Abstract
The construction industry occupies a high proportion of the global economy. However, with the energy consumption of construction enterprises, it still brings a series of serious environmental problems. Construction enterprises should take active green development behavior to respond. Based on enterprises’ green development behavior, this paper explores the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises in China. Through literature analysis, this paper identifies that construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors is influenced by technological, organizational and environmental factors. Then this paper constructs an index system of the influencing factors of green development behaviors adopted by enterprises. According to the data of construction enterprises from 2000 to 2020 of National Bureau of Statistics, an artificial neural network is used to construct the prediction model of influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises. The conclusions are as follows. (1) Construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior shows an upward trend over time. (2) Market share of construction enterprises is the most important factor to promote construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. (3) The prediction model of influencing factors constructed in this paper is verified to be effective by the technology-organization-environment framework. This paper provides a reference for construction enterprises and the government to promote enterprises to adopt green development behavior, which is beneficial for construction enterprises to achieve green development faster.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
With the rapid development of economy, the construction industry occupied a high proportion of the global economy (Huang et al., 2021). However, the development of construction enterprises consumed a lot of energy and natural resources, which brought serious environmental problems, such as air pollution and destruction of natural resources (Xie et al., 2020). In 2019, the total CO2 emissions of global construction enterprises were about 1 billion tons, accounting for 28% of the total global energy-related carbon emissions. For China, facing increasingly serious environmental problems, construction enterprises, as the main part of China’s national economy, should take active green development behavior to deal with the existing problems. In 2019, the total output of China’s construction enterprises exceeded 24 trillion yuan, accounting for 25% of the country’s total national economic output. However, in the same year, China’s construction enterprises accounted for 30% of China’s total carbon emissions, which was the main cause of China’s environmental pollution (Zhang et al., 2020). Many scholars have explored green development from the perspective of manufacturing enterprises (Yang et al., 2019), chemical enterprises (Chen et al., 2019a) and other industries. China’s construction enterprises should also take green development as the internal requirement of enterprise development and make a rapid transformation towards green development. As a means to achieve green development, green development behavior should be focused on by various industries, but most of the studies on green development behavior focused on industrial enterprises. Therefore, starting from construction enterprises, this paper explores the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, broadens the research scope of green development, and provides a theoretical supplement for the follow-up study of green development behavior.
Based on technology–organization–environment (TOE) framework, this paper aims to construct an index system of influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises. Through the index system, this paper analyzes the impact of technological, organizational, and environmental factors on enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior and provides practical suggestions for construction enterprises and the government to promote enterprises to adopt green development behavior. The innovations of this paper are as follows: First, the existing study on green development behavior mostly focused on industrial enterprises. Therefore, based on the new perspective of construction enterprises, this paper can supplement relevant researches on green development behavior of enterprises. Moreover, this paper provides evidence from the construction industry for predicting the influencing factors of enterprises’ green development behavior. Second, this paper selects the new index of technology learning rate to construct an index system of influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, which clearly reflects the influence of technological innovation on construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior in technical factors. Third, different from other prediction studies, this paper applies an artificial neural network to predict the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, which broadens the application scope of an artificial neural network. Fourth, TOE theory provides a new research idea for explaining the influencing factors of enterprises green development behavior, and broadens the scope of application of TOE theory.
In view of this, this paper answers the following scientific questions: (1) What are the factors that influence construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior? (2) What is the most important factor for construction enterprises or the government to pay attention to? (3) What is the evolution trend of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior in the future?
Firstly, this paper identifies the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises through literature analysis. Secondly, the index system of influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises is constructed. Finally, using an artificial neural network, this paper constructs the prediction model of the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, then draws the research conclusion and summarizes the theoretical and practical significance. In terms of theoretical significance, on the one hand, the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises are analyzed based on TOE framework. This is not only an expansion of the research on enterprise green development, but also a supplement to the research on enterprise green behavior. On the other hand, an artificial neural network is used to construct the prediction model of influencing factors for green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, which is a new application of this method into the field of the construction industry. In terms of practical significance, this paper is beneficial for construction enterprises to actively adopt green development behavior. At the same time, it provides a basis for the government to promote enterprises to adopt green development behavior.
The rest of this paper is arranged as follows. The second section reviews the relevant literature from the perspective of enterprise green development behavior and its influencing factors. The third section constructs the index system of the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises. The fourth section describes the research methods. The fifth section describes the similarities and differences between the results of this study and those of similar studies, and summarizes the limitations and future researches. The last section describes the conclusion of this paper, and summarizes the theoretical significance and practical enlightenment.
Literature review
This paper analyzes the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, and believes that construction enterprises and the government should actively take measures to promote enterprises to adopt green development behavior, so as to achieve the effect of effective environmental protection and economic development. Table 1 shows the research progress of enterprises green development behavior and its influencing factors.
Enterprise Green development behavior
Green development is closely related to environmental protection and economic development, and has been highly concerned by domestic and foreign research scholars. Scholars made great efforts in exploring the concept of green development and achieved some results. Wang et al. (2006) pointed out that green development is a development model in which the environment and resources are sustainable, human and nature coexist in harmony, and the environment is the internal productive force. Li et al. (2019) believed that green development is an emerging development model that protects the ecological environment and achieves sustainable development under the constraints of ecological capacity and resource carrying capacity. Li et al. (2019) found that green development is a complex adaptive system closely related to social, economic and natural environments. Due to serious environmental problems, people’s demand for green development is increasing day by day. People’s demand for green development generated green development motives and ultimately green behaviors (Li et al., 2018). Green behavior was a kind of environmental protection behavior, such as cleaner production, energy saving behavior, green consumption and so on (Li et al., 2019). As for green behavior, many scholars explored green purchasing behavior (He et al., 2021), green procurement behavior (Yang et al., 2019), green consumption behavior (Shiel et al., 2020), green management behavior (Chang and Hung, 2021) and green development behavior (Li et al., 2019) from the perspective of enterprises.
At present, the relevant research on the green development behavior of enterprises is gradually attracting the attention of academic circles. The influencing factors of enterprises green development behavior have been verified through different methods, such as: meta-analysis (Li et al., 2022) and grounded theory analysis (Li et al., 2019). In addition, the green development behavior of enterprises in different industries has also received attention from scholars, such as the green development behavior of industrial enterprises (Li et al., 2020) and the green development behavior of building materials enterprises (Li, 2022).
Although the research on the green development behavior of industrial enterprises is relatively complete, the research on the green development behavior of construction enterprises is not been conducted. And the research on the green development behavior of enterprises is not systematic enough to effectively reveal the influencing factors of the green development behavior of construction enterprises. Therefore, from the perspective of construction enterprises, this paper analyzes the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, and supplements the research on enterprise green development behavior.
Influencing factors of enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior
The theoretical basis of this paper is the TOE framework, which was proposed by Tornatzky and Fleischer in processes of technological innovation in 1990 and it was expanded based on information technology innovation adoption and its related theories. It summarized the factors that influence the enterprise technology innovation or technology adoption into three categories: technological, organizational and environmental factors (Tornatzky et al., 1990).
TOE framework provided a new theoretical perspective for the research of enterprise technology innovation and enterprise technology adoption, which was widely used in the research of information technology. Such as, TOE framework was used to determine the factors that influence the information technology capabilities of e-commerce (Yeh et al., 2015); TOE framework was used to explore the factors influencing the adoption of hospital information system (Ahmadi et al., 2017). TOE framework can also be applied in other research fields. Such as, it identified the determining factors that influence the adoption of radio frequency identification technology (Wang et al., 2010); it also researched the determining factors of online financial transparency in America (Chen et al., 2019b).
To verify whether the three factors of TOE framework influence enterprises’ adoption of technological innovation behavior, relevant studies were carried out in China and abroad. In China, through the integration of TOE framework and technology acceptance model, it is verified that technological, organizational and environmental factors were the key factors influencing enterprises’ adoption of internet of things technology (Zhang et al., 2018). On abroad, through the research on the adoption of radio frequency identification technology in the retail industry, the influence of technological, organizational and environmental factors on the adoption behavior was verified (Brown and Russell, 2007).
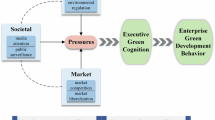
To sum up, according to the analysis of TOE framework and considering the quantifiable influencing factors, this paper summarizes the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises into three main aspects: technological, organizational and environmental factors. The influencing factors of these three aspects are analyzed in detail below, and the analysis framework is shown in Fig. 1.
Technological factors
As a way for enterprises to achieve green development, green technology innovation was an emerging field of a new round of global industrial revolution and scientific and technological competition, and it was the first time for China to put forward the construction of innovation system in the field of technology (Zhuang et al., 2020). At present, many studies found that technological factors were the influencing factors of enterprises’ adoption of green technology innovation behavior. Through the empirical research on green technology innovation capability and its influencing factors, it was found that the technological factor is one of the most important factors (Yin et al., 2020). When analyzing the influencing factors of green innovation adopted by small and medium-sized enterprises, it was found that technological factors have a significant impact on the adoption of green innovation by small and medium-sized enterprises (Weng and Lin, 2011).
The existing literature found that the technological factor is the key factor for enterprises to adopt technological innovation behavior, but none of them aimed at enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. Therefore, this paper studies and verifies the technological factors that influence enterprises’ adoption of technological innovation behavior as the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior.
Organizational factors
Most studies showed that enterprise size in organizational factors influences enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. When studying the behavior decision of enterprises’ adoption of environmental technological innovation, it was found that enterprise size is the influencing factor in enterprises’ adoption of environmental technological innovation (Du and Zhu, 2010). To study the environmental management of road transportation, it was found that enterprise size has an impact on enterprise’s environmental behavior (Fürst and Oberhofer, 2012). Although the subject of the above studies is enterprises’ adoption of environmental behavior, environmental behavior referred to the behavior which has an impact on the environment, including reducing pollution, saving resource consumption and so on (Wu and Su, 2006). Therefore, environmental behavior also plays an important role in the green development of enterprises.
The existing literature found that the organizational factor is the key factor for enterprises to adopt environmental behavior, but none of them aimed at enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. Therefore, this paper studies and verifies the organizational factors that influence enterprises’ adoption of environmental behavior as the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior.
Environmental factors
According to the TOE framework, the main factors influencing enterprises’ adoption of technological innovation behavior were: technological, organizational and environmental factors, among which environmental factors included industry environment, social environment and so on (Tornatzky et al., 1990). This paper summarizes the environmental factors through literature analysis, and regards enterprise demand, market share and the government behavior as the environmental factors that affect the green development behavior of construction enterprises.
The existing studies made specific analysis of the above three types of environmental factors. Firstly, for the enterprise demand, to study how internal and external factors drive enterprises to adopt green supply chain plan at the same time, it was pointed out that competitors in external factors have an impact on promoting or hindering enterprises to implement green supply chain management (Huang et al., 2017). Similarly, competitive advantage was also the most important driving factor influencing small and medium-sized enterprises to adopt environmental management behavior (Zhang et al., 2009). Therefore, this paper analyzes enterprises’ demand as an index to measure competitiveness (Wang et al., 2012). Second, market share was also an index of competitiveness (Huang and Xu, 2008). Finally, for the government behavior, the government policies can be studied as environmental factors (Stern and Paul, 2000).
To sum up, industrial environment, customer demand and social environment among environmental factors are included into the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises. The existing literature found that the environmental factor is the key factor for enterprises to adopt environmental behavior, but none of them aimed at enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. Therefore, this paper studies and verifies the environmental factors that influence enterprises’ adoption of environmental behavior as the influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises.
Based on the above analysis, this paper constructs an index system of influencing factors of green development behavior adopted by construction enterprises, which is composed of 3 first-level indicators, 5 second-level indicators and 12 third-level indicators, as shown in Table 2.
Research methods
Data sources
The main data in this paper comes from the relevant data of construction enterprises in the whole society from 2000 to 2020 released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China, and the rest of the data comes from China National Intellectual Property Administration and CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure). The specific data sources are shown in Table 3.
Among them, the urbanization level is the ratio of the urban population to the total population. Total output value of real estate is the total income of all projects operated by the real estate industry, including the main business income of real estate enterprises, the income from land transfer, the income from the sale of commercial housing, the income from housing rental and other income. The number of policies is government documents searched with “green” and “environment” as keywords after consultation with experts. The number of patents is obtained by searching through the keywords of “green building”, “building energy saving”, “low carbon building”, “environmentally friendly building”, “sustainable building” and “ecological building” after consultation with experts.
In addition, for technological learning rates in the construction industry through experience and technological learning rates in the construction industry through research, this paper refers to the research of Yang et al. (2012), and uses a dynamic two-factor measurement model to measure it. First, choosing variables. According to the research on the calculation of the technological learning rate of the construction industry, this paper selects the cost per unit area of China’s construction industry as the dependent variable to measure the technological learning rate (Zhang et al., 2020). The cost per unit area is the ratio of the total construction cost (fixed asset investment + main business cost - fixed asset depreciation) to the total construction area of the construction enterprises. This paper selects the cumulative construction area of China’s construction industry and the cumulative R&D expenditure of China’s construction industry as independent variables. Among them, the cumulative construction area and main business cost of the construction industry are from China Statistical Yearbook on Construction, the cumulative R&D expenditure of the construction industry is from China statistical yearbook on science and technology, and the fixed asset investment and fixed asset depreciation of the construction industry are from the China fixed asset investment statistical yearbook. Second, processing the data. Based on the research of Zhang et al., this paper determines R&D lag periods and the depreciation rate of R&D expenditures as 3 years and 20%, and processes the accumulated R&D expenditures (Zhang et al., 2020). At the same time, to eliminate the influence of inflation, this paper uses the GDP deflator to deal with the cost per unit area. Finally, calculating technological learning rate. This paper uses Eviews10 to perform regression analysis on the above data. According to the results of regression analysis, the dynamic two-factor measurement model formula is used to calculate technological learning rates in the construction industry through experience and technological learning rates through research.
Methods introduction
The research method uses in this paper is an artificial neural network, which was a mathematical model that simulates biological neural network for information processing (Zhang et al., 2021). It was developed based on M-P neuron model (McCulloch and Pitts, 1943). M-P neuron model was the first neuron model proposed by McCulloch and Pitts (1943) to simulate the human brain. This model regards a single neuron as a computing unit, and each computing unit is connected through some weighted lines to form a hierarchical network structure. Artificial neural network can be used to predict the importance of influencing factors. Many studies proved that this method can accurately predict the importance of influencing factors. Such as, predicting influencing factors of traffic accident risk by an artificial neural network (Sliupas and Bazaras, 2013), artificial neural network was used to identify the correlation between some chronic diseases and behavior habits (Raghupathi and Raghupathi, 2017).
This paper uses IBM SPSS modeler 18.0 to construct a prediction model of the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. SPSS modeler provides various data mining algorithms, which can solve specific types of problems and is widely used in some fields. Such as, evaluating the performance of infection risk factors in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in the medical field (Park et al., 2015); solved the problem of improving the mathematical modeling competence of undergraduates in the field of education (Xiao et al., 2015). In addition, SPSS Modeler provides two artificial neural network model algorithms, one is the multi-layer perceptron (MLP) and another is the radial basis function (RBF). MLP was proposed to solve the problem of multi-class decomposition of nonlinear data in a single-layer perceptron model (Sampson, 1987). Compared with MLP, RBF can only contain one hidden layer at most, and its prediction ability is relatively weak. Therefore, in order to improve the accuracy of model prediction, this paper uses MLP to construct an artificial neural network prediction model.
Model construction
The technology roadmap of this paper is shown in Fig. 2.
Referring to the research of Dumitrașcu-Băldău et al. (2021), this paper completes data import, variable setting, missing value processing and model construction successively, as shown in Fig. 3.
To ensure the validity of the research results, this paper uses IBM SPSS Statistics 27 to conduct a Pearson correlation analysis on the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors. The analysis results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 shows the correlation between the various influencing factors and the correlation of each influencing factor to the target variable number of patents. Considering the correlation between a total number of construction machinery and equipment, technical equipment rate, power equipment rate, technological learning rates in the construction industry through experience, and technological learning rates in the construction industry through research are not significant. Therefore, this paper excludes these five influencing factors, and finally selects total power of the construction enterprise’s own construction machinery and equipment, R&D expenditures, the number of construction enterprises, the number of employees in construction enterprises, total assets of construction enterprises, total profits and taxes of construction enterprises, and urbanization level, total output value of real estate, total output value of construction industry, building construction area, completed area of house, and the number of policies are used as 12 input variables to construct the artificial neural network prediction model of influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
Moreover, to improve the accuracy of the prediction model, this paper uses the “partition” node to randomly divide the data into training data set and testing data set. The training data set and testing data set are divided into nine models: 10:90, 20:80, 30:70, 40:60, 50:50, 60:40, 70:30, 80:20 and 90:10, and the prediction accuracy is obtained by running the above nine models, as shown in Table 5.
It can be seen from Table 5 that the model (6) with a training-to-test ratio of 60:40 has the highest accuracy at 99.6%, indicating that the prediction results are feasible. Therefore, this paper finally selects model (6) to analyze the results.
Result analysis
The following is an analysis of the artificial neural network model, the importance of the predictor variables, and the target variables.
Artificial neural network model analysis
The best prediction model of an artificial neural network determined in this paper is shown in Fig. 4.
Figure 4 shows a complete artificial neural network model, which is composed of input layer, hidden layer and output layer from top to bottom. The input layer has 10 predictive variables and 1 bias, the hidden layer has 7 neurons and 1 bias, and the output layer has 1 target variable. Bias represents additional neurons contained in each pre-output layer (Dumitrașcu-Băldău et al., 2021). The input layer of the model is connected with the hidden layer through different weights, and the weights are assigned according to the importance of different predictive variables. The higher the weight, the more important the prediction variable is, and the thicker the connecting line between the prediction variable and the hidden layer is. Figure 4 shows that total output value of construction industry, R&D expenditure and several construction enterprises are the most important prediction variables.
Analysis of importance of predictive variables
The importance of influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors to the target variable (number of patents) is shown in Fig. 5.
The total output value of the construction industry, R&D expenditure, number of construction enterprises, total output value of real estate, total power of machinery and equipment, number of employees in construction enterprises, building construction area, urbanization level, number of policies, and total profit and tax of construction enterprises have an impact on the number of patents.
Figure 5 shows that total output value of the construction industry, R&D expenditure, number of construction enterprises, total output value of real estate, total power of machinery and equipment, number of employees in construction enterprises, building construction area, urbanization level, number of policies, and total profit and tax of construction enterprises have an impact on the number of patents. The total output value of the construction industry, R&D expenditure and a number of construction enterprises are the most influential factors in the number of patents. Among them, the importance of total output value of construction industry is 0.18, the importance of the predictive variable of R&D expenditure is 0.17, and the importance of the predictive variable of several construction enterprises is 0.16.
Target variables analysis
Based on the partition of the training data set and testing data set, the number of patents is analyzed by using “analysis” nodes, analysis results are shown in Table 6.
From the analysis results in Table 6, it can be seen that the linear correlation between the actual value and the predicted value of the number of patents is 0.903, and the positive correlation is strong, indicating that the prediction result of the target variable is reliable.
In addition, to intuitively present the prediction results of the number of patents, this paper selects the line chart to analyze it, as shown in Fig. 6.
As seen in Fig. 6, the number of patents increases with time evolution. Moreover, the trend of the actual patent number and the predicted patent number curve is roughly the same, indicating that the prediction of the target variable is reliable.
Discussion
Based on the research results, this section discusses the relationship between the three most important predictors of total output value of construction industry, R&D expenditure and a number of construction enterprises and construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors, to verify the impact of technological, organizational and environmental factors on construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
Important influencing factors
The importance of the predictive variable of total output value of construction industry is 0.18, which is the most important prediction variable and one of the indicators to measure market share in environmental factors. Therefore, for construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors, the market share of construction enterprises should be regarded as a key factor. This result is similar to a large number of previous studies that have pointed out that environmental factors have an impact on enterprises’ adoption behavior. For the market share in environmental factors, some studies have considered the multi-agent interaction between the government, enterprises and consumers to analyze the prefabricated building model and the evolution of market share of enterprises. It founds the price factors and quality factors of prefabricated buildings have an important impact on the increase in market share (Li et al., 2021). At the same time, Chinese government pays more and more attention to the green development of enterprises, and promotes the transformation of construction enterprises from the traditional construction mode to the prefabricated construction mode through policies such as technical subsidies, which accelerates the transformation of enterprises. In addition, enterprises have also increased market share by adjusting the price factors and quality factors of prefabricated buildings, thereby improving the impact of environmental factors. In addition, for enterprise adoption behavior, environmental factors are also the influencing factors for enterprises to adopt radio frequency identification technology (Chen and Wang, 2013). To sum up, environmental factors are an important factor affecting construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
The importance of the predictive variable of R&D expenditure is 0.17, which is the second important prediction variable and one of the indicators of technological innovation among technological factors. Therefore, in the process of green development of construction enterprises, the level of green technology innovation should be improved. This result is similar to a large number of previous studies. Due to the continuous decline of economic globalization, the intensification of enterprises’ competitiveness and the deterioration of the environment brought about by enterprises development, enterprises transformation has become an important part of enterprises green development. In order to study enterprise transformation, Song et al. constructed a structural equation model from the driving factors of enterprises to analyze the impact of technological innovation on enterprise transformation, and found that technological innovation significantly affects enterprise transformation (Song et al., 2021). Therefore, improving the level of technological innovation of enterprises can promote the transformation of enterprises to green development. In addition, to promote enterprises to establish a more comprehensive and efficient technology management system, based on edge computing technology, the enterprise technology innovation management system is studied, and the relationship between knowledge depth, knowledge breadth and enterprise innovation performance is analyzed, so as to improve the efficiency of enterprise resource scheduling (Tian and Wang, 2022). This is conducive to more efficient management of enterprises, and it has a positive impact on the sustainable development of enterprises. To sum up, technological factors are an important factor affecting construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
The importance of the predictive variable of a number of construction enterprises is 0.16, which is the third most important prediction variable and one of the indicators to measure enterprise size in the organizational factor. Therefore, construction enterprises should consider expanding enterprise size and promoting enterprises to adopt green development behaviors. This result is similar to many previous studies. The enterprise size in the organizational factor has a significant impact on many aspects of the construction enterprise. Such as, for enterprise safety, given the high injury rate in construction enterprise jobs, a study investigated the relationship between the size of Danish construction enterprises and injury rates. It found that large enterprises place more emphasis on improving the safe working environment for construction enterprises (Pedersen et al., 2011). Therefore, expanding the construction enterprises size can reduce casualties and have a positive impact on human development and socio-economics. Furthermore, according to Negahban et al. (2012), it was found that the application of enterprise resource planning in the construction enterprises is limited to a few large organizations, and a large number of small and medium organizations have not yet adopted the technology due to their unfamiliarity with the technology. This shows that the larger the enterprise size, the more advanced the resources and technology of the enterprise, and the better the development of the enterprise. To sum up, according to the above-mentioned organizational factors, the enterprise scale affects enterprise security and enterprise resources, etc., organizational factors are also important factors affecting construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
In addition, the importance of other predictive factors is ranked as follows: total output value of real estate (0.13), total power of the construction enterprise’s own construction machinery and equipment (0.12), number of employees in construction enterprises (0.08), building construction area of construction enterprises (0.04), urbanization level (0.03), number of policies (0.02) and total profits and taxes (0.02). These factors also have an impact on construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
Limitations and future research
This paper also has some limitations. Firstly, this paper selects the best prediction model with the highest accuracy through the partition. Although the accuracy of the prediction model in this paper is as high as 99.6%, the large error between the actual value and the predicted value of the number of patents is still a problem in this paper. The analysis results in Table 4 show that the maximum error in the testing data set is as high as 456.234. After analysis, it is found that the possible reason is that in processing missing data, the average value method adopted has a great impact on the data of time series and cannot accurately replace the actual data. Therefore, if the complete data from 2000 to 2020 can be collected in future research, the prediction of the model will be more accurate. Secondly, this paper adopts quantifiable data and does not analyze the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior from a qualitative perspective. In the future research, if the quantitative and qualitative indicators are considered comprehensively, the research results will be more accurate. For example, when considering organizational factors, qualitative indicators such as employee attitude can be included in the research scope. Thirdly, this paper only analyzes China’s construction enterprises. Future research can take more countries as the research object as much as possible, so as to draw a more universal conclusion. Finally, this paper only adopts an artificial neural network to construct the model. In the future, a combination of multiple research methods can be considered to obtain a prediction model with higher accuracy. Such as, Bayesian networks, decision trees and so on. However, the prediction of the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors in this paper not only provides a basis for the future research on the green development behavior of enterprises, but also provides a preliminary result for the future research on the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors in more countries.
Conclusions and enlightenment
The purpose of this paper is to predict the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors. Through literature analysis, this paper identifies that the construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors is influenced by technological, organizational and environmental factors, and constructs an index system of the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors. According to the data of construction enterprises from 2000 to 2020 of National Bureau of Statistics, an artificial neural network is used to construct the prediction model of influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. Through running the model, it is found that total output value of construction industry, R&D expenditure and several construction enterprises are the three most important factors influencing construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors, and the other factors also have an impact.
Therefore, the research conclusions of this paper are as follows:
First, construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior shows an upward trend over time. As a quantifiable index, the number of patents can clearly show the increase or decrease each year, and can infer the trend of construction enterprises adopting green development behavior. In this paper, the number of patents related to “green building”, “building energy efficiency”, “low-carbon building”, “environmental protection building”, “sustainable building” and “ecological building” is taken as the target variable of the prediction model. The number of patents reflects the adoption trend of green development behavior in the development process of construction enterprises. The results show that the development trend of the number of patents increases with time evolution from 2000 to 2020.
Second, market share of construction enterprises is the most important factor to promote construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. The results show that the importance of the prediction variable of total output value of construction industry is 0.18, which is the most important prediction variable and has the greatest impact on the number of patents. At the same time, total output value of the construction industry is one of the indicators to measure market share in environmental factors, indicating that environmental factors are the most important factor to promote construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors.
Third, the prediction model of influencing factors constructed in this paper is verified to be effective by the technology–organization–environment framework. Through literature analysis and TOE framework, this paper summarizes the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior are technological, organizational and environmental factors. According to the research results of the artificial neural network prediction model, it is found that total output value of construction industry, R&D expenditure and a number of construction enterprises are the three most important factors that affect the green development behavior of construction enterprises. And these three influencing factors respectively represent the influence of environmental factors, technological factors and organizational factors on construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior, which is consistent with the analysis results of the TOE framework.
The theoretical contributions of this paper are as follows: on the one hand, for the research content, most of the previous studies focused on enterprises’ environmental behavior and green behavior, and none of them studied enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior. Based on TOE framework, this paper analyzes the influencing factors of construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior, which is not only an expansion of enterprise green development research, but also a supplement to enterprise green behavior research. On the other hand, for research methods, the previous application of the artificial neural network mostly focused on the field of medicine and education. In this paper, an artificial neural network is used to construct the prediction model of influencing factors for construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behavior, which is a new application of this method into the field of the construction industry.
The research conclusions of this paper have practical significance for construction enterprises and countries. For construction enterprises, technological factors and organizational factors, as the internal influencing factors of enterprises, can promote the green development of enterprises. Therefore, enterprises should consider green technology innovation and enterprise size expansion from their own perspective, and promote enterprises to actively adopt green development behavior. For the country, environmental factors, as the external influencing factors of construction enterprises, can promote the green development of enterprises. Therefore, the government should implement the new development concept, formulate more policies for green development and promote construction enterprises to adopt green development behaviors.
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or codes that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmadi H, Nilashi M, Shahmoradi L, Ibrahim O (2017) Hospital Information System adoption: expert perspectives on an adoption framework for Malaysian public hospitals. Comput Hum Behav 67:161–189
Brown I, Russell J (2007) Radio frequency identification technology: an exploratory study on adoption in the South African retail sector. Int J Inf Manag 27(4):250–265
Chang TW, Hung CZ (2021) How to shape the employees’ organization sustainable green knowledge sharing: cross-level effect of green organizational identity effect on green management behavior and performance of members. Sustainability 13(2):626
Chang RD, Soebarto V, Zhao ZY, Zillante G (2016) Facilitating the transition to sustainable construction: China’s policies. J Clean Prod 131:534–544
Chen G, Kang H, Luna-Reyes LF (2019b) Key determinants of online fiscal transparency: a technology–organization–environment framework. Public Perform Manag Rev 42(3):606–631
Chen Y, Hu S, Chen D, Zhai H, Bao S, Lv T (2019a) An evaluation method of green development for chemical enterprises. Sustainability 11(22):6491
Chen X, Wang F (2013) The impact factors for adopting RFID technology in Chinese enterprises. Sci Res Manag 34(2):1–9
China National Knowledge Infrastructure (2022) https://r.cnki.net/kns/brief/result.aspx?dbprefix=gwkt. Accessed 13 Apr 2022
Du J, Zhu F (2010) Research on behavioral decision—making of firm’s environmental technology innovation adoption. Sci Technol Prog Policy 27(7):68–72
Dumitrașcu-Băldău I, Dumitrașcu DD, Dobrotă G (2021) Predictive model for the factors influencing international project success: a data mining approach. Sustainability 13(7):3819
Fürst E, Oberhofer P (2012) Greening road freight transport: evidence from an empirical project in Austria. J Clean Prod 33:67–73
Gao Q (2008) An empirical analysis of technological innovation capability and its influencing factors of agricultural science and technology enterprises. Chin Rural Econ 7:32–38
He Z, Zhou Y, Wang J, Li C, Wang M, Li W (2021) The impact of motivation, intention, and contextual factors on green purchasing behavior: new energy vehicles as an example. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1249–1269
Huang B, Lei J, Ren F, Chen Y, Zhao Q, Li S, Lin Y (2021) Contribution and obstacle analysis of applying BIM in promoting green buildings. J Clean Prod 278:123946
Huang YC, Huang CH, Yang ML (2017) Drivers of green supply chain initiatives and performance: evidence from the electrical and electronics industries in Taiwan. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 47(9):796–819
Huang Y, Xu S (2008) Construction and engineering contracting services: competitiveness comparison between China and Korea. J Int Econ Cooperation 2:72–77
Li X, Du J, Long H (2019) Green development behavior and performance of industrial enterprises based on grounded theory study: evidence from China. Sustainability 11(15):4133
Li X, Du J, Long H (2019) Theoretical framework and formation mechanism of the green development system model in China. Environ Dev 32:100465
Li X, Du J, Long H (2018) A comparative study of Chinese and foreign green development from the perspective of mapping knowledge domains. Sustainability 10(12):4357
Li X, Du J, Long H (2019) Dynamic analysis of international green behavior from the perspective of the mapping knowledge domain. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):6087–6098
Li X, Dai J, Li J, He J, Liu X, Huang Y, Shen Q (2022) Research on the impact of enterprise green development behavior: a meta-analytic approach. Behav Sci 12(2):35
Li X (2022) Research on the improvement strategy of enterprise’s green development behavior performance: a case from the construction materia enterprises. J Henan Univ Technol (Soc Sci Edn) 1:39–48
Li X, Du J, Long H (2020) Mechanism for green development behavior and performance of industrial enterprises (GDBP-IE) using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(22):8450
Li K, Gao Y (2010) Research on xinjiang enterprise competitiveness based on principal component analysis. Seeker 12:27–29
Li Z, Chen Y, Liu Y (2022) Multidimensional performance of high-quality development from the perspective of “ governance of China”. Reform 2:88–100
Li Z, Zhang S, Meng Q (2021) Modeling adoption behavior of prefabricated building with multiagent interaction: system dynamics analysis based on data of Jiangsu Province. Comput Intell Neurosci 2021:3652706
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5(4):115–133
National Bureau of Statistics. https://data.stats.gov.cn/. Accessed 13 Apr 2022
Negahban SS, Baecher GB, Skibniewski MJ (2012) A decision-making model for adoption of enterprise resource planning tools by small-to-medium size construction organizations. J Civ Eng Manag 18(2):253–264
Park JH, Kim HY, Lee H, Yun EK (2015) A retrospective analysis to identify the factors affecting infection in patients undergoing chemotherapy. Eur J Oncol Nurs 19(6):597–603
Patent Search and Analysis. http://pss-system.cnipa.gov.cn/sipopublicsearch/patentsearch/tableSearch-showTableSearchIndex.shtml. Accessed 13 Apr 2022
Pedersen BH, Hannerz H, Christensen U, Tüchsen F (2011) Enterprise size and risk of hospital treated injuries among manual construction workers in Denmark: a study protocol. J Occup Med Toxicol 6(1):1–6
Raghupathi V, Raghupathi W (2017) Preventive healthcare: a neural network analysis of behavioral habits and chronic diseases. In: Healthcare, vol. 5(1). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, p. 8.
Sampson G (1987) Parallel distributed processing: explorations in the microstructures of cognition. MIT Press
Shiel C, do Paco A, Alves H (2020) Generativity, sustainable development and green consumer behaviour. J Clean Prod 245:118865
Stern P (2000) Toward a cohYanerent theory of environmentally significant behavior. J Soc Issues 56(3):407–424
Song Y, Shao L, You J (2015) Electric vehicle enterprise niche evaluation research in the complementary assets perspective. Manag Rev 27(9):108
Song H, Hongsuchon T, Kittikowit S, Dong Z (2021) Assessing the antecedents and consequence of enterprise. Transformation 12:813858–813858
Sliupas T, Bazaras Z (2013) Forecasting the risk of traffic accidents by using the artificial neural networks. Baltic J Road Bridge Eng 8(4):289–289
Tornatzky LG, Fleischer M, Chakrabarti AK (1990) Processes of technological innovation. Lexington Books
Tian Z, Wang X (2022) Construction of enterprise innovation performance model using knowledge base and edge computing. J Supercomput 78(7):9570–9594
Wang YM, Wang YS, Yang YF (2010) Understanding the determinants of RFID adoption in the manufacturing industry. Technol Forecast Soc Change 77(5):803–815
Wang J, Cao D, Chen X (2006) Conception of national green development strategic plan. Environ Prot 03B:39–43
Wang X, Pan H, Liu B (2012) Study on evaluation of competitiveness of Chinese regional construction industry based on cloud model. J Shanxi Finance Econ Univ 7:55–66
Wang W, Lin Z, Chou Y (2013) Evaluation and evolution of production efficiency in China’s construction industry. Statistics & Decision 24:95–98
Weng MH, Lin CY (2011) Determinants of green innovation adoption for small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs). Afr J Bus Manag 5(22):9154–9163
Wu C, Su Y (2006) Review on studies of environmental attitudes and behavior and the relationship between them. Forecasting 25(4):61–65
Xiao X, Xu H, Xu S (2015) Using IBM SPSS modeler to improve undergraduate mathematical modelling competence. Comput Appl Eng Educ 23(4):603–609
Xie L, Xu T, Le Y, Chen Q, Xia B, Skitmore M (2020) Understanding the CSR awareness of large construction enterprises in China. In: Advances in civil engineering 2020:8866511
Yang J, Su J, Song L (2019) Selection of manufacturing enterprise innovation design project based on consumer’s green preferences. Sustainability 11(5):1375
Yang S, Su Y, Wang W, Hua K (2019) Research on developers’ green procurement behavior based on the theory of planned behavior. Sustainability 11(10):2949
Yang Y, Yu B, Wu W (2011) The dynamic impacts of enterprises’ technological capability improvement on technological learning rate. Sci Res Manag 8:26–33
Yang Y, Wu W, Yu B (2012) Research on dynamic two -factor measurement model of industrys technological learning rate. J Ind Technol Econ 9:97–103
Yeh CH, Lee GG, Pai JC (2015) Using a technology-organization-environment framework to investigate the factors influencing e-business information technology capabilities. Inf Dev 31(5):435–450
Yin S, Zhang N, Li B (2020) Enhancing the competitiveness of multi-agent cooperation for green manufacturing in China: an empirical study of the measure of green technology innovation capabilities and their influencing factors. Sustain Prod Consum 23:63–76
Zhang B, Bi J, Liu B (2009) Drivers and barriers to engage enterprises in environmental management initiatives in Suzhou Industrial Park, China. Front Environ Sci Eng China 3(2):210–220
Zhang J, Ouyang Y, Philbin SP, Zhao X, Ballesteros‐Pérez P, Li H (2020) Green dynamic capability of construction enterprises: role of the business model and green production. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 27(6):2920–2940
Zhang T, Xu L, Wu Z (2018) Factors influencing the adoption of the Internet of Things in inbound logistics of automobile parts. J Syst Manag 27(2):254–263
Zhang L, Luan L, Zhang X (2020) Calculation of Technical Learning Rate in Construction Industry Based on Two-factor Learning Curve. J Liaoning Univ Technol (Nat Sci edn) 5:337–341
Zhuang Q, Wu B, Hong Q (2020) Market-oriented green technology innovation system: theoretical connotation, practical exploration and promotion strategy. Economist 11(11):29–38
Zhang M, Liu Y, Guo J (2021) Big Data research in the field of finance and accounting: technology and application. accounting and economics. Research 3:3–22
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Special Funds of the National Social Science Fund of China (grant number 18VSJ038), the Scientific Research Startup Foundation for Introducing Talents of Sichuan Agricultural University (grant number 2122996022), the Social Science Special Project of Sichuan Agricultural University Disciplinary Construction Dual Support Program (grant number 2021SYYB05), the Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Sichuan Agricultural University (grant number 202110626136), and the Sichuan Students’ Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship training program (grant number S202110626136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft preparation: XL, JH; Formal analysis and investigation: JH; Writing—review and editing: JH, YH, JL, XL; Funding acquisition, Supervision and Resources: XL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This research did not require any ethical approval.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., He, J., Huang, Y. et al. Predicting the factors influencing construction enterprises’ adoption of green development behaviors using artificial neural network. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9, 238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01253-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01253-x
This article is cited by
-
Study on the path of high-quality development of the construction industry and its applicability
Scientific Reports (2024)