Abstract
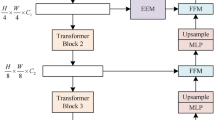
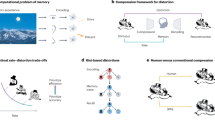
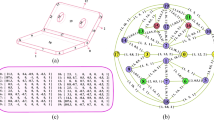
Few-shot semantic segmentation has gained significant attention in metal surface defect detection due to its ability to segment unseen object classes with only a few annotated defect samples. Previous methods constrained to single-episode training suffer from limited adaptability in semantic description of defect regions and coarse segmentation granularity. In this paper, we propose an episode-adaptive memory network (EAMNet) that specifically addresses subtle variances between episodes during training. The episode adaptive memory unit (EAMU) leverages an adaptive factor to model semantic dependencies across different episodes. The context adaptation module (CAM) aggregates hierarchical features of support-query pairs for fine-grained segmentation. The proposed global response mask average pooling (GRMAP) introduces a global response normalization to obtain fine-grained cues directly from the support prototype. We also introduce an attention distillation (AD), which leverages fine-grained semantic attention correspondence to process defect region cues and stabilize the cross-episode adaptation in EAMU. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach establishes new state-of-the-art performance on both Surface Defect-\(4^i\) and FSSD-12 datasets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and codes underlying the results of this study are available at the following URL: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.18174740.
References
Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Guo, X., Ling, X. & Geng, Q. Metal surface defect detection using slf-yolo enhanced yolov8 model. Sci. Rep. 15, 11105 (2025).
Chan, S. et al. Feature optimization-guided high-precision and real-time metal surface defect detection network. Sci. Rep. 14, 31941 (2024).
Zhou, C. et al. Metal surface defect detection based on improved yolov5. Sci. Rep. 13, 20803 (2023).
Lv, X., Duan, F., Jiang, J.-J., Fu, X. & Gan, L. Deep metallic surface defect detection: The new benchmark and detection network. Sensors 20, 1562 (2020).
Wang, W., Han, C., Zhou, T. & Liu, D. Visual recognition with deep nearest centroids. In the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 1–30 (2023).
Han, C. et al.\({\rm E}\hat{\,}{\rm 2vpt}\): An effective and efficient approach for visual prompt tuning. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 17491–17502 (2023).
Lu, Y. et al. Transflow: Transformer as flow learner. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18063–18073 (2023).
Liu, Q., Liu, M., Jonathan, Q. & Shen, W. A real-time anchor-free defect detector with global and local feature enhancement for surface defect detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 246, 123199 (2024).
Tabernik, D., Šela, S., Skvarč, J. & Skočaj, D. Segmentation-based deep-learning approach for surface-defect detection. J. Intell. Manuf. 31, 759–776 (2020).
Guo, B., Wang, Y., Zhen, S., Yu, R. & Su, Z. Speed: Semantic prior and extremely efficient dilated convolution network for real-time metal surface defects detection. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 19, 11380–11390 (2023).
Ma, J., Xie, G.-S., Zhao, F. & Li, Z. Afanet: Adaptive frequency-aware network for weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 1–11 (2025).
Wang, C. et al. Taylor series-inspired local structure fitting network for few-shot point cloud semantic segmentation. In: Proc. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 7527–7535 (2025).
Mai, H., Sun, R., Zhang, T. & Wu, F. Rankmatch: Exploring the better consistency regularization for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3391–3401 (2024).
Woo, S. et al. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 16133–16142 (2023).
Chao, C. et al. Iamf-yolo: Metal surface defect detection based on improved yolov8. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 74, 1–17 (2025).
Zhang, X., Fang, T., Saniie, J., Bakhtiari, S. & Heifetz, A. Unsupervised learning-enabled pulsed infrared thermographic microscopy of subsurface defects in stainless steel. Sci. Rep. 14, 14865 (2024).
Panić, B., Borovinšek, M., Vesenjak, M., Oman, S. & Nagode, M. A guide to unsupervised image segmentation of mct-scanned cellular metals with mixture modelling and markov random fields. Mater. Design 239, 112750 (2024).
Song, Z., Yao, H., Tian, D., Zhan, G. & Gu, Y. Segmentation method of u-net sheet metal engineering drawing based on cbam attention mechanism. Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 39, e14 (2025).
Zhang, H. et al. An efficient model for metal surface defect detection based on attention mechanism and multi-scale feature. J. Supercomput. 81, 40 (2025).
Zhang, L., Li, X., Sun, Y. & Guo, H. Triple-attentions based salient object detector for strip steel surface defects. Sci. Rep. 15, 2537 (2025).
Wei, H., Zhao, L., Li, R. & Zhang, M. Rfaconv-cbm-vit: enhanced vision transformer for metal surface defect detection. J. Supercomput. 81, 1–38 (2025).
Zhang, G. et al. Lggformer: A dual-branch local-guided global self-attention network for surface defect segmentation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 64, 103099 (2025).
Jin, Y., Zhang, Y., Shan, D. & Wu, Z. Human-guided zero-shot surface defect semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 74, 1–13 (2025).
Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., Duan, J. & Yu, J. Cross-supervised contrastive learning domain adaptation network for steel defect segmentation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 64, 102964 (2025).
Snell, J., Swersky, K. & Zemel, R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30, 4077–4087 (2017).
Ye, M. & Zhang, T. Sanet: similarity aggregation and semantic fusion for few-shot semantic segmentation. Appl. Intell. 55, 1–12 (2025).
Gong, W. et al. Cgnet: Few-shot learning for intracranial hemorrhage segmentation. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 102505 (2025).
Yang, A., Sang, Z., Zhou, Y., Cao, J. & Liu, L. Bi-orientated rectification few-shot segmentation network based on fine-grained prototypes. Neurocomputing 620, 129160 (2025).
Chen, S., Yu, Y., Li, Y., Lu, Z. & Zhou, Y. Mask-free iterative refinement network for weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 611, 128600 (2025).
Wang, X., Chen, Q. & Yang, Y. Word vector embedding and self-supplementing network for generalized few-shot semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 613, 128737 (2025).
Xiang, Q. et al. Dkdm: Data-free knowledge distillation for diffusion models with any architecture. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2955–2965 (2025).
Cai, S. et al. Diffusion self-distillation for zero-shot customized image generation. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18434–18443 (2025).
Li, Q., Wang, Y., Meng, L., Qin, Y. & Tang, B. Sdmc-net: A lightweight and deployable fault diagnosis network using self-distillation and multiscale-depth convolution. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 74, 1–13 (2025).
Lu, Z. et al. Self-distillation attention for efficient and accurate motion prediction in autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 26, 7262–7274 (2025).
Peng, B. et al. Hierarchical dense correlation distillation for few-shot segmentation. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 23641–23651 (2023).
Lang, C., Tu, B., Cheng, G. & Han, J. Beyond the prototype: divide-and-conquer proxies for few-shot segmentation. In: Proc. Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1024–1030 (2022).
Bao, Y. et al. Triplet-graph reasoning network for few-shot metal generic surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021).
Zhang, X., Wei, Y., Yang, Y. & Huang, T. S. Sg-one: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50, 3855–3865 (2020).
Song, K., Feng, H., Cao, T., Cui, W. & Yan, Y. Mfanet: multifeature aggregation network for cross-granularity few-shot seamless steel tubes surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 20, 9725–9735 (2024).
Yu, R., Guo, B. & Yang, K. Selective prototype network for few-shot metal surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–10 (2022).
Hochreiter, S. & Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9, 1735–1780 (1997).
Bulatov, A., Kuratov, Y. & Burtsev, M. Recurrent memory transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 11079–11091 (2022).
Lin, T.Y. et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2117–2125 (2017).
Roy, A. G., Navab, N. & Wachinger, C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 421–429 (2018).
Feng, H., Song, K., Cui, W., Zhang, Y. & Yan, Y. Cross position aggregation network for few-shot strip steel surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 72, 1–10 (2023).
Huang, J. et al. Multiscale adaptive prototype transformer network for few-shot strip steel surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 74, 1–14 (2025).
Tian, Z. et al. Prior guided feature enrichment network for few-shot segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 1050–1065 (2022).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S. & Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 770–778 (2016).
Simonyan, K. & Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556 (2014).
Xu, Q. et al. Hybrid mamba for few-shot segmentation. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 37, 73858–73883 (2024).
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Fujian Natural Science Foundation under Grants 2023J01978, 2023J01979 and 2024J01855, in part by the Fujian International Cooperation Program in Science and Technology under Grant 2024I0024, in part by the Fujian Regional Development Project under Grant 2025Y3009, and in part by the Doctoral Research Project of Longyan University under Grants LB2023008 and LB2023015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Z. and H.D. wrote the main manuscript text, J.Z. and M.P. prepared figures 1-2, H.D., M.P. and S.T. designed the experiments, G.C. and Y.L. provided critical revisions. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ding, H., Peng, M. et al. Few-shot cross-episode adaptive memory for metal surface defect semantic segmentation. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36445-x