synthesis of graphene oxide based on improved Hummers method. Sci. Rep. 6, 36143 (2016).
Loh, K. P., Bao, Q., Eda, G. & Chhowalla, M. Graphene oxide as a chemically tunable platform for optical applications. Nat. Chem. 2, 1015–1024 (2010).
Kim, J., Cote, L. J. & Huang, J. Two dimensional soft material: New faces of graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 45, 1356–1364 (2012).
Huang, X., Qi, X., Boey, F. & Zhang, H. Graphene-based composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 666–686 (2012).
Zhao, J., Pei, S., Ren, W., Gao, L. & Cheng, H.-M. Efficient preparation of large-area graphene oxide sheets for transparent conductive films. ACS Nano 4, 5245–5252 (2010).
Chen, L. et al. Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing. Nature 550, 380–383 (2017).
Mi, B. Scaling up nanoporous graphene membranes. Science 364, 1033–1034 (2019).
Xu, Z. & Gao, C. Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres. Nat. Commun. 2, 571 (2011).
Hu, W. et al. Graphene-based antibacterial paper. ACS Nano 4, 4317–4323 (2010).
Zhou, Y. et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene-reduced graphene oxide composite electrodes for stretchable supercapacitors. ACS Nano 14, 3576–3586 (2020).
Zheng, H. et al. Antibacterial applications of graphene oxides: Structure–activity relationships, molecular initiating events and biosafety. Sci. Bull. 63, 133–142 (2018).
Stankovich, S. et al. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442, 282–286 (2006).
Ma, Y., Zheng, Y. & Zhu, Y. Towards industrialization of graphene oxide. Sci. China Mater. 63, 1861–1869 (2020).
Brodie, B. C. X. I. I. I. On the atomic weight of graphite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 149, 249–259 (1859).
Staudenmaier, L. Verfahren zur darstellung der graphitsäure. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 31, 1481–1487 (1898).
Hummers, W. S. & Offeman, R. E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339–1339 (1958).
Marcano, D. C. et al. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806–4814 (2010).
Hong, Y., Wang, Z. & Jin, X. Sulfuric acid intercalated graphite oxide for graphene preparation. Sci. Rep. 3, 3439 (2013).
Lin, L., Peng, H. & Liu, Z. Synthesis challenges for graphene industry. Nat. Mater. 18, 520–529 (2019).
Peng, L. et al. An iron-based green approach to 1-h production of single-layer graphene oxide. Nat. Commun. 6, 5716 (2015).
Chao, Yu., Wang, C.-F. & Chen, S. Facile access to graphene oxide from Ferro-induced oxidation. Sci. Rep. 6, 17071 (2016).
Yang, S., Lohe, M. R., Muellen, K. & Feng, X. New-generation graphene from electrochemical approaches: Production and applications. Adv. Mater. 28, 6213–6221 (2016).
Yang, S. et al. Organic radical-assisted electrochemical exfoliation for the scalable production of high-quality graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 13927–13932 (2015).
Pei, S., Wei, Q., Huang, K., Cheng, H.-M. & Ren, W. Green synthesis of graphene oxide by seconds timescale water electrolytic oxidation. Nat. Commun. 9, 145 (2018).
Gurzęda, B. et al. Synthesis of graphite oxide by electrochemical oxidation in aqueous perchloric acid. Carbon 100, 540–545 (2016).
Yu, P. et al. Mechanically-assisted electrochemical production of graphene oxide. Chem. Mater. 28, 8429–8438 (2016).
Wu, L. et al. Powder, paper and foam of few-layer graphene prepared in high yield by electrochemical intercalation exfoliation of expanded graphite. Small 10, 1421–1429 (2014).
Tian, Z. et al. Facile electrochemical approach for the production of graphite oxide with tunable chemistry. Carbon 112, 185–191 (2017).
Dimiev, A. M. & James, M. T. Mechanism of graphene oxide formation. ACS Nano 8, 3060–3068 (2014).
Kim, J. et al. Direct exfoliation and dispersion of two-dimensional materials in pure water via temperature control. Nat. Commun. 6, 8294 (2015).
Li, Z. et al. Mechanisms of liquid-phase exfoliation for the production of graphene. ACS Nano 14, 10976–10985 (2020).
Ye, C. et al. Microfluidic oxidation of graphite in two minutes with capability of real-time monitoring. Adv. Mater. 34, 2107083 (2022).
Suk, J. W., Piner, R. D., An, J. H. & Ruoff, R. S. Mechanical Properties of Monolayer Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 4, 6557–6564 (2010).
Tian, Z., Cao, K., Bai, S., He, G. & Li, J. One-pot transformation of waste toner powder into 3D graphene oxide hydrogel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 496–501 (2019).
Tian, Z. et al. Facile synthesis of highly conductive sulfur-doped reduced graphene oxide sheets. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 1125–1130 (2016).
Moussa, H. et al. ZnO rods/reduced graphene oxide composites prepared via a solvothermal reaction for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B. 185, 11–21 (2016).
Tian, Z. et al. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide hydrogel. Sci. Adv. Mater. 7, 1415–1423 (2015).
Qin, X. et al. A green technology for the synthesis of cellulose succinate for efficient adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions. RSC Adv. 6, 26817–26825 (2016).
Du, J., Zhu, H., Li, Y., Zhang, T. & Yang, C. Simultaneous determination of trace Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ and Co2+ in zinc electrolytes by Oscillopolarographic second derivative waves. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28, 2592–2598 (2018).
Ramesha, G. K. et al. Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 361, 270–277 (2011).
El-Sharkaway, E. A. et al. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using polyaniline/graphene oxide or polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide composites. Environ. Technol. 41, 2854–2862 (2020).
Nguyen-Phan, T. D. et al. The role of graphene oxide content on the adsorption-enhanced photocatalysis of titanium dioxide/graphene oxide composites. Chem. Eng. J. 170, 226–232 (2011).
Huang, H. et al. Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater. Open. Chem. 18, 97–107 (2020).
Masoudzadeh, M. & Karachi, N. Removal of cadmium ion from wastewater using carboxylated nanoporous graphene (G-COOH). Eurasian. J. Anal. Chem. 13, 1–10 (2018).
Bai, S. et al. Facile preparation of porous biomass charcoal from peanut shell as adsorbent. Sci. Rep. 10, 15845 (2020).
Musielak, M. et al. Graphene oxide/carbon nanotube membranes for highly efficient removal of metal ions from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 28582–28590 (2019).
Li, B. et al. Green reduction of graphene oxide by sugarcane bagasse extract and its application for the removal of cadmium in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 189, 128–134 (2018).
Bian, Y. et al. Effect of the oxygen-containing functional group of graphene oxide on the aqueous cadmium ions removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 329, 269–275 (2015).
Qi, C., Zhao, L., Lin, Y. & Wu, D. Graphene oxide/chitosan sponge as a novel filtering material for the removal of dye from water. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 517, 18–27 (2018).
Rout, D. R. et al. Graphene-based materials for effective adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants: A critical and comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 863, 160871 (2023).
Huong, P. T. L. et al. Functional manganese ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites: effects of graphene oxide on the adsorption mechanisms of organic MB dye and inorganic As(V) ions from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 8, 12376–12389 (2018).
Molla, A. et al. Selective adsorption of organic dyes on graphene oxide: Theoretical and experimental analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 464, 170–177 (2019).
Arias, F. A. et al. The adsorption of methylene blue on eco-friendly reduced graphene oxide. Nanomaterials 10, 681 (2020).
Deshwal, N. et al. A review on recent advancements on removal of harmful metal/metal ions using graphene oxide: Experimental and theoretical approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 858, 159672 (2023).
Tan, P. et al. Adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous single metal solutions on graphene oxide membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 297, 251–260 (2015).
Chen, Y. & Yang, X. Molecular simulation of layered GO membranes with amorphous structure for heavy metal ions separation. J. Membrane Sci. 660, 120863 (2022).
Calimli, M. H. et al. Preparation, characterization and adsorption kinetics of methylene blue dye in reduced-graphene oxide supported nanoadsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 309, 113171 (2020).
Li, C. et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous single-metal solutions on graphene oxide-chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Langmuir 35(13), 4481–4490 (2019).
Zhang, L. et al. A graphene-based porous composite hydrogel for efficient heavy metal ions removal from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 305, 122484 (2023).
Peng, W., Li, H., Liu, Y. & Song, S. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 496–504 (2017).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for the High-Level Talents Start-up Fund (PXY-BSQD2016010) and the National Cultivation Fund (PXY-PYJJ2017001) of Pingdingshan University, the Natural Science Foundation of China (11904092), and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2019JJ50028).
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, K., Tian, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Green preparation of graphene oxide nanosheets as adsorbent. Sci Rep 13, 9314 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36595-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36595-2
This article is cited by
-
Estimating of contact area among carbon nanofibers in nanocomposites by the features of network, tunnel and interphase
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Characterization of mechanical properties of graphene nanoplates with vacancy defects using AFEM
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Graphene oxide supported oxidovanadium coordination compound as an efficient catalyst for the green oxidation of benzyl alcohol
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Pristine graphene oxide treatment of wastewater from a typical sub-tropical mine in Chegutu, Zimbabwe
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2025)
-
Star Anise Fruit Extract Mediated Synthesis of CoFe2O4 and GO-CoFe2O4 and Their Comparative Study on Adsorptive Dye Removal Performance
Chemical Papers (2025)