Abstract
Homologous recombination (HR) and mismatch repair (MMR) defects are driver mutational imprints and actionable biomarkers in DNA repair-defective tumors. Although usually thought as mutually exclusive pathways, recent preclinical and clinical research provide preliminary evidence of a functional crosslink and crosstalk between HRR and MMR. Shared core proteins are identified as key players in both pathways, broadening the concept of DNA repair mechanism exclusivity in specific tumor types. These observations may result in unexplored forms of synthetic lethality or hypermutable tumor phenotypes, potentially impacting the cancer risk management, and considerably expanding in the future the therapeutic window for DNA repair-defective tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
DNA damage and impaired DNA repair processes are the main endogenous sources of genomic and, in particular, chromosomal instability (CIN)1. The genes that encode components specifically involved in DNA repair pathways, genome and chromosome integrity are the main drivers of hereditary cancers2. Today, identifying driver mutational imprints of DNA repair that both predispose to cancer development and establish drug vulnerabilities is one of the main goals in cancer research3.
Within the network of known genome maintenance pathways, the key role of homologous recombination (HR) repair (HRR) and mismatch repair (MMR) emerges strongly from the observation that individuals carrying germline deleterious variants in HRR or MMR genes show a remarkably elevated lifetime risk for the development of several cancer types4,5. The mutated gene, the prevalence, and the DNA repair pathways involved varied across the cancer histologies6,7,8.
Importantly, DNA repair pathways have been usually thought as mutually exclusive, with implications for genetic screening strategies and treatment stratification9. Thus, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate hereditary cancers seem dominated mainly by HRR repair deficiency (HRD), and are historically recognized as HRD-cancers10; similarly, colorectal and endometrial hereditary cancers are primarily characterized by microsatellite instability (MSI), caused by defects in DNA MMR, resulting in a characteristic mutational footprint10,11.
Although the potential interactions between HRR and MMR mechanisms remain widely unexplored, recent research provides preliminary evidence of a functional crosslink and crosstalk between different DNA repair deficiencies in small subsets of cancers, greatly increasing the repertoire of defects in these critical pathways12. These observations may result in unexplored forms of synthetic lethality or hypermutable tumor phenotypes, considerably expanding in the future the therapeutic window for DNA repair-defective tumors13. Tumors known as HRD-cancers, but showing predominant MMR deficiency (MMRd) signature, could present an increased mutation load, and could be potential candidates for the treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); conversely, a perturbed HR system in classically MSI-affected tumors, may represent an actionable biomarker for the treatments with poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors (PARPi). A deeper understanding of the signature lesions of DNA repair processes is a critical need, and future evidences in the clinical context could represent a novel starting point to expand the possibility to target DNA repair-defective tumors.
This review aims to outline the current scenario of tumors identified as HRD- or MMRd-associated and the underlying molecular mechanisms, exploring the evidence of the intersection or dichotomy of these two DNA damage repair pathways.
Homologous recombination and mismatch repair: critical drivers of hereditary cancers
Genomic instability is a hallmark of cancer14. Cellular exposure to environmental or endogenous stresses can generate various types of DNA damage. Specific DNA damage response pathways are activated by cells in response to DNA damage. If unrepaired, the altered genetic information leads to the acquisition of specific mutations, which may predispose to cancer onset15. At least eight distinct DNA repair pathways can be activated to repair damaged DNA, including HR, MMR, base-excision repair (BER), nucleotide-excision repair (NER), non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), translesion synthesis (TLS), the Fanconi anemia (FA) and the O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) pathways15.
The critical role of HR and MMR in DNA damage response (DDR) and genome maintenance was widely determined. Notably, a large fraction of known drivers of hereditary cancers are genes involved in these two DNA repair pathways16 (Table 1).
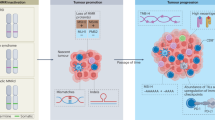
Breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer susceptibility gene 2 (BRCA2) are the main DNA repair genes linked to hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC)17,18. Currently, BRCA1/2 pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants (PV/LPVs) are associated with an increased lifetime risk of other cancers, mainly prostate and pancreatic cancers19, and the association between all these tumors and more moderate-penetrance genes in the HR pathway is continuously emerging5,20. Similar to the HRR, the MMR pathway plays an important role in hereditary cancers. Inactivating germline PVs in the MMR genes are the genetic background of Lynch syndrome (LS), an autosomal dominant disorder clinically also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) as defined by Amsterdam and Bethesda criteria (Table 2)21, associated with a significantly increased risk of several cancer types such as colorectal, but also endometrial, small bowel, gastric, ovarian, and ureteral cancers22 (Fig. 1). Importantly, these DNA repair defects in either the HR or MMR pathways, are also current biomarkers for guiding the use of PARPi and ICIs, respectively10,23.
Classically, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate hereditary cancers are known as HRD tumors; while, colorectal and endometrium, but also additional cancers, including cancers of the stomach and renal pelvis, are classified as MMRd-associated tumors. Determination of MSI/MMRd as well as HRD status in different cancer types, beyond their characteristic mutational footprints, may improve genetic screening strategies and treatment stratification (Created with BioRender.com).
However, deleterious variants in HRR or MMR genes only identified a low proportion of hereditary tumors16. Several inherited genetic drivers are still not fully understood. Understanding whether tumors associated with the HRD spectrum could arise in individuals with deficiencies in other DNA repair pathways, such as MMRd, and vice versa, would significantly increase opportunities for cancer risk management and therapeutic efforts.
HRR: role, crosstalk, and epistasis of key players
Among DNA damages, double-strand breaks (DSBs) represent the most damaging form of DNA lesions, resulting in deep and irreversible genomic wounds if not correctly healed24. The two main DSB repair pathways are the HR and the NHEJ, each of which is involved in different phases of the cell cycle with the first mainly involved during replication and the second throughout interphase10. The HRR is a highly conserved and accurate DNA repair pathway. In the absence of functional HRR, for example, when either BRCA1 or BRCA2 are defective, the preferential use of error-prone systems to repair DSBs leads to an increased burden of genomic alterations25. Deficiency in the HRR pathway is known as HRD, while tumors that are not HRD are termed homologous recombination proficient (HRP)25. The best-characterized HRR genes are certainly BRCA1 and BRCA2: germline and somatic PV/LPVs, as well as epigenetic modifications in BRCA1 and BRCA2, have been strongly associated with an HRD phenotype26. However, beyond BRCA, deleterious variants in HR-related genes other than BRCA1/2, such as Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), Partner and Localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2), checkpoint kinase 2 (CHEK2), RAD51 Recombinase (RAD51), BRCA1 Interacting Helicase 1 (BRIP1) and BRCA1 Associated RING Domain 1 (BARD1) genes, also confer an HRD or “BRCAness” phenotype. Their role in the DNA repair downstream pathway is well-defined and takes place through the interaction with both BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes27.
The presence of a BRCA PV/LPV directs therapeutic management with PARPi in patients with breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancers, leading to novel models of mainstreaming cancer genetics19,28.
The significant relationship among all proteins involved in DSB repair expands the possibility of a successful HRD-PARPi synthetic lethality. In fact, several approved PARPis are not restricted to BRCA1/2-mutated patients. In ovarian cancer patients with HRD-positive tumors, even in the absence of a BRCA1/2 PVs, recent clinical trials showed a clinically meaningful benefit of adding PARPi maintenance therapy, alone or in combination with bevacizumab, following response to platinum-based chemotherapy (PAOLA-1 and PRIMA trials)29,30. Although genomic scar assays provide information on the magnitude of PARPi benefits depending on HRD status, the optimal HRD biomarkers in this population are debated. At the same time, whether PARPi treatment can be proposed for cancer patients with non-BRCA HRR PV/LPVs remains controversial, highlighting how, beyond BRCA1/2 PVs, HRR multigene panel and HRD genomic instability tests are not interchangeable27.
The complementary effect between the HRR-related, non-BRCA, proteins, and BRCA1/2, reinforces the need for an enhanced definition of HRD biomarkers of PARPi effectiveness.
MMR: a mutator phenotype that reshapes the tumor microenvironment
DNA MMR is a highly conserved mechanism that enables the recognition and repair of randomly incorporated errors during DNA replication, significantly enhancing genomic stability. The mispaired nucleotides are caused by polymerase misincorporation errors, recombination events between DNA double helix strands, as well as chemical or physical damages31. The genes codifying for the MMR proteins are named as the homologous counterpart of E. coli system; mutS homologs (MSH2, MSH3, MSH4, MSH5, MSH6), mutL homologs (MLH1, MLH3), and post-meiotic segregation increased (PMS1, PMS2)32.
All the proteins function as heterodimers allowing firstly the recognition and thereafter the repair of mispaired bases as well as small insertion/deletion. Several mechanisms can lead to MMR deficiency. The most common causes can be linked mainly to acquired somatic MMR mutations leading to gene function inactivation, along with MLH1 gene silencing due to hypermethylation of the MLH1 promoter region33,34. Deficiency can also occur due to germline mutations in the MMR genes. The germline mutations in the MMR genes MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, or deletion at the 3’ end of the EPCAM gene, which result in hypermethylation of the MSH2 promoter35 are the most commonly known cause of hereditary colorectal cancer (CRC); such mutations lead to the development of LS36. However, recently, MLH1 hypermethylation has been reported in rare cases of patients affected by LS, although it is often linked to sporadic CRCs37. In particular, simultaneous loss of MLH1 and PMS2 expression is the most common pattern of LS based on MLH1 germline mutations, followed by an MSH2/MSH6 loss due to MSH2 germline mutations38. The natural consequence of the presence of MMRd is MSI. Microsatellites are short tandem repeat DNA sequences of one to tetra base pairs distributed both in coding and non-coding regions of the human genome39. This instability arises as a consequence of the repetitive structure of microsatellites, which are particularly susceptible to replication errors normally repaired by the MMR system. However, recent findings have revealed that important mutational events are often a consequence of genomic destabilization and not only occur during replication, even in the presence of MMRd. This phenomenon is associated with the repair of DSBs occurring during replication stress through the microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) mechanism, mediated by enzymes such as DNA polymerase θ and PARP, as reported by Matsuno et al.40. Moreover, recent studies have raised several doubts about our understanding of immunogenicity in MMRd tumors. Indeed, the fact that MMRd tumors are typically associated with a rich immune microenvironment, with high infiltration of T lymphocytes and a consequent higher host anti-tumor response, represented the soil for the important benefits showed to immune checkpoint blockade, irrespective of the organ site of tumor origin41. For this reason, in the 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized the use of the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab for the treatment of patients with solid unresectable or metastatic tumors expressing MMRd/MSI, with progressive disease after prior treatment and without additional therapeutic options. The same treatment was approved for MMRd or MSI progressive CRC following fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan42,43. Importantly, this is the FDA’s first tissue/site-agnostic approval. In the same year, another anti-PD-1 drug, nivolumab, had obtained the FDA accelerated approval for the treatment of metastatic MMRd or MSI CRC with disease progression after standard chemotherapy36.
Interestingly, while it was expected that the presence of MSI would lead to increased production of a larger reservoir of novel frameshift peptides, the development of neoantigens, and consequently, a stronger immune response, recently the results of preclinical studies have suggested a discrepancy regarding this simplistic model. Indeed, it has been found that, contrary to expectations, the majority of antigens presented in MMRd CRCs are not mutated44, and antigens derived from mutated MHC-I-associated peptides are lost after the growth of such tumors in immunocompetent mice45. These findings revolutionize the neoantigen hypothesis as the sole explanation for the efficacy of ICIs in these tumors.
HRD and MMR/MSI testing in the clinic: still stuck at temporary snapshot?
HRD testing
The remarkable percentage of patients showing a BRCAness phenotype has opened numerous questions regarding new strategies and potential useful biomarkers for a proper patient selection in this specific setting. While the involvement and testing of BRCA1/2 genes have been deeply clarified as a predictor of sensitivity to PARPi, insufficient evidence supports the testing recommendation for other HRR-related genes, including ATM, ATR, PALB2, RAD51, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, BARD1, BRIP127. To date, several multigene panels, spanning from a small to a wider number of genes, have been exploited to identify PV/LPVs as well as large rearrangements affecting HRR-related genes. Consequently, depending on the available next-generation sequencing (NGS) platforms and size targets, different sequencing pipelines are thus needed, from amplicon-based to hybrid-capture-based target enrichment approaches. The former relies on different primer pool mixes for the selective amplification of DNA/RNA targets through multiple PCR steps. The latter, conversely, uses specifically designed small nucleic acid probes enabling the proper selection of common/unknown as well as larger regions of interest46,47.
In the recent years, a growing interest has been particularly focused on the genomic instability as a direct effect of such genetic alterations. This level of genomic instability has brought many advantages in terms of tailored treatment opportunities as remarkably highlighted in high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC)48. In this context, to properly address patients likely to benefit from the administration of PARPis, the FDA has approved several tests among which the two spread and known worldwide are the NGS-based companions Myriad myChoice® CDx and FoundationOne CDx. Both testing strategies enable the identification of alteration at the genetic and genomic levels49. The Myriad myChoice® CDx allows the identification of single nucleotide variant (SNV)/indels/large rearrangements in several HRR-related genes along with the evaluation of the Genomic Instability Score (GIS) as a measure of loss of heterozygosity (LOH), telomeric allelic imbalance (TAI), and large-scale state transitions (LST). A score greater than 42 is suggestive of HRR deficiency and this value has been clinically used to further target patients likely to benefit from PARPi administration. Moreover, the reliability of this parameter has been extensively adopted in several clinical trials, such as PRIMA and PAOLA-150. The FoundationOne CDx (F1CDx) is a hybrid-capture NGS-based comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) that allows the identification of multiple genetic alterations in 324 cancer genes along with tumor mutational burden (TMB) and MSI51. Furthermore, this companion testing allows the identification of the percentage of neoplastic tissue specimens showing genomic LOH. The percentage cut-off used has been 14% and 16% in the ARIEL 2 and ARIEL 3 randomized clinical trials, respectively52. Most recently, the measurement of RAD51 foci accumulation through immunohistochemistry (IHC) and/or immunofluorescence (IF), is gaining attraction as a novel approach to unraveling HRD27,53.
In this scenario, several technical and clinical issues for the current testing and assays exist. Although our ability to stratify patients with HRD-related tumors improved the treatment selection, the different approaches that recognize the causes of HRD, such as the HRR deleterious variants, the functional alteration of HRR activity itself, such as the RAD51 foci assay, or the HRD consequences, through the genomic scar assays, are not interchangeable testing and require a better optimization in the clinic27.
MMRd/MSI testing
Defective DNA MMR results, generally, in MSI in tumor tissue. For this reason, MSI is recognized as a hallmark of LS, and up to 30% of several cancer types54.
The current tumor testing provides the possibility to identify LS by direct and indirect methods. The standard diagnostic procedure recommended by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) involves analyses of tumor and normal tissues using five microsatellite markers (Bethesda panel), including two for mononucleotide repeats (BAT-26 and BAT-25) and three for dinucleotide repeats (D2S123, D5S346, and D17S250)33. The ESMO recommendations on MSI testing for immunotherapy in cancer recommended the Bethesda panel, or an alternative panel with five poly-A mononucleotide repeats (BAT-25, BAT-26, NR-21, NR-24, NR-27), characterized by higher sensitivity and specificity55. MSI was defined as loss of stability in ≥ 2 out of the five microsatellite markers. As suggested in the revised Bethesda guidelines for CRC33, and endorsed by the ESMO recommendations55, the terms MSI-high and MSI-low should be overcome, and MSI-low grouped with microsatellite stable (MSS) tumors.
The IHC can indicate the presence or absence of a functional MMR system, and thus indirectly the presence of MSI. It allows to identification of the defective protein and then leads to the mutational analysis of the relevant gene56. The so-called universal tumor screening, followed by constitutional testing, estimated 3% of consecutive, unselected, colorectal and endometrial cancer patients, and 10–15% of tumors with MMRd, associated with LS54,57.
However, one relevant observation should be made on MSI and MMR protein expression in tumor tissue of individuals with constitutional defects of MMR. Although immunohistochemical analysis showed the absence of one or more MMR proteins, the MSI frequency in the same tumor tissue varied according to the tumor type: 80–100% for the primary tumors of colon, stomach, ureter, and ovary; 50% for endometrium, bladder, and kidney tumors, and 35% for breast cancer54. At the same time, LS cancer patients with MSI tumors often showed tumors other than colorectal and endometrium, or canonical LS-spectrum tumors, such as prostate cancer, melanoma, soft tissue sarcoma, and mesothelioma54.
Although IHC and pentaplex PCR remain the gold standard procedures, recent efforts have been made to develop NGS-based diagnosis tools, including the FDA-approved Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center’s (MSK)-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (IMPACT) MSISensor algorithm. This technology showed that NGS improves recognition of patients with MSI in pan-cancer by comparing sequencing reads around microsatellite regions in the tumor and paired normal samples, and reporting the percentage of unstable loci as a cumulative score in the tumor58,59.
Irrespective of the diagnostic method used, the diagnosis of LS ultimately requires constitutional genetic testing to identify the deleterious variants in the MMR genes. Constitutional sequencing-based variant detection is coming to a paradigm shift toward universal germline genetic testing60. Recent studies in unselected population for high-risk features showed 3% and 6% of LS among colorectal and endometrium cancers, respectively, investigated using hereditary multigene cancer panel testing54. Certainly, the possibility to detect all mutation carriers is appealing, but the frequent occurrence of variants of uncertain significance (VUS), or deleterious variants of uncertain clinical interpretation, makes the topic an ongoing debate.
In the future, novel minimally invasive options, such as the liquid biopsy61 or the emerging “liquidomics”62, could represent a dynamic and sensitive approach to simultaneously screening MMR and HRR-associated alterations, and to expand genetic and genomic knowledge on these tumors.
MMRd signature in the HRD-spectrum tumors: broadening the concept of DNA repair exclusivity
The evaluation of MMR and HRR status is essential in the clinical decision-making process to tailor both the diagnostic and therapeutic approach in the sporadic setting of MMRd and HRD tumors. Unsurprisingly, the inactivation of MMR genes in the germline leads to an increased susceptibility and earlier onset of various cancer types, a direct consequence of heightened mutation rates. The occurrence of inherited heterozygous mutations in the MMR genes is considered to be the hallmark of LS, implicated in the familial clustering of colorectal and endometrial cancers while also being associated with an elevated risk of other cancers, including but not limited to stomach, ovaries, prostate, and bladder63. Alternatively, biallelic germline mutations of one of the four MMR genes result in a distinct phenotypically and extremely aggressive cancer predisposition syndrome defined as Constitutional Mismatch Repair Deficiency (CMMRD), commonly predisposing to brain, gastrointestinal, and hematopoietic malignancies64.
Although the majority of causal variants impact the core MMR genes, such pathogenic events are only detectable in a fraction of familial cancer cases65. Intriguingly, in around half of hereditary MMRd CRCs, a genetic cause cannot be identified, leading to a phenomenon known as “Lynch-like syndrome”66. One possible explanation for this limitation is that familial cancer risk may be attributed to conditions beyond LS, potentially involving epigenetic or somatic changes of modifier genes unrelated to MMR, such as APC, BER genes like MUTYH and NTHL1, or replicative DNA polymerases such as POLE or POLD167. Recent discoveries have shown that biallelic somatic mutations in MMR genes are possible and can account for up to 50% of unexplained MMRd tumors. Additionally, although rare, somatic mosaicism has been observed, contributing to the complexity of understanding the genetic basis of MMRd tumors68. It could also be plausible that these individuals do have LS, but the sensitivity of current genetic testing technologies may be insufficient to detect the germline mutations in these cases. There are documented rare heritable causes of LS, such as constitutional MLH1 hypermethylation and complex rearrangements of MMR genes, which may currently escape detection by clinically available genetic testing technologies69.
The knowledge-driven advancement of immunotherapy designed to address both inherited and sporadic MSI cancers seems to complement the knowledge-based development of PARPis intended for the treatment of both inherited and somatic DNA DSB-associated cancers linked to BRCA1/2 deficiency70. Mutational signatures might offer a potential avenue to elucidate relevant biological and mechanistic insights. Deconvoluting the diversity of somatic mutations and tumor mutational burden into individual mutational signatures would provide a powerful tool for identifying processes generating somatic mutations in different cancer types71. In this context, there is a clear imperative for additional studies aimed at uncovering the causes of unexplained familial tumor risk, which is likely attributable, at least in part, to failures in the MMR system. Nonetheless, it must be considered that malfunctions in a single DNA repair pathway can be offset by alternative pathways, implying that simultaneous flaws in these compensatory pathways may lead to synthetic lethality. Consequently, identifying defects that manifest in mutually exclusive patterns can be utilized for the treatment of tumors with deficiencies in DNA repair mechanisms. This approach leverages the concept that targeting multiple compensating pathways concurrently could be an effective strategy for treating DNA repair-defective tumors.
Gastrointestinal malignancies, especially colorectal cancer, exhibit frequent silencing of HRR and MMR pathways, contributing to a high mutational burden. MSI tumors, constituting about 15% of colorectal and 10% of gastric tumors, result from defects in the MMR system, exhibit a slightly better prognosis, and respond to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. MSS tumors, constituting the majority, are characterized by chromosomal instability, show resistance to immune checkpoint blockade therapy, and present a challenge in terms of treatment options. However, the prevalence and prognostic roles of HRD in relation to MMRd in cancer require further exploration. Recent findings have unveiled a mutual exclusivity between MMRd and HRD mutational signatures in colorectal and stomach cancers13, aligning with previous reports in gynecological malignancies12 while offering valuable biological insights into the intricate relationship between the MSI/MSS status of tumors and the presence of HRD. It was observed that MSS tumors exhibited a higher degree of heterogeneity in their mutational signatures compared to MSI tumors: namely, MSI tumors usually showcase Single Base Substitution (SBS) signatures that distinctly represent a robust indication of MMRd, dominating the mutational signature profiles and suggesting potential selective advantages of these signatures which imply a driver role in shaping the mutational landscape of tumors.
Breast cancer (BC)
In BC, MMR genetic alterations are rare, occurring in 3% of cases, with a substantial intratumor heterogeneity. Notably, some studies have shown that breast cancers developed in women with LS are more likely to exhibit MMR protein loss and/or MSI, compared with sporadic tumors72. However, whether BC developing in the context of LS are causally related to MMRd, remains controversial. The existing literature on BC highlights how the tissue spectrum of LS patients may vary depending on the specific gene affected. Carriers of mutations in MSH6 and PMS2 have been reported to have an elevated risk of BC, in contrast to MLH1 and MSH2 carriers73. Despite the prognostic value of MMR is still controversial, several studies confirmed that MMRd is significantly associated with the worst prognosis and, especially in hormone receptor-positive patients, with an endocrine-resistant phenotype potentially susceptible to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition74,75. Regarding molecular subtypes, the distribution of MMRd BC is more prevalent in HER2-enriched and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtypes compared to luminal BCs76. In TNBC, the evaluation of both mismatch repair defect and TILs could be useful for selecting PD-L1-negative patients likely responding to immunotherapy77. For individuals with hormone receptor-positive BC undergoing tamoxifen treatment, the presence of MMRd is associated with poorer OS and DSS outcomes (HR 2.29, 95% CI 1.02–5.17, P = 0.040 and HR 2.71, 95% CI 1.00–7.35, P = 0.042, respectively). This observation implies that the MMR status might have a potential role in identifying hormone receptor-positive patients who might derive greater benefit from treatments other than endocrine therapy75.
Pancreatic cancer (PaC)
The interest in MMR deficiency in PaC derives from its predictive role as an agnostic biomarker for immunotherapy. The prevalence of MSI in PaC is relatively low, accounting for around 2% of all cases78. The intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas differs from its invasive counterpart for an incidence of 6.9% of MSI/MMRd79. Instead, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and MMRd are associated in rare cases (1–2%)78,80,81,82. Luchini et al.82 represented the most extended evaluation of this issue. MMR deficiency has been associated with a better prognosis, despite with not statistically significant data, and with mucinous/colloid histological phenotype. Of interest, KRAS is not the driver gene in this specific subtype population81, whereas JAK2-KMT2 gene mutations are frequently associated. Concerning the efficacy of immunotherapy, findings from the KEYNOTE-158 study indicated that MSI PaC exhibited a lower likelihood of response when compared to various other cancer types. Notably, the response rate to pembrolizumab in individuals with MSI pancreatic cancer stood at 18%, whereas response rates for other gastrointestinal cancers—such as gastric, bile duct, and small intestine cancers—were within the more robust range of 40%83.
Prostate cancer (PrC)
In the context of prostate cancer, MSI is infrequently observed in the general population, and it does not represent a predominant pathway driving prostate carcinogenesis84. The majority of cases involve somatic mutations, with ~20% linked to LS, particularly in cases diagnosed before the age of 6084. Sporadic MSI prostate cancers are primarily associated with deactivating mutations in MSH2 and MSH6, in contrast to colon and endometrial cancers, where MSI status arises through MLH1 epigenetic silencing85. The activation of androgen receptor (AR) is implicated in the development of sporadic MSI prostate cancers, contributing to DNA DSBs86. MMRd is observed in 5% of metastatic PaC patients and is even less common in locally confined disease, with nearly half of MSI tumors presenting with metastatic disease. Comparative analyses of primary hormone-naïve tumors and their corresponding castration-resistant metastatic counterparts have revealed focal MMRd in the primary disease, suggesting that MMRd in the advanced setting may develop through clonal selection. Mutations in the MSH2 gene have been identified as the most prevalent, although MSH6 loss is more frequent in certain studies. Histologically, MSI has been detected in both adenocarcinomas and pure small-cell carcinomas, typically associated with aggressive disease, high-grade pathology, and metastasis. MSH2 loss is correlated with dense CD8+ lymphocytic infiltration and a higher mutational load86. MSI is also associated with intraductal carcinoma and simultaneous TP53 alterations. Clinically, MSI tumors exhibit a favorable response to androgen deprivation therapy and moderate sensitivity to docetaxel compared to MMR-proficient tumors (pMMR). Notably, patients with MMRd or MSI prostate cancer demonstrate significant responses to the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. In their study of 127 patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer, Rodrigues et al.87 showed that MMRd was linked to a reduced median overall survival (mOS, 7.0 years for MMRp vs. 3.8 years for MMRd; P = 0.003), suggesting the negative prognostic significance of the MSI status in this setting. Activating mutations in the MAPK pathway, PI3K pathway, and WNT/b-catenin pathway were common88. About 50% of primary PrC exhibit ETS rearrangements, with TMPRSS2::ERG fusion being the most prevalent89. In MSI/MMRd-prostate cancer, however, TMPRSS2::ERG rearrangements seemed to be less represented.
Ovarian cancer (OC)
Previously reported frequencies of MSI in OC, based on individual locus assays rather than genome-wide searches, were ~10–12%90. However, when using a classifier that replicates the Bethesda MSI label through genomics, only 3.2% of ovarian tumors were classified as MSI91. This suggests that the commonly employed Bethesda panel-based readout might underestimate the prevalence of MSI in certain cancer types, such as OC, as well as head-and-neck and cervical cancer. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis reported that MMRd by immunohistochemistry and MSI analysis were detected in 6.7% and 10.4% cases, respectively, with a prevalence in endometrioid histotype and a 47% of cases with germline MMRd92. Diagnosis of OC with MMRd occurs at a median age of 52.3 years (interval 33.6–62.2), with an early stage mostly stage I (50%)93. The MMR deficient status is homogeneous in the entire tumor mass, suggesting an early inactivation in tumorigenesis in OC94. The association between MMR status and clinical features in Asian patients has been reported by Ye et al.95 showing a higher rate of MMRd in women affected by ovarian carcinoma, with ≤50 years and a slightly higher median progression-free survival (PFS) than in their intact counterparts (30 vs 27 months), without a statistical significance (P = 0.471). OC in LS carriers exhibit a distinct profile compared to OC in individuals carrying BRCA1/2 PV/LPVs96. The observed risk of mortality from gynecologic cancer diagnosed before the age of 40 in carriers of MMR PVs was found to be 0%. Consequently, it has been concluded that the practice of prophylactic hysterectomy and/or oophorectomy before the age of 40 solely for cancer prevention reasons is unwarranted and ethically questionable97. Similarly, the observed risk of mortality from OC in carriers of pathogenic MSH6 or pathogenic PMS2 variants diagnosed before the age of 50 was also found to be 0%. For these carriers, the recommendation is that prophylactic oophorectomy before the age of 50 solely for cancer prevention reasons is considered unwarranted and ethically questionable.
HRD signature in non-common HRD-spectrum tumors
Pan-cancer analyses from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset have revealed that HRD impacts more than 5% of tumors, beyond the traditionally recognized HRD-spectrum cancers98. Notably, mutations in canonical HRR genes, typically associated with breast, ovarian, pancreatic and prostate cancers, have also been identified in a diverse range of cancers including colorectal (7–12%), esophagogastric (7.7%), hepatobiliary (6.6%), melanoma (18–57%), non-melanoma skin (10.5%), lung (6.3%), kidney (4.4%), endometrial (12.1%), and bladder cancer (10.0%)99,100,101.
In a recent study on CRC, the presence of tumor deleterious variant in 33 genes involved in the HRR pathway was evaluated102. HRD tumors, defined as samples with 1 or more PV/LPVs, accounted for ~10% of MSS/pMMR CRCs, were more frequently TMB-high and PD-L1 positive, with important therapeutic implications In the same research, the analysis of the association between HRR alterations and genomic LOH in an independent cohort of CRC samples, showed that only HRD tumors in the MSS/pMMR group were LOH-high102. Both esophagogastric and colorectal cancers with HRD signatures are significantly associated with improved responses to platinum-based chemotherapy, attributed to the susceptibility of HRD tumors to DNA-damaging agents. This insight has spurred the development of clinical trials investigating the synergistic effects of combining platinum-based chemotherapy with PARPi103. Furthermore, the presence of HRD has been associated with elevated immune infiltration and TMB, critical determinants of efficacy for ICIs102. These discoveries establish HRD as a pivotal biomarker for guiding a range of therapeutic strategies—including chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy in gastrointestinal cancers, potentially enhancing survival for patients with specific genomic features linked to HRD104,105.
In lung cancer, particularly non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), HRD is emerging as an important factor in predicting treatment responses. Studies suggest that tumors with HRD may respond more favorably to immuno-neoadjuvant therapy, highlighting HRD status as a key marker for assessing the effectiveness of combined ICIs and chemotherapy106,107. Moreover, HRD serves not only as a predictive biomarker but also as a prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and endometrial cancer, where a high HRD score is associated with poorer outcomes108,109,110. Specifically, in ccRCC, genomic and transcriptomic analyses have shown that HRD-positive patients exhibit upregulated DNA damage response and immune-related signaling pathways110.
Overall, the expanding recognition of HRD in a wider array of tumor types highlights its potential as an agnostic biomarker for cancer management, guiding more personalized treatment approaches and influencing the development of new therapeutic strategies tailored to exploit this genomic instability signature.
HRR and MMR in DNA repair: dichotomy or synergism?
MMR and HRR pathways could be, at the molecular level, closely linked111. Interestingly, even if not still fully clarified, several preclinical studies highlighted the crosstalk between MMR and HRR actors, with some proposed functions of MMR proteins during specific steps of HRR. In 2023, the workgroup headed by K. Myung highlighted the possible involvement of MMR protein complexes such as MSH2 and its partners (MSH3 or MSH6) and common proteins such as exonuclease 1 (Exo1) and SMARCAD1 (SWI/SNF-related Matrix-Associated Actin-Dependent Regulator of Chromatin Subfamily A containing DEAD/H Box1) in the regulation of HRR. In particular, it seems that the complex MRE11-RAD50-NBS1, after a proper recognition of DSB sites, generally followed by an ATM-dependent DNA damage signal, degrades ssDNA by generating a short single-stranded gap which in turn can be recognized by the heterodimer MSH2-MSH3 facilitating the action of Exo1 which can initiate DNA end resection by generating a longer ssDNA through its 5’–3’ exonuclease activity (Fig. 2). The recruitment of MSH2-MSH3 to DSBs could be facilitated as a result of a fine chromatin unwinding process in the nearby DSBs operated by remodeling complexes such as SMARCAD1. Indeed, SMARCAD1 has shown highly conserved interaction domains with MSH2. In addition, another finding reported the blockade of DNA polymerase θ-mediated end joining (TMEJ) by the heterodimer MSH2-MSH3 preventing consequently the misincorporation of errors during HR112.
Emerging studies highlight potential interactions of mechanisms that underly different forms of DNA repair, such as MMR and HRR. Shared core proteins, including RPA, EXO1, RFC, MSH2/3, MLH3, and PMS2, are identified as key players in both pathways, broadening the concept of DNA repair mechanism exclusivity in specific tumor types (Created with BioRender.com).
Recent studies further elucidate the intricate synergistic cooperation between MMR and HR pathways. Interestingly, as demonstrated by the research group headed by Yang-Xin Fu and Guo-Min Li, MutLα subunit MLH1 deficient mice show a higher chromosomal instability. In particular, MLH1 regulates Exo1 nuclease activity during DNA repair, and loss of MLH1 causes unrestrained DNA excision by Exo1, leading to increased single-strand DNA formation, DNA breaks, and, ultimately, chromosomal instability. This mechanism activates the cGAS-STING pathway, with important clinical implications for cancer immunotherapy113.
Moreover, HRR contributes to fork maintenance and the repair of spontaneous and induced DSBs111. The proteins involved in both systems partly overlap, up to now the molecular mechanisms underlying the activity of this system are only partially known but their cooperation is already demonstrated111. Bacterial but also yeast and mammalian cell models have highlighted the involvement of MMR proteins, in particular, the heterodimer MSH2-MSH6, in the interruption of recombination products generated from the genetic exchange between not perfectly homologous DNA strands in a process termed homeologous recombination111.
Furthermore, a recent finding highlighted the pivotal role of MutSβ, which corresponds to the heterodimer MSH2 and MSH3, in modulating HRR-mediated repair by resolving Holliday junctions (HJs). Specifically, the interaction of MutSβ with the SMX complex, comprising SLX4-SLX1, MUS81-EME1, and XPF-ERCC1, introduces a novel perspective on HRR regulation. MutSβ directly interacts with SLX4, a central component of the SMX complex, suggesting a targeted influence on the resolution of critical intermediates in HRR. Such findings further highlight the complex interplay between MMR and HRR pathways, extending their role beyond mere suppression or correction of mismatches through close collaboration in resolving recombination intermediates, thereby ensuring accurate and efficient DSB repair114.
Despite these preliminary evidence, elucidation of how this partial crosslink and crosstalk is regulated, and its full biological and clinical implications, require further research.
Clinical insights on HRR-MMR intersection: therapeutic consequences
The interactions of mechanisms that underly different forms of DNA repair could make the potential use of PARPi and ICIs significantly broader than initially recognized.
The relationships between HRR and MMR were recently investigated in gynecological cancers12. As well known, MMRd and HRD are distinctive signatures of uterine endometrial carcinoma and epithelial ovarian carcinoma, respectively. Farmanbar et al.12 studied the mutational signature profiles in gynecological cancers. A pattern of mutual exclusivity of DNA repair pathways was observed: a subset of uterine endometrial tumors showed HRD, a subset of epithelial ovarian tumors showed MMRd signature, while, in a cohort of cervical tumors, APOBEC was the most prevalent signature, co-occurred with POLE and was mutually exclusive with the MMRd signatures12. The authors concluded by highlighting a potential cancer type-independent ternary relation between HRD, MMRd, and APOBEC, where MMRd mutational signature is mutually exclusive with HRD, and APOBEC co-occurring with HRD is mutually exclusive with MMRd12.
The following research data were consistent with the reports on gynecological cancers. Mutual exclusivity of MMRd and HRD mutational signatures in colorectal and gastric tumors was shown. However, in the context of MSS tumors, a distinct subset of HRD tumors, characterized by poor outcome, was identified. Because HRD is a predictive biomarker of PARPi response, this finding could have important implications for therapy management of MSS tumors13. Furthermore, preclinical studies have suggested that MSI-mediated loss of DSB repair genes could confer sensitivity to PARPi also in MMRd cells115,116. Future studies in clinical setting confirming these data could open the way to novel therapeutic opportunities, beyond the immunotherapy, for the treatment of MMRd-related cancers. A following study of Sokol et al.117 explored the genomic overlap of MSI with the LOH, as a genomic measure of HRD, and the BRCA1/2 variant zygosity across multiple tumor types. The results highlighted that MSI and HRD status were generally mutually exclusive phenomena across breast, ovarian, and pancreatic tumors, with rare co-occurrence of BRCA mutations in the context of MSI. Notably, in prostate cancers, 12.8% of BRCA1 and 3.4% of BRCA2 mutations co-occurred with MSI. However, in these tumors, the BRCA1/2 mutations were generally monoallelic and were not associated with high LOH scores, ultimately not leading to an HRD phenotype117. Despite the authors suggesting less benefit from PARPi than ICIs, the small number of patients with combined BRCA mutations and MSI status does not allow any clinical recommendation in this subgroup of patients. A recent phase III clinical trial explored whether HRD-positive ovarian cancers patients benefitted from atezolizumab (IMagyn050 Trial, NCT03038100). The results showed that most ovarian cancers had low TMB despite HRD, and the presence of genomic instability did not improve sensitivity to ICI atezolizumab118. Thus, future efforts in clinical context are needed to further elucidate the clinical impact of genomic integrity maintaining mechanisms intersection, and to introduce novel concepts and hypotheses for novel therapeutic opportunities.
In conclusion, the number of innovative cancer therapies on the basis of the genetic background and genomic profile has dramatically increased in the last few years. Defective DNA repair processes are among the main targets for cancer therapeutics. HRR and MMR seem to have biological points of intersection. The clinical effects of this interaction remains unclear. Although MMRd and HRD were often identified as mutually exclusive genetic phenomena, recent evidences suggest that sensitivity to PARPi could be not associated with HRR defects alone115,116. HRD could occur in the context of MSI status, MMRd or MSS tumors, resulting in potential PARPi benefit. The attention is now turning to in depth studying mutational imprints of DNA damage also in non-canonical HRD or MMRd/MSI tumors, considerably increasing the opportunities for targeting DNA repair-defective cancers.
References
Tubbs, A. & Nussenzweig, A. Endogenous DNA damage as a source of genomic instability in cancer. Cell 168, 644–656 (2017).
Curtin, N. J. DNA repair dysregulation from cancer driver to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 801–817 (2012).
Russo, A. et al. The challenge of the Molecular Tumor Board empowerment in clinical oncology practice: a position paper on behalf of the AIOM- SIAPEC/IAP-SIBioC-SIC-SIF-SIGU-SIRM Italian Scientific Societies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 169, 103567 (2022).
Garber, J. E. & Offit, K. Hereditary cancer predisposition syndromes. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 276–292 (2005).
Bono, M. et al. Impact of deleterious variants in other genes beyond BRCA1/2 detected in breast/ovarian and pancreatic cancer patients by NGS-based multi-gene panel testing: looking over the hedge. ESMO Open 6, 100235 (2021).
Roy, R., Chun, J. & Powell, S. N. BRCA1 and BRCA2: different roles in a common pathway of genome protection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 68–78 (2011).
Lynch, H. T., Snyder, C. L., Shaw, T. G., Heinen, C. D. & Hitchins, M. P. Milestones of Lynch syndrome: 1895-2015. Nat. Rev. Cancer 15, 181–194 (2015).
Incorvaia, L. et al. BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants in triple-negative versus luminal-like breast cancers: genotype-phenotype correlation in a cohort of 531 patients. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 12, 1758835920975326 (2020).
Dietlein, F., Thelen, L. & Reinhardt, H. C. Cancer-specific defects in DNA repair pathways as targets for personalized therapeutic approaches. Trends Genet. 30, 326–339 (2014).
Groelly, F. J., Fawkes, M., Dagg, R. A., Blackford, A. N. & Tarsounas, M. Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 23, 78–94 (2023).
Adar, T. et al. Universal screening of both endometrial and colon cancers increases the detection of Lynch syndrome. Cancer 124, 3145–3153 (2018).
Farmanbar, A., Firouzi, S., Kneller, R. & Khiabanian, H. Mutational signatures reveal ternary relationships between homologous recombination repair, APOBEC, and mismatch repair in gynecological cancers. J. Transl. Med. 20, 65 (2022).
Farmanbar, A., Kneller, R. & Firouzi, S. Mutational signatures reveal mutual exclusivity of homologous recombination and mismatch repair deficiencies in colorectal and stomach tumors. Sci. Data 10, 423 (2023).
Negrini, S., Gorgoulis, V. G. & Halazonetis, T. D. Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 220–228 (2010).
Huang, R. & Zhou, P. K. DNA damage repair: historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 254 (2021).
McGrail, D. J. et al. Widespread BRCA1/2-independent homologous recombination defects are caused by alterations in RNA-binding proteins. Cell Rep. Med. 4, 101255 (2023).
Venkitaraman, A. R. Cancer suppression by the chromosome custodians, BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 343, 1470–1475 (2014).
Kuchenbaecker, K. B. et al. Risks of breast, ovarian, and contralateral breast cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 317, 2402–2416 (2017).
Russo, A. et al. Implementation of preventive and predictive BRCA testing in patients with breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer: a position paper of Italian Scientific Societies. ESMO Open 7, 100459 (2022).
Fanale, D. et al. Detection of germline mutations in a cohort of 139 patients with bilateral breast cancer by multi-gene panel testing: impact of pathogenic variants in other genes beyond. Cancers 12, 2415 (2020).
Win, A. K. et al. Colorectal and other cancer risks for carriers and noncarriers from families with a DNA mismatch repair gene mutation: a prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 30, 958–964 (2012).
Abildgaard, A. B. et al. Lynch syndrome, molecular mechanisms and variant classification. Br. J. Cancer 128, 726–734 (2023).
Guan, J. & Li, G. M. DNA mismatch repair in cancer immunotherapy. NAR Cancer 5, zcad031 (2023).
Jeggo, P. A. & Löbrich, M. DNA double-strand breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene 26, 7717–7719 (2007).
Stewart, M. D. et al. Homologous recombination deficiency: concepts, definitions, and assays. Oncologist 27, 167–174 (2022).
Fanale, D. et al. Prevalence and spectrum of germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance in breast/ovarian cancer: mysterious signals from the genome. Front. Oncol. 11, 682445 (2021).
Incorvaia, L. et al. Theranostic biomarkers and PARP-inhibitors effectiveness in patients with non-BRCA associated homologous recombination deficient tumors: Still looking through a dirty glass window? Cancer Treat. Rev. 121, 102650 (2023).
Gori, S. et al. Recommendations for the implementation of BRCA testing in ovarian cancer patients and their relatives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 140, 67–72 (2019).
González-Martín, A. et al. Niraparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 381, 2391–2402 (2019).
Ray-Coquard, I. et al. Olaparib plus bevacizumab as first-line maintenance in ovarian cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 381, 2416–2428 (2019).
Gupta, D. & Heinen, C. D. The mismatch repair-dependent DNA damage response: mechanisms and implications. DNA Repair 78, 60–69 (2019).
Marti, T. M., Kunz, C. & Fleck, O. DNA mismatch repair and mutation avoidance pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 191, 28–41 (2002).
Umar, A. et al. Revised Bethesda Guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 96, 261–268 (2004).
Boland, C. R. & Goel, A. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 138, 2073–2087.e3 (2010).
Huang, R., Deng, X., Zhang, Z., Wen, Q. & Li, D. Lynch syndrome-associated endometrial cancer with combined EPCAM-MSH2 deletion: a case report. Front. Oncol. 12, 856452 (2022).
Yurgelun, M. B. et al. Identification of a variety of mutations in cancer predisposition genes in patients with suspected Lynch syndrome. Gastroenterology 149, 604–13.e20 (2015).
Carnevali, I. W. et al. Promoter methylation could be the second hit in Lynch syndrome carcinogenesis. Genes 14, 2060 (2023).
Alpert, L. et al. Colorectal carcinomas with isolated loss of PMS2 staining by immunohistochemistry. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 142, 523–528 (2018).
Vilar, E. & Gruber, S. B. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer-the stable evidence. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 153–162 (2010).
Matsuno, Y. et al. Replication stress triggers microsatellite destabilization and hypermutation leading to clonal expansion in vitro. Nat. Commun. 10, 3925 (2019).
Russo, A. et al. The tumor-agnostic treatment for patients with solid tumors: a position paper on behalf of the AIOM- SIAPEC/IAP-SIBioC-SIF Italian Scientific Societies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 165, 103436 (2021).
André, T. et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 383, 2207–2218 (2020).
Diaz LA et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer (KEYNOTE-177): final analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 23, 659–670 (2022).
Hirama, T. et al. Proteogenomic identification of an immunogenic HLA class I neoantigen in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer tissue. JCI Insight 6, e146356 (2021).
Rospo, G. et al. Evolving neoantigen profiles in colorectal cancers with DNA repair defects. Genome Med. 11, 42 (2019).
Wagener-Ryczek, S., Merkelbach-Bruse, S. & Siemanowski, J. Biomarkers for homologous recombination deficiency in cancer. J. Pers. Med. 11, 612 (2021).
Singh, R. R. Target enrichment approaches for next-generation sequencing applications in oncology. Diagnostics 12, 1539 (2022).
Miller, R. E. et al. ESMO recommendations on predictive biomarker testing for homologous recombination deficiency and PARP inhibitor benefit in ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 31, 1606–1622 (2020).
Ngoi, N. Y. L. & Tan, D. S. P. The role of homologous recombination deficiency testing in ovarian cancer and its clinical implications: do we need it? ESMO Open 6, 100144 (2021).
Vergote, I. et al. European experts consensus: BRCA/homologous recombination deficiency testing in first-line ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 33, 276–287 (2022).
Takeda, M. et al. Clinical application of the FoundationOne CDx assay to therapeutic decision-making for patients with advanced solid tumors. Oncologist 26, e588–e596 (2021).
Swisher, E. M. et al. Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): an international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18, 75–87 (2017).
Compadre, A. J. et al. RAD51 foci as a biomarker predictive of platinum chemotherapy response in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 29, 2466–2479 (2023).
Peltomäki, P., Nyström, M., Mecklin, J. P. & Seppälä, T. T. Lynch syndrome genetics and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 164, 783–799 (2023).
Luchini, C. et al. ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: a systematic review-based approach. Ann. Oncol. 30, 1232–1243 (2019).
McCarthy, A. J. et al. Heterogenous loss of mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression: a challenge for immunohistochemical interpretation and microsatellite instability (MSI) evaluation. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 5, 115–129 (2019).
Moreira et al. Identification of Lynch syndrome among patients with colorectal cancer. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 308, 1555–1565 (2012).
Niu, B. et al. MSIsensor: microsatellite instability detection using paired tumor-normal sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 1015–1016 (2014).
Middha, S. et al. Reliable pan-cancer microsatellite instability assessment by using targeted next-generation sequencing data. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, PO.17.00084 (2017).
Esplin, E. D. et al. Universal germline genetic testing for hereditary cancer syndromes in patients with solid tumor cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 6, e2100516 (2022).
Russo, A. et al. The molecular profiling of solid tumors by liquid biopsy: a position paper of the AIOM-SIAPEC-IAP-SIBioC-SIC-SIF Italian Scientific Societies. ESMO Open 6, 100164 (2021).
Santini, D. et al. Network approach in liquidomics landscape. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 42, 193 (2023).
Elze, L. et al. Microsatellite instability in noncolorectal and nonendometrial malignancies in patients with Lynch syndrome. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 115, 853–860 (2023).
Tabori, U. et al. Clinical management and tumor surveillance recommendations of inherited mismatch repair deficiency in childhood. Clin. Cancer Res. 23, e32–e37 (2017).
de la Chapelle, A. Genetic predisposition to colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 769–780 (2004).
Bucksch, K. et al. Cancer risks in Lynch syndrome, Lynch-like syndrome, and familial colorectal cancer type X: a prospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 20, 460 (2020).
Bellido, F. et al. POLE and POLD1 mutations in 529 kindred with familial colorectal cancer and/or polyposis: review of reported cases and recommendations for genetic testing and surveillance. Genet Med. 18, 325–332 (2016).
Pope, B. J. et al. Germline and tumor sequencing as a diagnostic tool to resolve suspected Lynch syndrome. J. Mol. Diagn. 23, 358–371 (2021).
Dempsey, K. M. et al. Is it all Lynch syndrome?: an assessment of family history in individuals with mismatch repair-deficient tumors. Genet. Med. 17, 476–484 (2015).
Ashworth, A. A synthetic lethal therapeutic approach: poly(ADP) ribose polymerase inhibitors for the treatment of cancers deficient in DNA double-strand break repair. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 3785–3790 (2008).
Petljak, M. et al. Characterizing mutational signatures in human cancer cell lines reveals episodic APOBEC mutagenesis. Cell 176, 1282–94.e20 (2019).
Roberts, M. E. et al. MSH6 and PMS2 germ-line pathogenic variants implicated in Lynch syndrome are associated with breast cancer. Genet. Med. 20, 1167–1174 (2018).
Mas-Ponte, D., McCullough, M. & Supek, F. Spectrum of DNA mismatch repair failures viewed through the lens of cancer genomics and implications for therapy. Clin. Sci. 136, 383–404 (2022).
Sajjadi, E. et al. Mismatch repair-deficient hormone receptor-positive breast cancers: biology and pathological characterization. Cancer Cell Int. 21, 266 (2021).
Cheng, A. S. et al. Mismatch repair protein loss in breast cancer: clinicopathological associations in a large British Columbia cohort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 179, 3–10 (2020).
Hacking, S. et al. MMR deficiency defines distinct molecular subtype of breast cancer with histone proteomic networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 5327 (2023).
Özcan, D., Lade-Keller, J. & Tramm, T. Can evaluation of mismatch repair defect and TILs increase the number of triple-negative breast cancer patients eligible for immunotherapy? Pathol. Res. Pr. 226, 153606 (2021).
Ghidini, M. et al. Immune-based therapies and the role of microsatellite instability in pancreatic cancer. Genes 12, 33 (2020).
Lupinacci, R. M. et al. Prevalence of microsatellite instability in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastroenterology 154, 1061–1065 (2018).
Ahmad-Nielsen, S. A., Bruun Nielsen, M. F., Mortensen, M. B. & Detlefsen, S. Frequency of mismatch repair deficiency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pr. 216, 152985 (2020).
Scheidt, S. Therapy for angina pectoris: comparison of nicardipine with other antianginal agents. Am. Heart J. 116, 254–259 (1988).
Luchini, C. et al. Comprehensive characterisation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with microsatellite instability: histology, molecular pathology and clinical implications. Gut 70, 148–156 (2021).
Marabelle, A. et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab in patients with noncolorectal high microsatellite instability/mismatch repair-deficient cancer: results from the phase II KEYNOTE-158 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 38, 1–10 (2020).
Sedhom, R. & Antonarakis, E. S. Clinical implications of mismatch repair deficiency in prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 15, 2395–2411 (2019).
Pritchard, C. C. et al. Complex MSH2 and MSH6 mutations in hypermutated microsatellite unstable advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 5, 4988 (2014).
Antonarakis, E. S. et al. Clinical features and therapeutic outcomes in men with advanced prostate cancer and DNA mismatch repair gene mutations. Eur. Urol. 75, 378–382 (2019).
Nava Rodrigues, D. et al. Immunogenomic analyses associate immunological alterations with mismatch repair defects in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 128, 4441–4453 (2018).
Zhang, H. et al. Clinicopathological and molecular analysis of microsatellite instability in prostate cancer: a multi-institutional study in China. Front. Oncol. 13, 1277233 (2023).
Schweizer, M. T. et al. Genomic characterization of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies a high prevalence of DNA repair gene mutations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 3, 1–9 (2019).
Pal, T., Permuth-Wey, J., Kumar, A. & Sellers, T. A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of ovarian cancers: estimation of microsatellite-high frequency and characterization of mismatch repair deficient tumor histology. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6847–6854 (2008).
Cortes-Ciriano, I., Lee, S., Park, W. Y., Kim, T. M. & Park, P. J. A molecular portrait of microsatellite instability across multiple cancers. Nat. Commun. 8, 15180 (2017).
Atwal, A. et al. The prevalence of mismatch repair deficiency in ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 151, 1626–1639 (2022).
Kim, S. R. et al. Comprehensive molecular assessment of mismatch repair deficiency in Lynch associated ovarian cancers using next generation sequencing panel. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 34, 267–276 (2023).
Fraune, C. et al. High homogeneity of MMR deficiency in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 156, 669–675 (2020).
Ye, S. et al. The frequency and clinical implication of mismatch repair protein deficiency in Chinese patients with ovarian clear cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 22, 449 (2022).
Finch, A. P. et al. Impact of oophorectomy on cancer incidence and mortality in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 32, 1547–1553 (2014).
Dominguez-Valentin, M. et al. Risk-reducing hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy in female heterozygotes of pathogenic mismatch repair variants: a Prospective Lynch Syndrome Database report. Genet Med. 23, 705–712 (2021).
Riaz, N. et al. Pan-cancer analysis of bi-allelic alterations in homologous recombination DNA repair genes. Nat. Commun. 8, 857 (2017).
Alexandrov, L. B., Nik-Zainal, S., Siu, H. C., Leung, S. Y. & Stratton, M. R. A mutational signature in gastric cancer suggests therapeutic strategies. Nat. Commun. 6, 8683 (2015).
Akinjiyan, F. A. et al. Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) in cutaneous oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 10771 (2023).
Weiss, J. M. et al. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome: a misnomer? J. Clin. Oncol. 41, 10594 (2023).
Moretto, R. et al. Homologous recombination deficiency alterations in colorectal cancer: clinical, molecular, and prognostic implications. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 114, 271–279 (2022).
Fan, Y. et al. The mutational pattern of homologous recombination (HR)-associated genes and its relevance to the immunotherapeutic response in gastric cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 17, 1002–1013 (2020).
Lin, Y. et al. Homologous recombination repair gene mutations in colorectal cancer favors treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Mol. Carcinog. 62, 1271–1283 (2023).
Cecchini, M. et al. NCI10066: a Phase 1/2 study of olaparib in combination with ramucirumab in previously treated metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 130, 476–482 (2024).
Zhou, Z. et al. Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) can predict the therapeutic outcomes of immuno-neoadjuvant therapy in NSCLC patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 15, 62 (2022).
Li, G. et al. Correlation of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) score with response to the first-line treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitors plus chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 41, e21121–e21121 (2023).
Feng, J. et al. Combination of genomic instability score and TP53 status for prognosis prediction in lung adenocarcinoma. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 7, 110 (2023).
Siedel, J. H. et al. Clinical significance of homologous recombination deficiency score testing in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 160, 777–785 (2021).
He, L. et al. Homologous recombination deficiency serves as a prognostic biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 26, 429 (2023).
Spies, M. & Fishel, R. Mismatch repair during homologous and homeologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7, a022657 (2015).
Oh, J. M. et al. MSH2-MSH3 promotes DNA end resection during homologous recombination and blocks polymerase theta-mediated end-joining through interaction with SMARCAD1 and EXO1. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, 5584–5602 (2023).
Guan, J. et al. MLH1 deficiency-triggered DNA hyperexcision by exonuclease 1 activates the cGAS-STING pathway. Cancer Cell 39, 109–121.e5 (2021).
Young, S. J. et al. MutSβ stimulates Holliday junction resolution by the SMX complex. Cell Rep. 33, 108289 (2020).
Vilar, E. et al. MRE11 deficiency increases sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 71, 2632–2642 (2011).
Gaymes, T. J. et al. Microsatellite instability induced mutations in DNA repair genes CtIP and MRE11 confer hypersensitivity to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in myeloid malignancies. Haematologica. 98, 1397–1406 (2013).
Sokol, E. S. et al. PARP inhibitor insensitivity to BRCA1/2 monoallelic mutations in microsatellite instability-high cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 6, e2100531 (2022).
Landen, C. N. et al. Influence of Genomic Landscape on Cancer Immunotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Ovarian Cancer: Biomarker Analyses from the IMagyn050 Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Cancer Res. 29, 1698–1707 (2023).
Acknowledgements
Incorvaia L., Badalamenti G., and Russo A. were supported by the Piano Nazionale di Ripresa e Resilienza (PNRR) project—Italian Network of excellence for advanced diagnosis (INNOVA); PNC-E3-2022-23683266; PNC-HLS-DA (C43C22001630001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L. Incorvaia: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and supervision; A. Russo and V. Bazan: conceptualization and supervision. C. Brando, C. Mujacic, E. Di Giovanni, M. Bono, S. Contino, C. Ferrante Bannera, M.C. Vitale, A. Gottardo, M. Peri, A. Galvano, and G. Badalamenti: writing—original draft. T.D. Bazan Russo, V. Gristina, and A. Perez: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. The manuscript has been read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Incorvaia, L., Bazan Russo, T.D., Gristina, V. et al. The intersection of homologous recombination (HR) and mismatch repair (MMR) pathways in DNA repair-defective tumors. npj Precis. Onc. 8, 190 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-024-00672-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-024-00672-0
This article is cited by
-
Functional footprints of homologous recombination deficiency in prostate cancer revealed by ctDNA fragmentation and transcription factor accessibility
British Journal of Cancer (2026)
-
Does PARP1 up-regulation correlate with PSMA expression in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer studied with [18F]PARPi and [68Ga]PSMA PET/CT?
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2026)
-
Predictive value of homologous recombination-related gene mutations in survival outcomes of first-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy for gastric cancer
Gastric Cancer (2025)