Abstract
Previous observational studies have indicated a significant correlation between plasma proteome composition and cataract pathological status; however, the direction of causality remains uncertain. In light of the aforementioned findings, the present study employs a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomisation strategy, with the objective of elucidating the direct causal link between plasma proteome changes and cataract development. Following rigorous data analysis and validation, a series of plasma proteins were identified as being strongly associated with cataract risk. These included ILF3, FAM171A1, ARHGEF2, LPR1B, CRYGD, GLT8D1, ARHGEF10 and LRRTM1, all of which were confirmed to be potential risk factors for cataract. In contrast, proteins such as MXRA7, ZHX3, SPAG11B, ARID1A, DNASE1L2, COX7A1 and EEF2K were found to exert a protective effect against cataract. To gain further insight into the specific mechanisms by which these causally related proteins contribute to cataract pathology, we subsequently performed an exhaustive bioinformatics analysis. This analysis not only deepened our understanding of the functional properties of these proteins, but also revealed their possible involvement in signalling pathways and molecular interactions, thereby providing new insights into the pathogenesis of cataract.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The 2020 Global Burden of Disease study clearly identified cataracts as the leading cause of blindness, accounting for an estimated 15.2 million cases and 45% of the world’s blind population1. Phacoemulsification, currently considered the preeminent technology, has been widely acclaimed for its remarkable therapeutic efficacy, offering a beacon of hope for vision restoration to countless patients2. However, it is worth noting that this technology primarily addresses advanced stages of cataract development, which somewhat limits its broad application benefits. Common postoperative complications, such as peripheral visual impairment and worsening of dry eye symptoms, reported by patients not only affect their visual experience, but also significantly reduce their daily quality of life - a pressing challenge in the field of cataract treatment3,4. Given the profound and long-lasting negative impact of these problems on patients’ quality of life, there is an urgent need to redirect research efforts towards effective interventions aimed at halting cataract progression at an early stage.Thus, the active exploration and development of novel therapeutic strategies to achieve early prevention and control of cataract disease has emerged as a crucial and pressing task in contemporary ophthalmic research and clinical practice.
Blood proteomics plays a pivotal role in biomarker exploration, as it facilitates the identification of disease-specific molecular markers5. A notable focus on serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels has revealed a robust correlation between these levels and the pathological mechanisms underlying cataract development6. Furthermore, a comparative analysis of plasma protein profiles revealed markedly elevated adiponectin levels in individuals with cataracts relative to healthy controls7. This provides novel insights into the pathophysiological alterations associated with this condition.It is of the utmost importance to acknowledge that, whilst observational studies provide invaluable insights into these associations, their outcomes are frequently influenced by a multitude of confounding factors, thereby limiting the establishment of direct causality.
Mendelian randomization (MR) represents a novel statistical approach that provides robust methodological support for the evaluation of potential causal relationships between plasma proteins and cataracts. This strategy employs naturally occurring genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), as instrumental variables (IVs). This approach serves to mitigate the biases commonly encountered in traditional observational studies, thereby facilitating the unravelling of genuine relationships8. Should a clear causal relationship between plasma proteins and cataracts be successfully established through Mendelian randomisation analysis, this groundbreaking discovery will not only deepen our understanding of cataract pathogenesis but also establish a new precedent in early diagnosis and intervention strategies. This will facilitate the development of more timely and effective treatment options for patients, which will lead to a notable improvement in outcomes.
Research design and data source
A MR study will be conducted to investigate the potential causal relationship between 4907 plasma proteins and the onset of cataracts. To guarantee the scientific of the research, it is imperative to adhere rigorously to three fundamental assumptions in MR analysis:1. The instrumental variable correlation hypothesis necessitates a stable and significant correlation between the selected SNPs and the target exposure factor, thus ensuring that the SNPs serve as a valid proxy variable (i.e. IVs). 2. The instrumental variable independence hypothesis emphasises the necessity for the selected SNPs to be independent of any potential confounding factors in order to mitigate bias on causal inference and uphold the purity of the causal relationship. 3. The instrumental variable exclusivity hypothesis posits that SNPs exert their influence on outcome variables indirectly, through their impact on exposure factors, with no other direct pathways influencing outcomes9,10. This assumption is of critical importance for the validation of the specificity of causal chains. Figure 1 provides an illustration of the fundamental structure of a MR analysis framework.
The proteomic data employed in this study were derived from the Icelandic deCODE study, a biomedical research initiative encompassing 35,559 individuals of European ancestry and encompassing quantitative analysis of 4,907 proteins11. Proteomic profiling was performed using a modified, multiplexed aptamer-based binding assay (SOMAscan version 4). Protein levels were rank-inverse normal transformed by age and sex. The residuals were standardised using rank-inverse normal transformation, after which the standardised values were treated as phenotypes in genome-wide association analyses under the BOLT-LMM linear mixed model. Genomic Association Studies (GWAS) data for cataracts were obtained from Finland’s Finngen database (access link: https://finngen.gitbook.io/documentation/), which comprises individuals of exclusively European descent. The database includes genetic information from 65,235 cataract patients and 341,546 control samples, thereby providing robust support for this study’s genetic component. For details of the GWAS statistics, please refer to Supplementary Table 1.
As this study makes use of exclusively publicly accessible data sources, no further ethical review or approval is required, nor is informed consent from participants necessary.
IVs selection
In our investigation, we devised and implemented a meticulous and structured screening mechanism with the aim of accurately identifying and integrating high-quality SNPs as IVs, thus enhancing the robustness and reliability of subsequent MR analyses12,13,14. First, we extracted all SNPs available in both the exposure GWAS and the chosen reference panel. SNPs not present in the reference panel were excluded to ensure accurate linkage disequilibrium (LD) estimation. Second, 1. Significance Correlation Threshold Screening: In MR analysis, a stringent statistical significance threshold (P-value < 5 × 10⁻⁸) is initially applied as a filtering step to identify SNP loci with highly significant associations with exposure factors. In reverse MR analysis, the selection criteria for instrumental variables (IVs) were adjusted to require a strong statistical association with the outcome variable (P-value < 5 × 10⁻⁸) to ensure alignment with the design logic of reverse causality inference.
This approach guaranteed that the included SNPs were not only biologically relevant but also statistically significant, thus providing a robust foundation for subsequent analysis. 2. Correction for Linkage Imbalance: To address potential confounding effects arising from linkage imbalance among SNPs, more refined screening criteria were introduced, including R² values less than 0.001 and genetic distances less than 10,000 KB. This measure effectively mitigates potential bias caused by tight interloci linkage, while ensuring the independence and accuracy of the analysis results. 3. An evaluation and screening of instrumental variable intensity was conducted. Subsequently, the F statistic (F = β²/SE², where β represents the estimated effect of SNPs on exposure factors and SE is the corresponding standard error) was employed as the primary indicator for the assessment of instrumental variable intensity. The retention of only those SNPs with an F-value exceeding 10 ensured the statistical efficacy of the selected IVs, thereby circumventing the potential for bias associated with inadequate effectiveness in MR analysis while enhancing the precision of causal inference. Morever, We excluded exposures with a SNP-based heritability (h²_snp) estimate of less than 0.05. 4. Verification of Allelic Effect Consistency: To conclude the verification steps, a detailed allelic effect consistency analysis was conducted to ensure that the selected SNPs exhibited a consistent effect direction between the exposure factors and the outcomes. By comparing the allele frequencies and their effect directions in the exposure and outcome datasets, it was possible to eliminate any SNPs that exhibited palindromic or intermediate allelic frequencies, which could disrupt the accurate assessment of causality. The implementation of this step has further enhanced the robustness and reliability of the analysis results.To avoid bias from rare variants, we excluded SNPs with a MAF below 0.01 (or below the threshold used in the original GWAS, if more stringent) in the reference panel.INFO score < 0.9 were excluded to ensure the accuracy of the effect size estimates.
MR analysis and sensitivity analysis
To guarantee the precision and dependability of the findings, the assessment of MR analysis employed five distinct and sophisticated techniques. The aforementioned methods are as follows: random-effects inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method, the MR-Egger regression method, the simple model method, the weighted model method, and the weighted median method. As a fundamental approach for the aggregation of MR data, the IVW method assesses the causal effects of each IV independently through the utilisation of Wald ratio estimation. Subsequently, it generates highly accurate and informative insights into the causal relationships through the implementation of weighted aggregation analyses. This approach not only improves the efficiency of the analyses, but also significantly enhances the accuracy of the causal inference15.The MR-Egger regression method has been developed with the objective of assessing and correcting for potential horizontal pleiotropy, thereby ensuring an unbiased and consistent estimate of causal effects within the InSIDE hypothesis, which posits that “tool strength is independent of direct effects”. The MR-Egger method effectively addresses the potential impact of confounding factors on causal inference by employing a regression model16. The weighted median method places a premium on robustness, necessitating the assignment of a minimum of 50% weight to IVs as a robust foundation for estimating causal effects. To further enhance the robustness of MR analysis, the weighted mediation model employs a novel approach that incorporates similarity information between SNPs as a basis for weight adjustment16. By accounting for the correlation and independence of SNPs, the weighted model method effectively controls for potential confounding factors, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of causal inference17.The simple model method represents a valuable tool for the assessment of potential causality, offering an alternative perspective through which the findings of other sophisticated methods can be scrutinised and substantiated17.In bidirectional Mendelian randomisation analysis, the statistical power in both directions may be affected by the strength of the instrumental variables (e.g. the F-statistic) and the size of the available sample. Therefore, we calculated and compared the average F-statistic of the instrumental variables used for each of the 4,907 plasma proteins and cataracts, while also noting the main GWAS sample sizes used to estimate their respective causal effects. The results showed that this difference was insufficient to affect the interpretation of the symmetry of the bidirectional results significantly. The core objective of this Mendelian randomisation study was to assess the causal association between a single protein and the target trait. In the absence of strong prior evidence of confounding factors among the included proteins, we set a lenient linkage disequilibrium screening threshold (R² < 0.001, 10,000 kb) to incorporate more genetic instrumental variables and enhance statistical power while ensuring the likelihood of strong correlations among the selected instrumental variables was extremely low. Consequently, we did not perform multivariate MR to correct for associations between proteins.It is important to note that all of the above analyses were performed using the latest version (4.3.3) of the R software package ‘TwoSampleMR’, thereby ensuring efficient, reproducible analysis processes and the scientific of the results.
As a fundamental aspect of evaluating the reliability of statistical inferences, sensitivity analyses encompass three essential dimensions: the assessment of heterogeneity, horizontal multiple validity testing, and leave-one-out sensitivity analysis.The Cochran’s Q statistic is calculated using IVW and MR-Egger regression models in order to determine the degree of heterogeneity. A P-value greater than 0.05 indicates that the observed heterogeneity is not statistically significant, thereby increasing the confidence in the results. Furthermore, the MR-Egger intercept test serves to confirm the absence of significant horizontal multidirectionality or bias. A P-value exceeding 0.05 provides substantial evidence for the absence of significant horizontal multidirectionality in the research data, thereby reducing the potential for bias. Furthermore, this test serves to validate hypotheses (2) and (3), thereby enhancing the nature of the analyses.To assess whether our overall MR estimate was unduly influenced by any single instrumental variable, we performed a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis. This was done by iteratively removing each SNP from the full set of instruments one at a time, performing a random-effects inverse-variance weighted MR analysis on the remaining SNPs, and then plotting the resulting causal estimates and confidence intervals for each iteration. This process allowed us to visually inspect the stability of the results and confirm that our findings were robust and not driven by any individual SNP. To reduce the occurrence of false positives resulting from multiple testing, the Benjamini-Hochberg method balances sensitivity and specificity by controlling for the false discovery rate (FDR). With a significance threshold set at p < 0.05 for both the original and FDR-corrected P values, factors below 0.05 were considered statistically significant, thus ensuring the of the results and enhancing the credibility of the research conclusions18,19.
Bioinformatics analysis
Construction of protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks
A systematic search and rigorous validation of specific protein collections that showed positive results in MR analyses was performed using the GeneMANIA database (https://genemania.org/). Based on the established physical interactions and functional relationships of these proteins, we constructed a detailed and model of the PPI network. The network encompasses not only direct physical interactions between proteins but also indirect connections through shared functional pathways, co-expression patterns and genetic interactions. This provides a multidimensional view of protein functional networks.
Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis
With a p-value < 0.05 as the screening criterion, we used the R software package clusterProfiler to perform gene ontology (GO) and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) analyses on differentially expressed plasma protein genes, successfully obtaining detailed information on cellular components (CC), molecular functions (MF), biological processes (BP), and KEGG pathways20,21,22.
Result
MR result
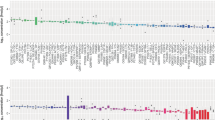
The objective of this study was to conduct a investigation into the potential causal relationship between 4907 plasma proteins and cataracts, with rigorous validation of the three core instrumental variable (IV) assumptions—foundational to robust Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses—via targeted sensitivity analyses as detailed below. For IV Assumption 1 (Relevance: strong association between IVs and plasma protein exposure), we calculated F-statistics. All IVs exhibited F-values > 10 ; for the 17 plasma proteins with significant causal associations (after strict FDR correction, FDR < 0.05), confirming strong IV-plasma protein associations.For IV Assumption 2 (Independence: no association between IVs and confounders), we queried associations between IVs of the 17 proteins and known cataract confounders using the IEU OpenGWAS database, ruling out shared causal variants between IVs and confounders. For IV Assumption 3 (Exclusion restriction: no horizontal pleiotropy), we employed three complementary methods: (1) MR-Egger regression intercept test, all intercept P-values > 0.05) ; (2) Cochran’s Q test 17 proteins had Q-test P > 0.05; (3) MR-PRESSO test (global test P > 0.05, no outlier IVs detected). These sensitivity analyses confirmed no impactful horizontal pleiotropy.Following validation of all three IV assumptions, IVW analysis identified 17 plasma proteins with significant causal associations with cataracts (Fig. 2): 9 protective proteins (MXRA7, ZHX3, SPAG11B, ARID1A, DNASE1L2, COX7A1, CD79B, PPY, EEF2K) that may inhibit cataract progression, and 8 risk-associated proteins (ILF3, FAM171A1, ARHGEF2, LPR1B, CRYGD, GLT8D1, ARHGEF10, LRRTM1) whose aberrant expression or dysfunction may drive cataract onset. Detailed IVW results are presented in Fig. 3, with full outputs of MR-Egger intercept tests and Cochran’s Q tests in Supplementary Tables 2, and sensitivity analysis data in Supplementary Tables 3—collectively ensuring the rigor and credibility of our conclusions.
Forest plot of 17 plasma proteins on Cataract.MR estimation uses IVW as the primary method. nSNP represents the number of SNPs discovered in GWAS; pval represents the statistical threshold; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; the reference line for OR = 1 is shown as a red dashed line; the effect size is represented by a black square, and the 95% confidence interval is shown as a black solid line.
The results of the inverse MR analysis
By employing SNPs that are highly associated with cataracts as IVs, we conducted a investigation into the potential reverse causality between cataracts and the 17 aforementioned plasma proteins. The analytical findings of this intricate relationship are presented in a clear and intuitive manner through the use of a meticulously designed Fig. 4. To rigorously assess the stability and consistency of the MR analysis method, an additional MR-Egger intercept test and Cochran’s Q test were conducted, with detailed results presented in Table 4 of the supplementary materials. The P-value of the MR-Egger intercept test for PPY and CD79B was less than 0.05, indicating significant horizontal pleiotropy. In light of the analysis presented above, we have exercised caution and excluded data from these two proteins from our final analysis. This was done in order to mitigate the potential impact of heterogeneity on our overall conclusions.
Forest plot of 17 Cataract on plasma proteins.MR estimates were calculated using five methods: IVW, MR-Egger, Simple model, Weighted model, and Weighted median method. nSNP represents the number of SNPs identified in GWAS; pval represents the statistical threshold; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; the reference line for OR = 1 is shown as a red dashed line; the effect size is represented by a black square, and the 95% confidence interval is shown as a black solid line.
Bioinformatics analysis results
To gain further insight into the mechanism of biological processes involved in these 15 proteins, we conducted a GO enrichment analysis and a KEGG pathway analysis. These analytical strategies integrate multi-source protein functional annotation information in a systematic manner, thereby enabling the accurate prediction and elucidation of the potential association of various proteins with specific biological processes. The KEGG pathway analysis revealed a significant enrichment of candidate proteins in actin skeleton construction, mitochondrial function regulation, glucocorticoid receptor signalling pathways, and cellular response to osmotic pressure changes (see Fig. 5 and supplementary Table 5 for details). Moreover, the GO enrichment analysis indicated that the candidate proteins were significantly involved in thermogenesis regulation and myocardial contraction (Fig. 6, supplementary Table 5). Furthermore, the protein-protein interaction network was constructed to demonstrate how these 15 proteins collaborate with other key proteins to form a complex regulatory network that plays a central role in the initiation and progression of the aforementioned processes and eventual pathology of cataracts (Fig. 7).
Protein-protein interaction network. Purple edges indicate co-expression, suggesting that these genes are transcriptionally coordinated across multiple cellular conditions; Blue edges represent co-localization, implying that these proteins are found within the same or functionally related subcellular compartments; Yellow edges denote shared protein domains, reflecting common evolutionary or structural features that may underlie similar biochemical functions; Green edges signify genetic interactions, often indicating synthetic lethality, epistasis, or other functional compensation mechanisms.
Discussion
Due to its thermodynamic stability, gamma D-crystallin occupies a central position within the eye lens and constitutes a principal component thereof. The distinctive stability and prevalence of this protein are vital for the maintenance of optimal lens transparency. However, the abnormal accumulation of gamma D-crystallin as a result of misfolding is widely acknowledged as a significant pathological mechanism that contributes to the development of cataracts, a prevalent ocular disorder23. The results of our MR analysis indicate a causal relationship between structural abnormalities in gamma D-crystallin and loss of lens clarity. Moreover, recent scientific research has revealed the potential of various compounds in modulating gamma D-crystallin function. Specifically, quercetin, carbamazepine, resveratrol and myricetin have been demonstrated to effectively bind to specific sites on γD-crystallin, thereby significantly inhibiting its misfolding and abnormal aggregation23,24. This discovery not only enhances our comprehension of cataract pathogenesis but also furnishes a pivotal molecular target for the development of innovative prevention and treatment strategies for cataracts.The process of epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation (EMT) in lens epithelial cells (LECs), particularly the aberrant transformation of LECs into myofibroblasts, is characterised by the up-regulation of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), which plays a common and critical role in the pathogenesis of cataract25. Our study utilized GO enrichment analysis to uncover the central role and key function of the FAM171A1/ARHGEF10 protein complex in dynamically regulating actin cytoskeleton structure. However, the specific involvement and mechanism of FAM171A1/ARHGEF10 in the pathological progression of cataract have not been clearly elucidated and confirmed in existing literature, necessitating further investigation.
The GO enrichment analysis has unveiled the pivotal role of the DNASE1L2 gene in promoting keratinocyte development. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), a significant member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, is widely recognised as FGF-7, while another related member, KGF-2, is known as FGF-1026,27. Recent studies have extensively investigated the impact of FGF-7 (i.e., KGF) on the biological behavior of lens epithelial cells. It was observed that the up-regulation of this growth factor was closely associated with the abnormal proliferation and premature differentiation of lens epithelial cells28,29.Oxidative stress represents a fundamental etiological factor in the pathogenesis of diverse cataract disorders. This process is characterised by a complex cascade of events, primarily involving the degradation and aberrant accumulation of lens proteins, as well as the acceleration of apoptosis in lens epithelial cells30. In this challenging context, KGF-2 (i.e., FGF-10) is noteworthy for its remarkable cellular protective properties. It has been demonstrated to exhibit strong protective effects in vivo experimental models and to effectively counteract the negative effects of oxidative stress in vitro simulated systems. In particular, KGF-2 displays remarkable resilience to H₂O₂ -induced apoptosis in lens epithelial cells and associated oxidative stress through the precise modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant stress signalling pathway and the PI3K/Akt cell survival signalling pathway26. Nevertheless, our study has identified DNASE1L2 as a significant risk factor for the development of cataracts. Further investigation is required to elucidate the influence of DNASE1L2 on the development of cataract-related keratinocytes and to identify the specific KGF that directly causes cataract development.
This study has identified the potential protective role of the MXRA7 gene in the pathogenesis of cataracts, offering a novel perspective on the aetiology of this condition. A analysis of BioGPS platform data and a precise examination of MXRA7 gene expression revealed a significant expression of MXRA7 in key eye regions, including the retina, cornea, and lens, in both mouse models and human biology. This observation indicates that MXRA7 is a crucial factor in the development and functionality of the visual system31. Although initial evidence suggests that MXRA7 may have a protective effect, the precise molecular mechanism through which it exerts this protective influence remains to be elucidated. It is therefore recommended that future research should prioritise the functional verification of the MXRA7 gene, the analysis of its downstream signalling pathway and the construction of an interaction network between MXRA7 and genes or proteins related to cataracts. These endeavours will be pivotal for the complete elucidation of the molecular mechanism underlying MXRA7’s protective role in the prevention of cataracts and the establishment of a robust theoretical foundation for the development of novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of cataracts.
This study has successfully identified a series of plasma proteins with a clear causal relationship with cataracts. This discovery offers valuable insights into potential new treatment pathways that extend beyond reliance on single surgical therapies. It is, however, important to acknowledge certain limitations of the study that require further attention in future research. Firstly, while various proteins with a strong association with cataract pathology have been identified, there is currently a lack of direct experimental evidence to support their specific roles. It is therefore recommended that future research should give priority to an extensive analysis of the functional mechanisms of these proteins through the design of meticulously planned experimental studies, with a view to elucidating their involvement in influencing cataract development.To validate the expression changes of these candidate proteins in cataract patients, future studies should prioritise targeted proteomics or high-sensitivity immunoassays to precisely quantify the abundance and post-translational modification status of these proteins in cataract patient lens samples and matched controls. Further utilise human eye bank tissues or suitable animal models (such as age-related cataract models) to spatially localise the expression patterns of candidate proteins in the lens using techniques such as immunohisto-chemistry/immunofluorescence, in situ hybridisation, or single-cell RNA sequencing, and analyse their association with cataracts.Moreover, future studies that incorporate TWAS alongside pQTL analyses will be crucial in order to fully understand the flow of genetic information from transcription to translation, and ultimately to complex phenotypes.Secondly, the results derived from GO enrichment analysis, KEGG analysis, and protein-protein interaction networks are based on bioinformatics predictions. We observe that certain pathways exhibit enrichment for only one to three genes (see Figs. 5 and 6). While these results are statistically significant, we recognise that it may be challenging to infer biological mechanisms directly from enrichment based on such a small number of genes. The significant enrichment of these few genes may be related to one or more of the following factors: (1) these genes may represent key regulatory nodes within the pathway whose expression changes are sufficient to influence pathway function; (2) limitations in sample size or detection methods may have prevented the capture of some associated genes; or (3) the pathway may occupy a secondary regulatory position in the biological process under investigation, resulting in the enrichment of only a few core genes being observed. Consequently, we propose that the biological significance could be validated in future studies through expanded sample sizes and functional experiments.In lens epithelial cell lines or primary cell models, investigate the effects of altered levels of candidate proteins on key lens physiological processes (e.g., antioxidant defence, protein homeostasis, cell survival/apoptosis, gap junction communication) through gene overexpression, knockdown/knockout, or drug intervention, and whether these changes induce lens opacity-related phenotypes (e.g., protein aggregation).In genetically modified mice or other cataract animal models, specifically overexpress or knockout candidate genes in the lens to assess their long-term effects on lens transparency, histological structure, and molecular phenotypes, thereby validating their pathogenic roles in vivo.Therefore, their accuracy requires verification through both in vitro and in vivo experiments. Thirdly, the utilisation of GWAS summary data from European populations somewhat restricts the generalisability of the findings; caution must be exercised when extrapolating these findings across diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds. It is recommended that specific validation studies be conducted in different populations. Fourth, since the pathogenesis of cataracts is driven by changes in the lens and intraocular fluids, the lack of GWAS data on aqueous humour or tears currently limits further analysis. Although plasma proteomics data provide feasibility for large-scale causal inference, plasma protein levels cannot accurately reflect local changes in the ocular microenvironment. Using plasma proteins as surrogate markers for intraocular biological activity has biological limitations. Future studies could combine intraocular fluid proteomics and ocular tissue-specific genetic data to further validate the causal association between plasma proteins and cataracts.Furthermore, the utilisation of aggregated statistics in lieu of raw data constrained the capacity for more detailed group analyses, including those stratified by gender or race. It would be beneficial for future research to focus on acquiring raw data, which would allow for more in-depth examinations.
Conclusion
Our study identified 15 proteins, including ILF3, FAM171A1, ARHGEF2, LPR1B, CRYGD, GLT8D1, ARHGEF10, LRRTM1, ZHX3, ARID1A, DNASE1L2, COX7A1, EEF2K, SPAG11B and MXRA7 as having a significant causal effect on cataract remission and development.
Data availability
Data Availability Statement: The datasets generated during the current study or made available during the analysis period can be found in public repositories. Summary statistics for the cataract genome-wide association study (GWAS) are derived from FinnGen Consortium Release 10 (https://storage.googleapis.com/finngen-public-data-r10/summary_stats/finngen_R10_H7_CATARACTSENILE.gz). Plasma protein GWAS summary statistics are available from deCODE at: https://www.decode.com/publications/. The complete analysis pipeline, including scripts for data pre-processing, Mendelian randomisation and result visualisation, is available on GitHub: https://github.com/Sunchensong/hernia-ctss-MR-analysis.
References
Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study; GBD 2019 Blindness and Vision Impairment Collaborators. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by cataract: a meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye 38(11), 2156–2172. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-024-02961-1 (2024) (Erratum in: Eye (Lond). 2024 Aug;38(11):2229-2231. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03161-7).
Brown, G. C., Brown, M. M. & Busbee, B. G. Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the United States for the year 2018. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 45(7), 927–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2019.02.006 (2019).
Artal, P. et al. Peripheral vision in patients following intraocular lens implantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 264, 120–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2024.03.016 (2024).
Shaaban, Y. M. & Aziz, B. F. Tear film assessment before and after phacoemulsification in patients with age-related cataracts. BMC Ophthalmol. 24(1), 280. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-024-03542-2 (2024).
Mälarstig, A. et al. Evaluation of circulating plasma proteins in breast cancer using Mendelian randomisation. Nat. Commun. 14(1), 7680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43485-8 (2023).
Zou, X. et al. IGF-1 rs6218 polymorphisms modulate the susceptibility to age-related cataract. PeerJ 12, e17220. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.17220 (2024).
Sutkowy, P., Lesiewska, H., Woźniak, A. & Malukiewicz, G. Inflammation-Involved proteins in blood serum of cataract patients-A preliminary study. Biomedicines 11(10), 2607. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102607 (2023).
Horwitz, J. & Bok, D. Conformational properties of the main intrinsic polypeptide (MIP26) isolated from lens plasma membranes. Biochemistry 26(25), 8092–8098. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00399a012 (1987).
Gupta, V., Walia, G. K. & Sachdeva, M. P. Mendelian randomization’: an approach for exploring causal relations in epidemiology. Public. Health. 145, 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2016.12.033 (2017). (Epub 2017 Jan 21).
Verduijn, M., Siegerink, B., Jager, K. J., Zoccali, C. & Dekker, F. W. Mendelian randomization: use of genetics to enable causal inference in observational studies. Nephrol. Dial Transpl. 25(5), 1394–1398. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq098 (2010). (Epub 2010 Feb 26).
Ferkingstad, E. et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat. Genet. 53, 1712–1721. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00978-w (2021).
Burgess, S., Timpson, N. J., Ebrahim, S. & Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: where are we now and where are we going? Int. J. Epidemiol. 44(2), 379–388. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv108 (2015).
Paz, V., Dashti, H. S., Burgess, S. & Garfield, V. Selection of genetic instruments in Mendelian randomisation studies of sleep traits. Sleep. Med. 112, 342–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2023.10.036 (2023). (Epub 2023 Nov 2).
Stensrud, M. J. Mendelsk randomisering - genetisk Tilnærming Til epidemiologisk metode [Mendelian randomisation - a genetic approach to an epidemiological method]. Tidsskr Nor. Laegeforen. 136(11), 1002–1005 (2016).
Burgess, S., Butterworth, A. & Thompson, S. G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 37(7), 658–665. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21758 (2013).
Bowden, J., Davey Smith, G. & Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 44(2), 512–525. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv080 (2015).
Hartwig, F. P., Davey Smith, G. & Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 46(6), 1985–1998. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx102 (2017).
Han, X., Wang, J., Su, X., Guo, X. & Ye, H. Exploring the causal influence of 731 immune cells on 4 different glaucoma subtypes using a two-sample Mendelian randomization method. Sci. Rep. 15(1), 5987. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-90545-8 (2025).
Feng, Z., Dang, C., Xu, Z. & Zhang, Y. Genetic causality of hypothyroidism and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A combined Mendelian randomisation study and bioinformatics analysis. Int. J. Womens Health. 16, 2195–2202. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJWH.S474865 (2024).
Kanehisa, M. & Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27 (2000).
Kanehisa, M. Toward Understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 28(11), 1947–1951. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3715 (2019). (Epub 2019 Sep 9).
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Kawashima, M. & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51(D1), D587–D592. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac963 (2023).
Goswami, V., Das, S. M. & Deep, S. Quercetin-loaded nanocarriers as effective inhibitors for copper metal Ion-Induced γD-crystallin aggregation. Langmuir 40(31), 16093–16102. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c00933 (2024). (Epub 2024 Jul 24).
Panda, S. P., Pachauri, N., Kesharwani, A., Prasanth, D. & Singh, V. Participation of lens proteins and MiRs in traumatic and inheritance cataract: A review on diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for cataract management. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.2174/0113892010303094240613105517 (2024).
Xie, W. et al. Toll-like receptor 3 gene regulates cataract-related mechanisms via the Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway. Bioengineered 13(6), 14357–14367. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2085391 (2022).
Liu, S. et al. Protection of human lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress damage and cell apoptosis by KGF-2 through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 6933812. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6933812 (2022).
Lovicu, F. J., Kao, W. W. & Overbeek, P. A. Ectopic gland induction by lens-specific expression of keratinocyte growth factor (FGF-7) in transgenic mice. Mech. Dev. 88(1), 43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00169-0 (1999).
Fujimoto, M. et al. HSF4 is required for normal cell growth and differentiation during mouse lens development. EMBO J. 23(21), 4297–4306. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600435 (2004).
Lovicu, F. J. & Overbeek, P. A. Overlapping effects of different members of the FGF family on lens fiber differentiation in transgenic mice. Development 125(17), 3365–3377. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.125.17.3365 (1998).
Tian, X. & Wei, J. Sestrin 2 protects human lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide by regulating the mTOR/Nrf2 pathway. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 38, 3946320241234741. https://doi.org/10.1177/03946320241234741 (2024).
Jia, C., Zhang, F., Zhu, Y., Qi, X. & Wang, Y. Public data mining plus domestic experimental study defined involvement of the old-yet-uncharacterized gene matrix-remodeling associated 7 (MXRA7) in physiopathology of the eye. Gene 632, 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.018 (2017).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the colleagues who contributed to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuan Han wrote the main manuscript text.Xiaojuan Su, Jinyan Wang and Xingyu Guo prepared figures, Table and Supplementary. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Wang, J., Su, X. et al. Mendelian randomization and bioinformatics analysis identify the association between plasma proteins and cataract. Sci Rep 16, 3172 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-33095-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-33095-3