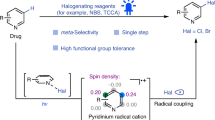
Abstract
Pyridine derivatives are one of the most common heterocycles in chemistry. The 3-halopyridines are generally synthesized by indirect methods, including functional group conversion or a temporary dearomatization–rearomatization process. Although the direct electrophilic halogenation of pyridines provides straightforward access to 3-halopyridines, it has been rarely reported owing to the poor π nucleophilicity of pyridines. Here we describe a general direct regioselective C-3 halogenation of pyridines promoted by an ether solvation effect. This radical process enables the regioselective reaction to occur at the C-3 position of pyridines, rather than other aromatic C–H bonds, and can be applied to the late-stage halogenation of complex molecules. The mechanistic studies show that the interaction between the pyridine substrate, ether solvent and haleniums plays a dominant role in the reactivity and regioselectivity.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Article and its Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Baumann, M. & Baxendale, I. R. An overview of the synthetic routes to the best selling drugs containing 6-membered heterocycles. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 9, 2265–2319 (2013).
Wurz, R. P. Chiral dialkylaminopyridine catalysts in asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Rev. 107, 5570–5595 (2007).
Sun, H., Keefer, C. E. & Scott, D. O. Systematic and pairwise analysis of the effects of aromatic halogenation and trifluoromethyl substitution on human liver microsomal clearance. Drug Metab. Lett. 5, 232–242 (2011).
Auffinger, P., Hays, F. A., Westhof, E. & Ho, P. S. Halogen bonds in biological molecules. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 48, 16789–16794 (2004).
Josephitis, C. M., Nguyen, H. M. H. & McNally, A. Late-stage C–H functionalization of azines. Chem. Rev. 123, 7655–7691 (2023).
Murakami, K., Yamada, S., Kaneda, T. & Itami, K. C–H functionalization of azines. Chem. Rev. 117, 9302–9332 (2017).
Tagata, T. & Nishida, M. Palladium charcoal-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura coupling to obtain arylpyridines and arylquinolines. J. Org. Chem. 68, 9412–9415 (2003).
Bunnett, J. F. & Zahler, R. E. Aromatic nucleophilic substitution reactions. Chem. Rev. 49, 273–412 (1951).
Fier, P. S. & Hartwig, J. S. Selective C-H fluorination of pyridines and diazines inspired by a classic amination reaction. Science 342, 956–960 (2013).
Levy, J. N., Alegre-Requena, J. V., Liu, R., Paton, R. S. & McNally, A. Selective halogenation of pyridines using designed phosphine reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 11295–11305 (2020).
Zhang, L., Yan, J., Ahmadli, D., Wang, Z. & Ritter, T. Electron-transfer-enabled concerted nucleophilic fluorination of azaarenes: selective C–H fluorination of quinolines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 20182–20188 (2023).
Li, C. et al. Regioselective synthesis of 4-functionalized pyridines. Chem 10, 628–643 (2024).
Sun, G. Q. et al. Electrochemical reactor dictates site selectivity in N-heteroarene carboxylations. Nature 615, 67–72 (2023).
Wubbolt, S. & Oestreich, M. Catalytic electrophilic C–H silylation of pyridines enabled by temporary dearomatization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 15876–15879 (2015).
Zhou, X. Y., Zhang, M., Liu, Z., He, J. H. & Wang, X. C. C3-selective trifluoromethyl thiolation and difluoromethyl thiolation of pyridines and pyridine drugs via dihydropyridine intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 14463–14470 (2022).
Liu, Z. et al. Asymmetric C3-allylation of pyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 11789–11797 (2023).
Larsen, M. A. & Hartwig, J. F. Iridium-catalyzed C–H borylation of heteroarenes: scope, regioselectivity, application to late-stage functionalization, and mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4287–4299 (2014).
Cheng, C. & Hartwig, J. F. Iridium-catalyzed silylation of aryl C–H bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 592–595 (2015).
Yang, L., Uemura, N. & Nakao, Y. meta-Selective C–H borylation of benzamides and pyridines by an iridium–Lewis acid bifunctional catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 7972–7979 (2019).
Petrone, D. A., Ye, J. & Lautens, M. Modern transition-metal-catalyzed carbon–halogen bond formation. Chem. Rev. 116, 8003–8104 (2016).
Saikia, I., Borah, A. J. & Phukan, P. Use of bromine and bromo-organic compounds in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 116, 6837–7042 (2016).
Barluenga, J., González, J. M., Campos, P. J. & Asensio, G. I(py)2BF4, a new reagent in organic synthesis: general method for the 1,2-iodofunctionalization of olefins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 24, 319–320 (1985).
Rodriguez, R. A. et al. Palau’chlor: a practical and reactive chlorinating reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6908–6911 (2014).
Snyder, S. A. & Treitler, D. S. Et2SBrSbCl5Br: an effective reagent for direct bromonium-induced polyene cyclizations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 7899–7903 (2009).
Wang, Y. et al. Discovery of N–X anomeric amides as electrophilic halogenation reagents. Nat. Chem. 16, 1539–1545 (2024).
Wang, W. et al. Catalytic electrophilic halogenation of arenes with electron-withdrawing substituents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 13415–13425 (2022).
Song, S. et al. DMSO-catalysed late-stage chlorination of (hetero)arenes. Nat. Catal. 3, 107–115 (2020).
Mo, F. Y. et al. Gold-catalyzed halogenation of aromatics by N-halosuccinimides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 2028–2032 (2010).
Nishii, Y., Ikeda, M., Hayashi, Y., Kawauchi, S. & Miura, M. Triptycenyl sulfide: a practical and active catalyst for electrophilic aromatic halogenation using N-halosuccinimides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 1621–1629 (2020).
Wang, W. et al. Oxoammonium salts are catalysing efficient and selective halogenation of olefins, alkynes and aromatics. Nat. Commun. 12, 3873 (2021).
Kona, C. N. et al. Aromatic halogenation using carborane catalyst. Chem 10, 402–413 (2024).
Xiong, X. & Yeung, Y. Y. Highly ortho-selective chlorination of anilines using a secondary ammonium salt organocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 16101–16105 (2016).
Eguchi, H. et al. Halogenation using N-halogenocompounds. II. Acid catalyzed bromination of aromatic compounds with 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 67, 1918–1921 (1994).
Prakash, G. K. S. et al. N-halosuccinimide/BF3H2O, efficient electrophilic halogenating systems for aromatics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 15770–15776 (2004).
Fosu, S. C., Hambira, C. M., Chen, A. D., Fuchs, J. R. & Nagib, D. A. Site-selective C–H functionalization of (hetero)arenes via transient, non-symmetric iodanes. Chem 5, 417–428 (2018).
Gupta, S. S., Manisha, Kumar, R., Dhiman, A. K. & Sharma, U. Predictable site-selective functionalization: Promoter group assisted para-halogenation of N-substituted (hetero)aromatics under metal-free condition. Org. Biomol. Chem. 19, 9675–9687 (2021).
Li, J. et al. Photoredox catalysis with aryl sulfonium salts enables site-selective late-stage fluorination. Nat. Chem. 12, 56–62 (2020).
Ni, S. et al. Nickel meets aryl thianthrenium salts: Ni(I)-catalyzed halogenation of arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 9988–9993 (2023).
Cao, H., Cheng, Q. & Studer, A. meta-Selective C-H functionalization of pyridines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202302941 (2023).
Olah, G. A. Aromatic substitution. XXVIII. Mechanism of electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Acc. Chem. Res. 4, 240–248 (1971).
Clososki, G. C., Rohbogner, C. J. & Knochel, P. Direct magnesiation of polyfunctionalized arenes and heteroarenes using (tmp)2Mg·2LiCl. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 7681–7684 (2007).
Murphy, J. M., Liao, X. & Hartwig, J. F. Meta halogenation of 1,3-disubstituted arenes via iridium-catalyzed arene borylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 15434–15435 (2007).
Chen, T. Q. et al. A unified approach to decarboxylative halogenation of (hetero)aryl carboxylic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 8296–8305 (2022).
Boyle, B. T., Levy, J. N., Lescure, L., Paton, R. S. & McNally, A. Halogenation of the 3-position of pyridines through Zincke imine intermediates. Science 378, 773–779 (2022).
Hilton, M. C., Dolewski, R. D. & McNally, A. Selective functionalization of pyridines via heterocyclic phosphonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13806–13809 (2016).
Zhang, X. et al. Phosphorus-mediated sp2–sp3 couplings for C–H fluoroalkylation of azines. Nature 594, 217–222 (2021).
Li, S. et al. C3 selective chalcogenation and fluorination of pyridine using classic Zincke imine intermediates. Nat. Commun. 15, 7420 (2024).
Cao, H., Cheng, Q. & Studer, A. Radical and ionic meta-C–H functionalization of pyridines, quinolines, and isoquinolines. Science 378, 779–785 (2022).
Cao, H., Bhattacharya, D., Cheng, Q. & Studer, A. C–H functionalization of pyridines via oxazino pyridine intermediates: switching to para-selectivity under acidic conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 15581–15588 (2023).
Guo, S.-M., Xu, P. & Studer, A. meta-Selective copper-catalyzed C−H arylation of pyridines and isoquinolines through dearomatized intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202405385 (2024).
Xu, P. et al. Introduction of the difluoromethyl group at the meta- or para-position of pyridines through regioselectivity switch. Nat. Commun. 15, 4121 (2024).
Qin, S. et al. Electrochemical meta-C–H sulfonylation of pyridines with nucleophilic sulfinates. Nat. Commun. 15, 7428 (2024).
Wang, W. J., Song, S. & Jiao, N. Late-stage halogenation of complex substrates with readily available halogenating reagents. Acc. Chem. Res. 57, 3161 (2024).
Yamamoto, H., Zhang, Y. & Shibatomi, K. Lewis acid catalyzed highly selective halogenation of aromatic compounds. Synlett 37, 2837–2842 (2005).
Guan, D., Zhou, A. X., Chen, X. M., Guo, X. & Li, G. T. Method for preparation of nicergoline. CN patent 102,718,761 (2012).
Zhang, P., Liu, R. & Cook, J. M. Regiospecific bromination of 3-methylindoles with N-bromosuccinimide. Tetrahedron Lett. 36, 3103–3106 (1995).
Franck, G., Brill, M. & Helmchen, G. Dibenzo[a,e]cyclooctene: multi-gram synthesis of a bidentate ligand. Org. Synth. 89, 55–65 (2012).
Barluenga, J., González-Bobes, F., Ananthoju, S. R., García-Martín, M. A. & González, J. M. Oxidative opening of cycloalkanols: an efficient entry to ω-iodocarbonyl compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40, 3389–3392 (2001).
Schmid, H. & Leutenegger, W. E. Über die Einwirkung von N-Brom-succinimid auf Acridin. Helv. Chim. Acta 30, 1965–1975 (1947).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the National Key Research and Development Project (grant no. 2023YFF1205103 to S.S.) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 22071005 and 22371007 to S.S.) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L. and S.S. conceived and designed the experiments. X.L. supervised the mechanistic studies. C.L., J.L., Z.W. and D.O. performed the experiments. C.L., J.L., Z.W., D.O., N.J. and S.S. analysed data. C.L., N.J. and S.S. wrote the paper. N.J. and S.S. directed the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Synthesis thanks Xiao-Chen Wang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Thomas West, in collaboration with the Nature Synthesis team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections 1–9, Tables 1–5 and Schemes 1–23.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 5
13C NMR spectroscopy data for Fig. 5b,c.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Li, X., Li, J. et al. Direct regioselective C-3 halogenation of pyridines. Nat. Synth 5, 36–45 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-025-00915-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-025-00915-3
This article is cited by
-
meta-Selective radical halogenation of pyridines
Nature Synthesis (2026)