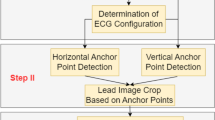
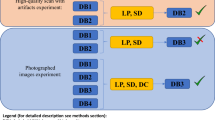
Abstract
Billions of clinical ECGs exist only as paper scans, making them unusable for modern automated diagnostics. We introduce a fully automated, modular framework that converts scanned or photographed ECGs into digital signals, suitable for both clinical and research applications. The framework is validated on 37,191 ECG images with 1596 collected at Akershus University Hospital, where the algorithm obtains a mean signal-to-noise ratio of 19.65 dB on scanned papers with common artifacts. It is further evaluated on the Emory Paper Digitization ECG Dataset, comprising 35,595 images, including images with perspective distortion, wrinkles, and stains. The model improves on the state-of-the-art in all subcategories. The full software is released as open-source, promoting reproducibility and further development. We hope the software will contribute to unlocking retrospective ECG archives and democratize access to AI-driven diagnostics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Both the Ahus and Emory Paper Digitization ECG Datasets will be released jointly as part of the ECG-Image-Database. The Ahus Paper Digitization ECG Dataset will be made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
The full software, including instructions, can be found on: github.com/Ahus-AIM/Open-ECG-Digitizer.
References
Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2023. JACC S0735109725074285, https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735109725074285 (2025).
Liu, X., Wang, H., Li, Z. & Qin, L. Deep learning in ECG diagnosis: a review. Knowl. Based Syst. 227, 107187 (2021).
Wu, Z. & Guo, C. Deep learning and electrocardiography: systematic review of current techniques in cardiovascular disease diagnosis and management. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 24, 23 (2025).
Jiang, R. et al. Deep learning-augmented ECG analysis for screening and genotype prediction of congenital long QT syndrome. JAMA Cardiol. 9, 377–384 (2024).
Zhu, H. et al. Automatic multilabel electrocardiogram diagnosis of heart rhythm or conduction abnormalities with deep learning: a cohort study. Lancet Digital Health 2, e348–e357 (2020).
Ribeiro, A. H. et al. Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network. Nat. Commun. 11, 1760 (2020).
Al-Zaiti, S. S. et al. Machine learning for ECG diagnosis and risk stratification of occlusion myocardial infarction. Nat. Med. 29, 1804–1813 (2023).
Kwon, J. -m et al. A deep learning algorithm to detect anaemia with ECGs: a retrospective, multicentre study. Lancet Digital Health 2, e358–e367 (2020).
Ouyang, D. et al. Electrocardiographic deep learning for predicting post-procedural mortality: a model development and validation study. Lancet Digital Health 6, e70–e78 (2024).
Badilini, F., Erdem, T., Zareba, W. & Moss, A. J. ECGScan: a method for conversion of paper electrocardiographic printouts to digital electrocardiographic files. J. Electrocardiol. 38, 310–318 (2005).
Ravichandran, L. et al. Novel tool for complete digitization of paper electrocardiography data. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 1, 1800107 (2013).
High precision digitization of paper-based ECG records: a step toward machine learning. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 7, 1900808 (2019).
Mishra, S. et al. ECG paper record digitization and diagnosis using deep learning. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 41, 422–432 (2021).
Fortune, J. D., Coppa, N. E., Haq, K. T., Patel, H. & Tereshchenko, L. G. Digitizing ECG image: a new method and open-source software code. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 221, 106890 (2022).
Wu, H. et al. A fully-automated paper ECG digitisation algorithm using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 12, 20963 (2022).
A. Reyna, M. et al. Digitization and classification of ECG images: the George B. Moody PhysioNet Challenge 2024. In Computing in Cardiology, https://www.cinc.org/archives/2024/pdf/CinC2024-011.pdf (2024).
H. Krones, F., J. Lyons, T., Mahdi, A. & Walker, B. Combining hough transform and deep learning approaches to reconstruct ECG signals from printouts. In Computing in Cardiology, https://www.cinc.org/archives/2024/pdf/CinC2024-097.pdf (2024).
Yoon, H.-C. et al. Segmentation-based extraction of key components from ECG images: a framework for precise classification and digitization. In Computing in Cardiology, http://www.cinc.org/archives/2024/pdf/CinC2024-227.pdf (2024).
Stenhede, E., Singstad, B.-J. & Ranjbar, A. ECG-DUaL: pose-invariant Digitization of printed electrocardiograms via U-net and Local edge detection. In Computing in Cardiology, https://www.cinc.org/archives/2024/pdf/CinC2024-262.pdf (2024).
Demolder, A. et al. High precision ECG digitization using artificial intelligence. J. Electrocardiol. 90, 153900 (2025).
Reyna, M. A. et al. ECG-image-database: a dataset of ECG images with real-world imaging and scanning artifacts; a foundation for computerized ECG image digitization and analysis. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.16612 (2024).
Ranjbar, A. & Ravn, J. Data quality in healthcare for the purpose of artificial intelligence: a case study on ECG digitalization. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 305, 471–474 (2023).
Ranjbar, A., Ravn, J., Ronningen, E. & Hanseth, O. Enabling clinical trials of artificial intelligence: infrastructure for heart failure predictions. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 302, 177–181 (2023).
Himmelreich, J. C. L. & Harskamp, R. E. Diagnostic accuracy of the PMcardio smartphone application for artificial intelligence-based interpretation of electrocardiograms in primary care (AMSTELHEART-1). Cardiovasc. Digital Health J. 4, 80–90 (2023).
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P. & Brox, T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. MICCAI. 234-241 (2015).
Azad, R. et al. Medical image segmentation review: the success of U-Net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 46, 10076–10095 (2024).
Duda, R. O. & Hart, P. E. Use of the Hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures. Commun. ACM 15, 11–15 (1972).
Crouse, D. F. On implementing 2D rectangular assignment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 52, 1679–1696 (2016).
Ribeiro, A. H. et al. CODE-15%: a large scale annotated dataset of 12-lead ECGs. https://zenodo.org/records/4916206 (2021).
Shivashankara, K. K. et al. ECG-Image-Kit: a synthetic image generation toolbox to facilitate deep learning-based electrocardiogram digitization. Physiological Meas. 45, 055019 (2024).
Ma, J. et al. Loss odyssey in medical image segmentation. Med Image Anal. 71, 102035 (2021).
Kingma, D. P. & Ba, J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. ICLR (2015).
Loshchilov, I. & Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. ICLR (2019).
Jammoul, S., Hassan, A., Zhang, E., Warrick, P. & Afilalo, J. Layout-invariant U-Net segmentation for time-series reconstruction from noisy ECG images. https://www.cinc.org/archives/2024/pdf/CinC2024-481.pdf (2024).
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at the Department of Cardiology at Akershus University Hospital for helping us in data collection, and James Weigle and Matthew Reyna for kindly evaluating our framework on the Emory Paper Digitization ECG Dataset.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.S. and A.B. designed the software as well as designed and performed experiments for evaluation, with supervision from A.R. E.S. and A.B. wrote the article with input from A.R.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Stenhede, E., Bjørnstad, A.M. & Ranjbar, A. Digitizing paper ECGs at scale: an open-source algorithm for clinical research. npj Digit. Med. (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-02327-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-02327-1