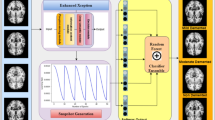
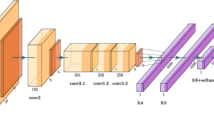
Abstract
Intelligent decision-making systems using wearable electronics and deep learning (DL) might identify Alzheimer’s disease (AD) early for treatment. These technologies can continually monitor vital signs and behavioral characteristics to identify early cognitive deterioration in patients. Clinical examinations, neuroimaging, and cognitive testing are the main ways to identify Alzheimer’s, but they are difficult, expensive, and frequently miss the illness early on. Such approaches lack the sensitivity and real-time monitoring essential for early intervention. Through wearable technology and sophisticated DL approaches, Early Detection using Deep Learning Algorithm (ED-DLA) tackles these constraints. In real time, wearable sensors capture data on heart rate, sleep habits, and physical activity. DL algorithms evaluate this data to identify early Alzheimer’s. Continuous and non-invasive monitoring improves detection sensitivity and accuracy. To evaluate sequential wearable device data, the suggested technique uses an RNN-based image classification model. Temporal patterns are essential for understanding AD development, and the RNN does so well. The slight changes in cognitive and physical activities may indicate early-stage dementia. The suggested AD diagnosis and management system improves early detection accuracy and real-time monitoring, making it more dependable and scalable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are taken from the following publicly available website.http://adni.loni.usc.edu.
References
Arunachalam, R. et al. A smart alzheimer’s patient monitoring system with IoT-assisted technology through enhanced deep learning approach. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 65 (12), 5561–5599 (2023).
Yang, P. et al. Multimodal wearable intelligence for dementia care in healthcare 4.0: A survey. Information Syst. Frontiers 27, 1–18 (2021).
Chudzik, A., Śledzianowski, A. & Przybyszewski, A. W. Machine learning and digital biomarkers can detect early stages of neurodegenerative diseases. Sensors 24 (5), 1572 (2024).
Sharma, S., Dudeja, R. K., Aujla, G. S., Bali, R. S. & Kumar, N. DeTrAs: deep learning-based healthcare framework for IoT-based assistance of Alzheimer patients. Neural Comput. Applications 37, 1–13 (2020).
Gillani, N. & Arslan, T. Intelligent sensing technologies for the diagnosis, monitoring and therapy of alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Sensors 21 (12), 4249 (2021).
Kute, S. S., Madhav, S., Kumari, A. V. & Aswathy, S. U. Machine learning–based disease diagnosis and prediction for E-healthcare system. Adv. Analyt. Deep Learn. Models https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119792437.ch6 (2022).
Bazarbekov, I. et al. A review of artificial intelligence methods for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis: insights from neuroimaging to sensor data analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 92, 106023 (2024).
Haghayegh, F. et al. Revolutionary Point-of‐care wearable diagnostics for early disease detection and biomarker discovery through intelligent technologies. Advanced Science 11, 2400595 (2024).
Husnain, A., Hussain, H. K., Shahroz, H. M., Ali, M. & Hayat, Y. A precision health initiative for chronic conditions: design and cohort study utilizing wearable Technology, machine learning, and deep learning. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Innovations. 1 (2), 118–139 (2024).
Kale, M. B. et al. AI-Driven Innovations in Alzheimer’s Disease: Integrating Early Diagnosis, Personalized Treatment, and Prognostic Modelling. Ageing Res. Reviews 101, 102497 (2024).
Maleki, S. F. et al. Artificial intelligence in eye movements analysis for alzheimer’s disease early diagnosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 21 (3), 155–165 (2024).
Balamurali, A., Kumar, H. & Haritheesathan, S. Early Detection of Dementia: Machine Learning for Predictive Analysis. In 2024 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT). 973–980 (IEEE, 2024).
Ali, M. T., Turetta, C., Pravadelli, G. & Demrozi, F. ICT-based solutions for alzheimer’s disease care: A systematic review. IEEE Access (2024).
Sundar Raj, A., Gunasundari, C., Senthilkumar, S. & Sivamani, S. An optimized hybrid deep learning model to detect Alzheimer disease. Scientific Reports https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-14169-8 (2025).
Hsu, B. W. Y., Chen, Y. M., Yang, Y. H. & Tseng, V. S. Predicting Fine-grained Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia Based on Machine Learning and Smart Wearable Devices. arXiv preprint https://abs/arXiv.org/2410.18091. (2024).
Badidi, E. Edge AI for early detection of chronic diseases and the spread of infectious diseases: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. Future Internet. 15 (11), 370 (2023).
Alapati, N. K. & Valleru, V. AI-Driven predictive analytics for early disease detection in healthcare. MZ Comput. Journal, 4(2). (2023).
Bhuvaneswari, R., Prabu, M., Diviya, M., Subramanian, M. & Natarajan, A. K. Advancing Precision Medicine: Integrating AI and Machine Learning for Personalized Healthcare Solutions. In Artificial Intelligence Transformations for Healthcare Applications: Medical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Care 344–361 (IGI Global, 2024).
Manoharan, I., Sowmiya, E. C., Harishma, S. & Amose, J. Medical data analytics and wearable devices. EAI Endorsed Trans. Smart Cities https://doi.org/10.4108/eetsc.v6i4.2264 (2022).
Subetha, T., Khilar, R. & Sahoo, S. K. An Early Prediction and Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comparative Analysis on Various Assistive Technologies. In: 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Smart Power System and Sustainable Energy (CISPSSE). 1–5 (IEEE, 2020).
Salehi, W. et al. IoT-Based wearable devices for patients suffering from alzheimer disease. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging. 2022 (1), 3224939 (2022).
Vrahatis, A. G. et al. Revolutionizing the early detection of alzheimer’s disease through non-invasive biomarkers: the role of artificial intelligence and deep learning. Sensors 23 (9), 4184 (2023).
Alharbi, E., Alomainy, A. & Jones, J. M. Detecting cognitive decline in early Alzheimer’s patients using wearable technologies. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI) 1–4 (IEEE, 2020).
Sciarrone, A. et al. Leveraging IoT wearable technology towards early diagnosis of neurological diseases. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 39 (2), 582–592 (2020).
Saif, N. et al. Feasibility of using a wearable biosensor device in patients at risk for Alzheimer’s disease dementia. The journal of prevention of Alzheimer’s disease 7, 104–111 (2020).
Jeon, Y. et al. Early alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using wearable sensors and multilevel gait assessment: A machine learning ensemble approach. IEEE Sens. J. 23 (9), 10041–10053 (2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors (R. Sathish, R. Muthukumar, K. Manikanda Kumaran, S. Palani Murugan) contributed to the study, conception, and design. All authors commented on the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Sathish, R., Muthukumar, R., Kumaran, K.M. et al. Intelligent decision-making systems for early detection of alzheimer’s disease using wearable technologies and deep learning. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36895-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36895-3