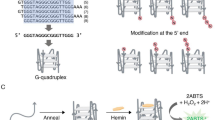
Abstract
G-quadruplex (G4) DNAzymes are guanine-rich oligonucleotides with intrinsic peroxidase-mimicking activity upon complexation with hemin, offering a promising alternative to protein-based enzymes in biosensing. However, their relatively low catalytic efficiency limits practical applications. Here, we present a structure-guided redesign of the high-activity aptamer [B7]-3-0 by incorporating strategic flanking and looping nucleobase modifications. Introduction of adenine and thymine–cytosine elements at the 3′ end led to up to 4-fold enhancements in reaction extent and a 3-fold increase in initial velocity under moderate hydrogen peroxide conditions (0.425 mM). Remarkably, the modified B730 variants retained activity at elevated H₂O₂ concentrations (4.25 mM), achieving up to 8-fold catalytic enhancement and outperforming high-activity DNAzymes including AS1411 and CatG4. These redesigned DNAzymes demonstrated improved peroxidase activity and resistance to oxidative inactivation, addressing a major limitation of both natural and artificial peroxidases. Our findings establish flanking and loop engineering as a cost-effective and broadly applicable strategy for optimizing G4 DNAzymes and underscore their potential in the development of next-generation biosensors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Aptamers are single-stranded oligonucleotides selected through in vitro screening for their ability to bind specific molecules, ions, or proteins with high affinity. They often exhibit greater specificity than typical antibody-antigen interactions. Aptamers can adopt various secondary structures such as loops, bulges, stems, pseudoknots, and G-quadruplexes1. G-quadruplexes (G4s) are formed by the stacking of G-quartets, planar assemblies of guanine bases connected via Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding. These structures arise from guanine-rich sequences in the presence of potassium ions, which coordinate with the oxygen atoms of guanine bases. When complexed with hemin (a cofactor in many oxidase systems), G4 structures function as DNAzymes with peroxidase-mimicking activity, using the same mechanism as the protein peroxidases (Fig. 1). These G4 DNAzymes are thermally and chemically stable, compact, inexpensive to produce, and easy to modify. Their molecular recognition abilities, programmability, and adaptability make them highly attractive for applications in biosensing and biotechnology2. Hemin’s planar aromatic structure allows π-π stacking interactions with the aromatic rings of bases in the external 3′-terminal G4. The accessibility of terminal G-quartets significantly influences hemin binding and, consequently, the catalytic efficiency of the G4 DNAzyme.
Peroxidase catalytic cycle. G4-DNAzyme complex reacts with and activates H2O2 to form the reactive Compound I (CI). CI oxidises a donor substrate (in this instance ABTS) using a mechanism similar to haem peroxidase-catalysed reactions and generating Compound II (CII) in the process. CII can react with H2O2 and initiate another round of ABTS oxidation. The reaction product (ABTS•) has a bright green colour with absorption maximum at 415 nm.
By modifying oligonucleotide sequences and incorporating specific recognition elements, G4 DNAzyme-based biosensors can be engineered to detect a wide range of analytes with high precision. The ability of G-quadruplex structures to form functional nucleic acids through aptamer recognition sites has significantly heightened interest in their application for biomolecular sensing3. These DNA-based catalysts offer exceptional versatility in diagnostic platforms, effectively detecting nucleic acids, proteins, and other biologically relevant molecules associated with pathogenic organisms. Their adaptability spans multiple detection modalities including chemiluminescent, colorimetric, and electrochemical techniques. Furthermore, their performance can be enhanced by integration with advanced technologies such as isothermal PCR, DNA walkers, and the CRISPR-Cas system, which boosts both specificity and sensitivity4.
Despite these advantages, G4 DNAzymes typically exhibit lower catalytic activity compared to natural peroxidases. Traditional nucleic acid detection methods often rely heavily on target amplification (e.g., PCR) or labelling, which increases complexity, cost, and the risk of contamination. To address these limitations, researchers have explored strategies to enhance DNAzyme catalytic efficiency. One such approach involves the addition of exogenous reagents, such as ATP and spermine, that modestly improve reaction rates5,6,7. However, these additives must be used at high concentrations, contributing to elevated costs while still falling short of the catalytic performance seen in natural enzymes. Despite ongoing progress, a degree of ambiguity remains regarding how specific modifications influence the catalytic activity of G4 DNAzymes, as their response to activation varies by sequence type. Previous studies have proposed that multimerisation can enhance catalytic efficiency by providing multiple active sites for hemin binding2,8,9,10. However, not all multimeric G4 DNAzymes yield synergistic or cooperative rate enhancement. In some cases, steric hindrance from bulky groups impedes effective π–π stacking, limiting hemin binding to the G-quartet and ultimately reducing catalytic efficiency, even in parallel structures.
Several approaches have been adopted to address these challenges. For instance, Kosman et al.11 showed enhanced activity through covalent G4-hemin linkage. Cheng et al.9. demonstrated that covalent dimerization of G4/hemin constructs significantly boosted biocatalytic performance by providing a preconfigured active site for H₂O₂-driven activation. Similarly, Li et al.12. introduced a “zippered” G4/hemin DNAzyme formed by hybridising short oligonucleotides near complementary G4 sequences, facilitating hemin interaction and improving peroxidase-mimicking activity. Beyond traditional 5′−3′ phosphodiester linkages, inversion of polarity sites (3′−3′ or 5′−5′ linkages) also offer structural advantages13. reported enhanced peroxidase activity in G4 DNAzymes featuring dual 3′-terminal G-tetrads in inverted configurations.
Conventionally, catalytically active G4 DNAzymes are isolated via SELEX, primarily based on hemin-binding affinity. However, post-SELEX modifications have emerged as a promising route to elevate activity, independent of binding affinity. Alterations in the catalytic core, such as base substitutions or extensions, can significantly impact performance. Notably, interactions between hemin and the bases in G4 loops and flanks have been shown to modulate redox activity. Incorporating specific nitrogenous bases within flanks, bulges, or linkers has become a targeted strategy for catalytic enhancement. Chang et al.14. found that flanking the G4 sequence with d(CCC) increased DNAzyme activity and broadened its pH tolerance. Similarly, Guo et al.15. demonstrated improved catalytic efficiency when adenine bases were flanked at both ends of the G-tract. While these loop and linker regions do not directly participate in G-quartet formation, structural studies (e.g., CD and NMR) reveal that such modifications do not disrupt parallel G4 conformations but still modulate activity. The precise molecular mechanisms behind this enhancement remain unclear, as changes in conformation, thermal stability, or hemin-binding affinity have not fully explained the observed improvements. Nonetheless, the overall catalytic activity of modified G4 DNAzymes, such as those flanked by adenine, still lags natural peroxidases.
Zhu et al.16 identified a highly active 20-nucleotide truncated aptamer, [B7]−3-0, here abbreviated as B730, selected via hemin-SELEX from an 81-nt ssDNA library with varying guanine content. B730 exists in a parallel configuration and it outperformed earlier designs like PS2.M and EAD2, representing a significant improvement in the catalytic performance of G-quadruplex DNAzymes. B730 remains one of the most active G4 DNAzymes without additional covalent modification and is often used to benchmark the peroxidase activities of novel aptamers17.
In this work, our aim is to better understand how the type and positional arrangement of nucleobases in flanks, linkers, and loops influence the catalytic activity of DNAzymes. We used B730 as a model system to show how a systematic approach can guide the rational design of next-generation high-activity G4 DNAzymes, using steps that do not require lengthy iterative process of directed evolution. We designed a variant of B730 with high activity and significant resistance to inactivation to high H₂O₂ concentration, demonstrating that the strategy provides a simple, cost-effective framework for designing highly active and inactivation-resistant G4 DNAzymes with improved functional resilience.
Materials and methods
Reagents
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-purified DNA oligonucleotides were obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies (Leuven, Belgium). Stock solutions (100 µM) were prepared by resuspending the oligonucleotides in Tris-EDTA buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5; 0.1 mM EDTA) in volumes specified in the synthesis report and stored at − 20 °C in Nunc tubes until use. Oligonucleotide concentrations were confirmed via absorbance at 260 nm (A260) measurements, with sequence-specific molecular weights applied for calculations.
The following reagents were used: 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline)−6-sulfonic acid (ABTS), hemin, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), tris(hydroxymethyl) amino- methane (Tris), 2-[N-morpholino] ethanesulfonic acid (MES), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), and Triton X-100 (all from Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK). Potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl) were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Leicestershire, UK).
Preparation of DNAzyme (Oligonucleotide-Hemin complex)
DNAzymes were prepared by complexing oligonucleotides with hemin to yield a 10 µM catalytically active unit, as previously described7µL of 100 µM oligonucleotide solution was added to 450 µL of reaction buffer RB1 (25 mM MES, pH 5.5; 20 mM KCl; 200 mM NaCl; 0.05% Triton X-100; 1% DMSO), heated to 95 °C for 10 min, rapidly cooled on ice for 15 min (0 °C), and equilibrated at 25 °C for another 15 min to facilitate G-quadruplex formation. To assemble the catalytic complex, 10 µL of 100 µM of hemin solution was added, mixed thoroughly, and incubated at 25 °C for 30 min.
Determination of peroxidase activity of dnazymes
Peroxidase activity of the DNAzyme (0.25 µM) was assessed in RB1 containing 2.5 mM ABTS and 0.425 mM H₂O₂. The reaction was initiated by addition of H₂O₂, and absorbance was monitored immediately at 415 nm every 5 s for 3 min using a CLARIOstar Plate Reader (BMG LABTECH). Initial velocities (Vo) were determined from the linear portion of the absorbance-time curve and calculated by dividing the rate of absorbance change by the extinction coefficient of ABTS, as previously established2,7.
Inactivation kinetics
The effect of increasing H₂O₂ concentrations on DNAzyme inactivation was evaluated for both wild-type and modified constructs. Reactions contained 0.25 µM DNAzyme, 2.5 mM ABTS, and H₂O₂ concentrations ranging from 0.106 to 4.250 mM (0.106, 0.213, 0.319, 0.425, 1.063, 2.125, 3.188, 4.250 mM). Absorbance changes were recorded as previously described2,18.
Circular dichroism spectra
Circular dichroism (CD) spectra (320–220 nm) were recorded for 10 µM G4 oligonucleotides in 25 mM MES buffer (pH 5.5) containing K⁺ ions with Jasco J-1100 CD spectrometer (Japan), to evaluate G-quadruplex conformation14,19,20,21,22,23,24A 4 mm path cell, 1 nm bandwidth, 0.1 data pitch and a scanning speed of 200 nm/min was used to collect average of three scans at 22 °C with MES buffer as baseline control.
Relative amount of compound I formed
Formation of Compound I, a transient peroxidase intermediate, was analysed by monitoring absorbance at 404 nm over time following the addition of 1 mM H₂O₂ to 1 µM DNAzyme. The degradation rate, reflective of Compound I formation, was calculated from the initial slope of the absorbance-time curve for both wild-type and modified DNAzyme variants14,21,23.
Results
Preliminary modifications to the B730 aptamer sequence
We performed a structure-guided redesign of the truncated high-activity G4 DNAzyme B730 by introducing flanking and looping nucleobases (Table 1). Adenine residues were inserted at various loop positions within the G-tracts, and their number at the 3′ end was varied. All reactions were conducted in MES buffer (pH 5.5), chosen for its ability to stabilize the reducing substrate ABTS and its alignment with the pKa of nucleobases, thereby favouring ionization of reactive groups. Since the pKa of hemin is approximately 4.3625, this shared chemical environment may enhance peroxidase activity by accelerating Compound I formation20.
Since some studies specifically on the effect of 3’ terminal adenine and cytosine nucleobases on the activities of G4 DNAzymes have been carried out in MES buffer ranging from pH 5.1 to 5.515,19,26 rather than at pH 7.0 reported for most studies, we carried out an initial comparison of activities at pH 5.5 and pH 7.0. We tested the activities of B730 and B730-1 in reaction buffers with MES pH 5.5 and HEPES pH 7. Although, there was no difference in the reaction extent from the two DNAzymes at pH 7.0, the DNAzyme with the 3’ modification was more active in MES pH5.5; maintaining a linear increase up till 180 s while the reaction of the unmodified base peaked after 50 s (data not shown).
The catalytic activities of each variant were assessed by monitoring ABTS oxidation kinetics in the presence of H₂O₂ (Fig. 2). Initial velocities for B730, B730-1, B730-2, B730-3, B730-4, and B730-5 were 51, 116, 100, 110, 110, and 110 nM/s, respectively. Corresponding reaction extents after 3 min were 3.49, 10.4, 8.69, 9.53, 9.38, and 9.23 µM. These results indicate that adenine looping within the G-tracts and flanking adenines at the 3′ end consistently enhanced both initial reaction rates (∼2-fold) and total product accumulation (∼3-fold) relative to unmodified B730.
Catalytic activities of B730 and its redesigned variants. (A) Time-course profiles of ABTS oxidation monitored at 415 nm, showing real-time progression of peroxidase activity. (B) Initial velocities (V₀) of DNAzyme-catalyzed reactions, expressed in nM/s. Reaction conditions: 0.25 µM DNAzyme, 2.5 mM ABTS, 0.425 mM H2O2, 25 MES buffer pH 5.5, 20 mM KCl, 200 mM NaCl, 0.05% Triton X-100.
Rate enhancement by flanking adenine and thymine-cytosine (TC)
Previous studies have shown that 3′-end flanking regions in G4 DNAzymes not only contribute to hemin binding but also facilitate substrate positioning via axial coordination, enhancing the rate of Compound I formation, the rate-limiting step in the peroxidase cycle14,19,20,21,22,23,24. To fine-tune the spatial arrangement between the G4 catalytic core and hemin’s hexacoordinated iron centre, we replaced the 3′ terminal adenine in B730-1 (the most active of the 5 variants) with a Thymine-Cytosine (TC) dinucleotide to create B730-1.2 (Table 1). This modification was inspired by earlier findings that TC addition at the 3′ end of the G3T sequence enhances peroxidase activity22,24. As anticipated, the combination of looped adenines and a TC tail in B730-1.2 resulted in a 3-fold increase in initial velocity and a 4-fold increase in reaction extent compared to the parent B730 sequence (Fig. 3).
Comparative analysis of activities of B730 flanked with Adenine (A) nucleotide (B730-1) and Thymine-Cytosine (TC) dinucleotide (B730-1.2) with other high-activity DNAzyme (A) Time course reaction (B) Initial velocity (Vo expressed as nM/s). Reaction conditions and analysis are as described in Fig. 2.
Comparison of activity of B730-1.2 with other high activity dnazymes
To assess the performance of B730-1.2, we compared its catalytic efficiency with two well-characterized high-activity DNAzymes: AS1411 and CatG42,5,27nucleolin-binding aptamer with anticancer properties and has been extensively evaluated for peroxidase activity. Remarkably, B730-1.2 outperformed both AS1411 and CatG4, exhibiting higher initial velocity and product yield. The initial velocities (V0) of B730-1.2, AS1411 and CatG4 at 0.25 µM DNAzyme, 2.5 mM ABTS and 0.425 mM H2O2 are 154, 53 and 100 nM/s respectively; while the extent of ABTS oxidation after 3 min are 13.6, 4.76 and 10.5 µM respectively in MES buffer pH 5.5 (Fig. 3).
We investigated the activities of the three DNAzymes at different DNAzyme concentrations [E] to determine the relative turnover rates. The specific activities (V0/[E]) determined for B730-1.2, AS1411 and CatG4 were 574.2, 197.2 and 395.4 mM/s, respectively (Fig. 4), showing that B730-1.2 is a significant improvement on non-modified DNA aptamers currently in use as G4 DNAzymes.
Effects of varying DNAzyme concentrations on oxidation of 2.5 mM ABTS at 0.425 H2O2 concentration. (A-C) Time courses of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS144 and CatG4 (D) Initial velocity of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS1411 and CatG4 at varying DNAzyme concentrations (0.0125–0.25.0125.25 µM). Inset: Specific activity (V0/[E]) of B730-1.2, AS1411 and CatG4.
B730-1.2 displays stable activity in the presence of high H2O2 concentration
Both natural peroxidases and G4 DNAzymes are prone to oxidative inactivation at high H₂O₂ concentrations due to accumulation of Compound III (peroxyiron(III) porphyrin radical), which irreversibly degrades the hemin cofactor28,29,30stability under this inactivating condition, we evaluated the activities of B730-1.2, CatG4, and AS1411 under increasing H₂O₂ concentrations at low (0.01 µM) and optimal (0.25 µM) DNAzyme concentrations (Figs. 5 and 6).
Effects of varying H2O2 concentrations on oxidation of 2.5 mM ABTS at moderate DNAzyme concentration (0.25 µM). (A-C) Time courses of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS144 and CatG4 at 0.106–4.250 mM H2O2 concentrations. (D) Initial velocity of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS144 and CatG4. H2O2 concentrations (0.106–4.250 mM).
B730-1.2 exhibited substantial tolerance to high H₂O₂ concentration, maintaining activity even at 4.25 mM H₂O₂. Under these conditions, its initial velocity increased by 5- to 8-fold relative to the wild-type B730, and significantly more active than CatG4 and AS1411. To further test the resilience of the DNAzymes to inactivation induced by exposure to very high H₂O₂ concentrations, we tested their activities using very low DNAzyme concentration (0.05 µM). Under these conditions, the very high H₂O₂/DNAzyme ratio would normally trigger irreversible inactivation and decrease in peroxidase activity for G4 DNAzymes and natural peroxidases2,29 As shown in Fig. 7, B730-1.2, CatG4 and AS1411 displayed initial velocities of 2310, 370 and 1200 nM/s at 50 mM H₂O₂, indicating that the modified B730 variant was more resilient to inactivating conditions than the two controls we used. The higher activities suggest that in the absence of inactivating events, the rate of reaction catalysed by G4 DNAzymes can be enhanced by using higher H₂O₂ concentrations.
Effects of varying H2O2 concentrations on oxidation of 2.5 mM ABTS at very low DNAzyme concentration (0.05 µM). (A-C) Time courses of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS144 and CatG4 respectively at of 0.425–50 mM H2O2 concentrations. (D) Initial velocity of ABTS oxidation by B730-1.2, AS144 and CatG4. H2O2 concentrations (0.425–50 mM).
Circular dichroism spectra reveal preserved G4 folding
To confirm whether the sequence modifications we made to B730 altered their G4 structures, we determined circular dichroism spectra of the G4 sequences, the standard approach used in similar studies that investigated the mechanism of terminal nucleobase addition on rate enhancement11,15,19,21. We collected circular dichroism spectra (220–320 nm) for wild-type and variant sequences (Fig. 8). Both B730-1 and B730-1.2 exhibited characteristic peaks of parallel G4 topology: positive peak at ∼265 nm and negative peak at ∼240 nm16,20,23 strategy with native folding.
Enhanced compound I formation in B730 and its variant
To explore the mechanistic basis for the observed catalytic enhancement, we monitored the formation of Compound I, the oxoiron(IV) porphyrin radical cation intermediate that mediates the initial oxidation step of the peroxidation reaction, by tracking absorbance at 404 nm following H₂O₂ addition14,21,23DNAzymes, formation of Compound I is the key rate-limiting transition from ferric hemin to the reactive catalytic state. Variants of B730 demonstrated more rapid Compound I formation than the wild type, confirming that peripheral base modifications accelerate activation of the DNAzyme–hemin complex (Fig. 9).
Discussion
In this study, we show that modifying flanking and loop-region nucleobases enhances the intrinsic peroxidase activity of G4 DNAzymes. Our best construct, B730-1.2, showed 3-fold enhancement of activity compared to the unmodified B730 aptamer, which is one of the best non-modified G4 DNAzymes reported so far16. Bhuyan et al.17 used directed evolution to design a novel G4 DNAzyme, msBDZ-X-3, that was at best twice as active as B730 in all assay conditions. Although, we have not made a direct comparison between B730-1.2 and msBDZ-X-3 in this work, the comparisons with B730 here and in that study suggest that B730-1.2 could be the most active non-modified G4-quadruplex DNAzymes reported to date. Although higher activities have been reported when G4 DNAzymes are covalent modified by chemical linkage with hemin or other cofactors17,31, the additional cost and complexities associated with making these covalent modifications limit their incorporation into routine diagnostic or biosensing applications.
The data presented in this study are not sufficient to provide direct explanations for the mechanistic basis for the enhanced activities and stability of B730-1.2, but the modifications made are similar in design to those reported earlier in the literature suggesting that the changes likely creates a localized, buffered microenvironment that sustains catalysis even at elevated H₂O₂ concentrations. Studies in which the rate enhancement effects of the adenine and TC nucleobases were investigated showed that the terminal 3’ base modifications did not affect the binding of hemin to the DNA sequences of both the parent sequence and the modified one15,19,21. G-quadruplex (G4) DNAzymes derive their catalytic power from a finely tuned interplay of structural elements: a hydrophobic hemin binding pocket, monovalent cation (e.g., K⁺) coordination sites that stabilize the G4 fold, substrate recognition regions, and residues that stabilize reaction intermediates and facilitate proton transfer20. Enhanced folding stability and optimized stacking interactions between guanine quartets and hemin have been linked to improved catalytic activity16.
One likely explanation for the observed increased activity of the modified sequences at pH 5.5 may be due to increased tendency to deprotonate adenine and cytosine and make them facilitate redox reaction by acting as general acid-base species in G4 DNAzyme reactions in a way similar to the role of distal histidine in natural peroxidase reactions. The pKa of adenine and cytosine are 4.2 and 4.6, respectively, which is closer to pH 5.5 than pH 7 that seems to work better for G4 sequences with no terminal adenine or guanine bases. Similar effects were observed in earlier studies in which flanking nucleobases were studied. Guo et al.15 (SI Fig. 10) reported high activity for DNAzyme flanked with nucleobases at pH 5.5 than pH 7. Li et al.19 also reported high activity at pH 5.1 in various nitrogenous and oxyanion buffers for modified G4 DNAzyme.
Parallels between these synthetic systems and natural peroxidases such as horseradish peroxidase provide mechanistic insights. Key catalytic residues including His170 (proximal ligand), His42, and Arg38 (distal ligands) orchestrate the conversion of ferric-hydroperoxide to the highly reactive Fe(IV) = O (Compound I) species32. In G4 DNAzymes, loop and flanking regions can functionally mimic these residues, influencing substrate access, folding topology, and catalytic turnover. Several studies have established that the mechanism through which the adenine residues at the 3’ end enhance activity is to mimic the histidine residue at the active centre of natural peroxidases15,19,21,26. In this role, a cascade of redox reactions leads to the increase in the formation of Compound I, the rate-limiting catalytic entity in peroxidase reactions. Our result of the initial degradation velocity of DNAzymes when exposed to H2O2 provided mechanistic insight that the enhanced catalytic activity of the modified DNAzyme was due to rate of compound I formation.
Our circular dichroism spectral data suggest parallel G4 conformation for B730 based on positive peak at 264 nm and negative peak at 240 nm; this agrees with initial report by Zhu et al.16. Similar G4 conformations suggests that flanking and loop modifications enhances peroxidase activity by a different mechanism other than structural alteration. The 2’ methyl modification in B730 has been reported to stabilise their parallel conformation, thermal stability and by extension their peroxidase activity16. Potassium ions are well known to stabilize this parallel topology, and their presence likely maintained conformational integrity across variants, even following hemin complexation33. Minor increases in thermal stability as shown through melting temperatures of 68.7, 69.5, and 70.1 °C for B730, B730-1, and B730-1.2, respectively suggest that rate enhancement stems not from global stabilization, but from fine-tuned molecular interactions at the catalytic interface. Our findings based on CD spectral analyses agree with earlier studies that the 3’ nucleobase additions did not change the overall G4 topology of the modified sequences15,19,21,26.
Adenine residues, especially in 3′ flanking positions, may accelerate Compound I formation by mimicking the distal histidine’s role in general acid-base catalysis19. The unprotonated N1 of adenine can directly interact with H₂O₂, facilitating O-O bond cleavage, a key step in peroxidase catalysis. Furthermore, flanking bases may support proper alignment of hemin with the G4 scaffold, improving electron transfer, folding kinetics, and hemin accessibility19,20. Enhanced π–π stacking and electrostatic interactions from additional adenines may also contribute to hemin stabilization19.
Our B730-1.2 variant, incorporating a 3′-terminal TC dinucleotide, further optimized the catalytic interface. Molecular modelling studies carried out by Li et al.19 and Qiu et al.22 suggest that the hemin centre sits ~ 4.5–5.9 Å from the N3 and 4-NH₂ atoms of dC in TC-flanked G4s, distances suitable for forming dual hydrogen bonds with H₂O₂. Although thymine lacks amino or basic nitrogen atoms, its compact pyrimidine structure likely helps position cytosine favourably relative to the iron centre. In contrast, bulkier purine rings in adenine may impose less optimal spatial constraints. Thus, the TC flanks appear to balance proximity, orientation, and chemical functionality, enhancing substrate coordination and catalytic efficiency24.
Resistance to inactivation under high H₂O₂ concentration conditions is a major advantage of the redesigned B730-derived DNAzyme. In conventional peroxidases, Compound I (Fe(IV) = O + radical) is formed by heterolytic cleavage of H₂O₂ and normally proceeds via two one-electron reductions to regenerate the resting ferric state34. Under excess H₂O₂, however, these enzymes often form Compound III, an inactive peroxyiron(III) species that triggers haem degradation29,30. This vulnerability is exacerbated by the Fe³⁺ redox centre’s susceptibility to radical attack35. Remarkably, our flanking and looping modifications appear to mitigate this inactivation pathway. We hypothesize that adenine and Thymine-Cytosine bases help shuttle electrons and stabilise catalytic intermediates, shielding the hemin cofactor from oxidative damage.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that rationally designed flanking and loop modifications can significantly enhance the peroxidase activity and oxidative resilience of G4 DNAzymes. Strategic incorporation of adenine and TC motifs at the 3′ end of the B730 aptamer created a microenvironment conducive to faster Compound I formation, the rate-limiting step in the catalytic cycle. These structural adjustments improved catalytic turnover and enabled the DNAzyme to function under elevated H₂O₂ concentrations, where conventional DNAzymes often fail.
Our findings establish flanking and loop engineering as a simple, cost-effective, and scalable strategy for developing robust G4 DNAzymes for biosensing applications. Importantly, the modifications preserve the inherent simplicity and parallel topology of the G4 scaffold while unlocking higher activity and chemical durability. This approach lays the groundwork for next-generation DNAzyme designs in diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and synthetic biocatalysis.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Liu, R., Li, J., Salena, B. J. & Li, Y. Aptamer and DNAzyme based colorimetric biosensors for pathogen detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64 (4), e202418725. (2025).
Adeoye, R. I. et al. Catalytic activities of multimeric G-quadruplex dnazymes. Catalysts 9 (7), 613 (2019).
Sahayasheela, V. J. & Sugiyama, H. RNA G-quadruplex in functional regulation of noncoding RNA: challenges and emerging opportunities. Cell. Chem. Biology. 31 (1), 53–70 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. A self-assembled G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme-driven DNA walker strategy for sensitive and rapid detection of lead ions based on rolling circle amplification. Biosensors 13 (8), 761 (2023).
Kong, D. M., Xu, J. & Shen, H. X. Positive effects of ATP on G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzyme-mediated reactions. Anal. Chem. 82 (14), 6148–6153 (2010).
Qi, C. et al. Activity enhancement of G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme by spermine. RSC Adv. 4 (3), 1441–1448 (2014).
Adeoye, R. I. et al. Spermine enhances the peroxidase activities of multimeric antiparallel G-quadruplex dnazymes. Biosensors 15 (1), 12 (2025).
Stefan, L., Denat, F. & Monchaud, D. Deciphering the DNAzyme activity of multimeric quadruplexes: insights into their actual role in the telomerase activity evaluation assay. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (50), 20405–20415 (2011).
Cheng, Y. et al. The noncovalent dimerization of a G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme improves its biocatalytic properties. Chem. Sci. 11 (33), 8846–8853 (2020).
Zhang, Y. et al. Design of a high-sensitivity dimeric G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme biosensor for Norovirus detection. Molecules 26 (23), 7352 (2021).
Kosman, J., Żukowski, K. & Juskowiak, B. Comparison of characteristics and DNAzyme activity of G4–Hemin conjugates obtained via two Hemin attachment methods. Molecules 23 (6), 1400 (2018).
Li, J. et al. Zippered G-quadruplex/hemin dnazyme: exceptional catalyst for universal bioanalytical applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (22), 13031–13044 (2021).
Virgilio, A., Esposito, V., Lejault, P., Monchaud, D. & Galeone, A. Improved performances of catalytic G-quadruplexes (G4-DNAzymes) via the chemical modifications of the DNA backbone to provide G-quadruplexes with double 3′-external G-quartets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 976–983 (2020).
Chang, T. et al. Activity enhancement of G-Quadruplex/Hemin DNAzyme by flanking d (CCC). Chemistry–A Eur. J. 22 (12), 4015–4021 (2016).
Guo, Y. et al. A thermophilic tetramolecular G-Quadruplex/Hemin DNAzyme. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (52), 16636–16640 (2017).
Zhu, L. et al. In vitro selection of highly efficient G-quadruplex-based dnazymes. Anal. Chem. 84 (19), 8383–8390 (2012).
Bhuyan, S. K. et al. Directed evolution of a G-quadruplex peroxidase DNAzyme and application in proteomic DNAzyme–aptamer proximity labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145 (23), 12726–12736 (2023).
Yang, X. et al. Characterization of G-quadruplex/hemin peroxidase: substrate specificity and inactivation kinetics. Chemistry–A Eur. J. 17 (51), 14475–14484 (2011).
Li, W. et al. Insight into G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzyme/RNAzyme: adjacent adenine as the intramolecular species for remarkable enhancement of enzymatic activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 44 (15), 7373–7384 (2016).
Chen, J., Guo, Y., Zhou, J. & Ju, H. The effect of adenine repeats on G-quadruplex/hemin peroxidase mimicking DNAzyme activity. Chemistry–A Eur. J. 23 (17), 4210–4215 (2017).
Chen, J. et al. How proximal nucleobases regulate the catalytic activity of G-quadruplex/hemin dnazymes. ACS Catal. 8 (12), 11352–11361 (2018).
Qiu, D. et al. Effect of distance from catalytic synergy group to iron porphyrin center on activity of G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme. Molecules 25 (15), 3425 (2020).
Cao, Y. et al. Investigation and improvement of catalytic activity of G-quadruplex/hemin dnazymes using designed terminal G-tetrads with deoxyadenosine caps. Chem. Sci. 11 (26), 6896–6906 (2020).
Connelly, R. P., Fonseca, V. & Gerasimova, Y. V. Peroxidase-like activity of G-Quadruplex/Hemin complexes for colorimetric nucleic acid analysis: loop and flanking sequences affect signal intensity. DNA 5 (1), 12 (2025).
Kong, D. M., Wu, J., Wang, N., Yang, W. & Shen, H. X. Peroxidase activity–structure relationship of the intermolecular four-stranded G-quadruplex–hemin complexes and their application in Hg2 + ion detection. Talanta 80 (2), 459–465 (2009).
Udomprasert, A., Chimasungkanun, S. & Kangsamaksin, T. Kinetic analysis of catalytic activity of G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme with flanking adenine nucleotides. Scientific Reports, 15(1), p.40260. (2025).
Bagheri, Z. et al. Spectral properties and thermal stability of AS1411 G-quadruplex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 72, 806–811 (2015).
Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Cytochrome c as a biocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzymatic. 7 (1–4), 241–249 (1999).
Valderrama, B., Ayala, M. & Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Suicide inactivation of peroxidases and the challenge of engineering more robust enzymes. Chem. Biol. 9 (5), 555–565 (2002).
Monte Carlo, A. R. III & Fu, J. Inactivation kinetics of G-Quadruplex/Hemin complex and optimization for more reliable catalysis. ChemPlusChem. 87 (7), e202200090. (2022).
Li, J. et al. Self-contained G-quadruplex/hemin dnazyme: a superior ready-made catalyst for in situ imaging analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 53 (6), gkaf227 (2025).
Liu, B. et al. Arginine-Modified Hemin enhances G-Quadruplex DNAzyme peroxidase activity for high sensitivity detection. Anal. Chem. 96 (36), 14590–14597 (2024).
Cheng, Y. et al. Highly selective detection of K + based on a dimerized G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Anal. Chem. 93 (18), 6907–6912 (2021).
Regelsberger, G. et al. Effect of distal cavity mutations on the formation of compound I in catalase-peroxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30), 22854–22861 (2000).
Rodríguez-López, J. N. et al. Mechanism of reaction of hydrogen peroxide with horseradish peroxidase: identification of intermediates in the catalytic cycle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123 (48), 11838–11847 (2001).
Funding
This work was supported by the UKRI/BBSRC grant BB/X012085/1 to F.J.O., and Liverpool John Moores University institutional support to R.I.A. Funding for open access charge: UKRI/BBSRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation: Raphael I. Adeoye and Femi J. Olorunniji; Methodology: Raphael I. Adeoye, Francesca Giuntini and Femi J. Olorunniji; Investigation: Raphael I. Adeoye, Nikhil Babbudas and Matthew Birchenough; Writing—Original Draft: Raphael I. Adeoye, Nikhil Babbudas, Matty Birchenough, and Femi J. Olorunniji; Writing—Review and Editing: Raphael I. Adeoye, Francesca Giuntini and Femi J. Olorunniji; Formal Analysis, Visualisation and Data Curation: Raphael I. Adeoye and Femi J. Olorunniji; Supervision and Project Administration, Femi J. Olorunniji; Funding Acquisition: Raphael I. Adeoye and Femi J. Olorunniji. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Adeoye, R.I., Babbudas, N., Birchenough, M. et al. Rational redesign of high-activity G-quadruplex DNAzyme through flanking and looping of nucleobases. Sci Rep 16, 5060 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35686-0