Abstract
Land cover conversions (LCC) have substantially reshaped terrestrial carbon dynamics, yet their net impact on carbon sequestration remains uncertain. Here, we use the remote sensing-driven BEPS model and high-resolution HILDA+ data to quantify LCC-induced changes in net ecosystem productivity (NEP) from 1981 to 2019. Despite global forest loss and cropland/urban expansion, LCC led to a net carbon gain of 229 Tg C. Afforestation and reforestation increased NEP by 1559 Tg C, largely offsetting deforestation-driven losses (−1544 Tg C), with newly established forests in the Northern Hemisphere driving gains that counterbalanced emissions from tropical deforestation. Regional carbon gains were concentrated in East Asia, North America, and Europe, while losses occurred mainly in the Amazon and Southeast Asia. Although smaller in area, newly established forests exhibited higher sequestration efficiency than degraded older forests, emphasizing the role of forest age in shaping global carbon sink dynamics. These findings highlight the critical importance of afforestation, forest management, and spatially informed land-use strategies in strengthening carbon sinks and supporting global carbon neutrality goals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Since the industrial revolution, massive burning of fossil fuels and land use activities have led to a surge in atmospheric levels of greenhouse gases, particularly CO21. As the world’s primary carbon sink, terrestrial ecosystems have captured about 20% of carbon dioxide (CO2) from anthropogenic emissions during the past three decades2,3. Land cover conversions (LCC) driven by anthropogenic land use modifications and natural disturbances constitutes one of the most dynamic components of global environmental change. Such alterations directly disrupt terrestrial ecosystem functions, with cascading implications for global carbon cycling. Notably, Land use/cover changes has exerted a profound influence on carbon sequestration dynamics4, with deforestation and forest degradation accounting for approximately one-third of anthropogenic carbon emissions since the industrial revolution5. Conversely, mitigation measures such as afforestation initiatives demonstrate the potential to amplify terrestrial carbon sinks and enhance atmospheric CO2 absorption6. The quantification of carbon sink dynamics in terrestrial ecosystems relies on bioproductivity parameters, among which Net Ecosystem Productivity (NEP) serves as a critical metric for assessing net carbon flux between terrestrial systems and the atmosphere7. NEP is mathematically defined as the residual of carbon assimilation through vegetation photosynthesis minus carbon losses from autotrophic respiration (RA) in plants and heterotrophic respiration (RH) in soil microbial communities8. Elucidating LCC-induced NEP variations is therefore imperative for advancing mechanistic understanding of ecosystem functional responses to environmental perturbations, and reducing uncertainties in modeling global and regional carbon budgets. This dual focus holds particular relevance for informing evidence-based climate mitigation strategies.
Significant spatial heterogeneity exists in LCC across various countries. Robust assessment of LCC-induced NEP variations demands modeling frameworks that explicitly resolve both spatial gradients and temporal trajectories of land surface transformations. Current mainstream methodologies, however, exhibit critical limitations in addressing this complexity. Bookkeeping models, which dominate historical carbon budget assessments, employ straightforward accounting principles by integrating static carbon density coefficients with land use/cover change areas derived from forest inventories or aggregated statistics9,10. While offering computational efficiency and policy-relevant simplicity, these models fail to incorporate transient ecosystem responses to environmental changes and lack the spatial resolution needed to capturing fine-scale LCC dynamics, thus partly ignoring spatial heterogeneity and propagating biases in carbon flux estimations. Process-based dynamic global vegetation models (DGVMs) provide physiological mechanisms by simulating coupled biogeochemical cycles across climate-vegetation-soil continua11,12. Despite their capacity to account for environmental effects on temporal carbon stock evolution, practical constraints persist: (1) Typical spatial resolutions (0.25°–2°) remain insufficient to resolve landscape-level LCC patterns; (2) Dependence on harmonized high-quality inputs restrict their ability to resolve fine-scale LCC effects. These dual limitations—oversimplification in bookkeeping models versus coarse resolutions and implementation barriers in DGVMs, have sustained persistent uncertainties in LCC-attributed carbon flux estimates.
Satellite remote sensing has emerged as a transformative tool for providing spatially consistent coverage of land conditions and vegetation status, with both high spatial detail and temporal frequency critical for resolving fine-scale ecosystem dynamics13. Remote sensing driven ecosystem models enable high-resolution tracking of NEP responses to LCC while incorporating ground-truthed vegetation information, a synergy that significantly reduces uncertainties inherent in conventional carbon flux estimations. Pioneering applications, such as the Coupled Carbon-Water (CCW) model leveraging photosynthetic indices from satellite retrievals to quantify U.S. LCC-induced GPP changes14, and Carnegie-Ames-Stanford Approach (CASA) model assessing LCC-induced NEP changes in Northwest China15, demonstrate the method’s capability to resolve regional heterogeneity. However, there remains a dearth of global-scale implementations. Furthermore, conventional remote sensing-based ecological models predominantly employ light-use efficiency (LUE) paradigms that derive GPP estimates from canopy-absorbed radiation and predefined LUE parameters. These formulations typically disregard crucial physiological regulators such as CO2 fertilization effects and nutrient effects16, while oversimplifying environmental controls to climate variables alone. Moreover, existing investigations have predominantly concentrated on carbon flux quantification within either individual ecosystem types (e.g., rice paddies, grasslands, or forests) or undifferentiated composite systems, but comparisons of the conversions between different ecosystems (land covers) are lacking. This knowledge gap substantially impedes the formulation of spatially optimized land management strategies tailored to specific ecological contexts.
This study aimed to investigate the impacts of global LCC, particularly across different conversion types, on NEP during 1981–2019. To achieve accurate quantification of LCC-induced NEP changes and delineate their spatial heterogeneity, we employed the high-resolution Historic Land Dynamics Assessment + (HILDA + ) dataset within the Biosphere-atmosphere Exchange Process Simulator (BEPS) model framework. The HILDA+ dataset, developed through a data-driven reconstruction approach, synergistically integrates multi-source open data streams including high-resolution remote sensing observations, long-term land use reconstructions, and statistical records. As a global-scale product with 0.01° × 0.01° spatial resolution encompassing major LCC categories over six decades (1960–2019), it provides optimal forcing data for carbon cycle modeling. The BEPS model, a process-based diagnostic framework operating at 0.073° × 0.073° resolution, which mechanistically includes the impacts of various drivers on gross primary productivity (GPP) (climate, CO2 concentration, and nitrogen deposition) and assimilates vegetation structure (LAI) satellite data, has demonstrated robust capability in terrestrial carbon sink monitoring17. Specifically, this research addresses three primary objectives: (1) to characterize the spatiotemporal patterns of global LCC from 1981 to 2019; (2) to quantify the effects of various land cover conversions on NEP at global and national scales; and (3) to discuss land management strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration based on LCC-induced NEP results. By addressing these scientific questions, our study would provide insights into dominant patterns of LCC-driven carbon flux variations, thereby advancing understanding of terrestrial carbon cycle dynamics and informing the development of carbon-neutral policies through optimized land management practices.
Results
General patterns of land cover conversions from 1981 to 2019
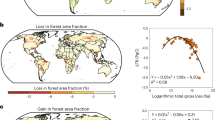
Global land cover has experienced significant and accelerating transformations since 198118, as evidenced by the HILDA+ land cover dataset (Fig. 1). During the 1981–2019 period, forest coverage exhibited a gross gain of 26.4 × 105 km2 and a gross loss of 34.3×105 km2, resulting in a net decline of 7.9 × 105 km2. Cropland expanded by 7.1 × 105 km² (gross gain: 27.2 × 105 km2; loss: 20.1 × 105 km2). Pasture areas decreased by 3.6 × 105 km² (gross gain: 39.0 × 105 km2; loss: 42.6 × 105 km2). Grassland/shrubland areas showed a net gain of 15.5 × 105 km2 (gross gain: 43.8 × 105 km2; loss: 28.3 × 105 km2). Urban areas expanded by 3.9 × 105 km2, while other land category contracted by 15.0 × 105 km². These patterns align with established trends of forest canopy loss, as corroborated by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) reports documenting 12.9 × 105 km2 net forest loss from 1990 to 201519. Land cover conversions primarily involved bidirectional conversions among forest, cropland, pasture, and grassland/shrubland categories, with forest and pasture reductions predominantly driven by conversion to cropland and grassland/shrubland.
Annual area variations of six land cover categories: a forest, b cropland, c pasture, d grass/shrubland, e urban, and f other land. The vertical axis represents the annual areal change relative to the 1981 baseline (unit: 105 km2), where positive values indicate gain through conversion to the focal category and negative values denote loss via conversion from the category. Blue and red lines respectively represent gross gains (total area converted into the category) and gross losses (total area converted out), with the purple line showing net change (gains minus losses).
Spatiotemporal analysis of fractional land cover conversions reveals substantial geographic heterogeneity (Figs. S1–S2). From 1981 to 2019 at a spatial resolution of 0.073°, 58.7% of global land surfaces experienced measurable LCC, with 30.1%, 19.1%, 12.8%, and 5.7% of terrestrial areas exceeding 10%, 20%, 30%, and 50% change magnitudes, respectively. Major LCC hotspots emerged in Australia, China, Europe, the United States, and tropical rainforest regions. Forest regeneration predominated in northern temperate and boreal zones, while tropical regions accounted for disproportionate deforestation. This spatial dichotomy explains the global net forest loss, as gains in temperate/boreal forests failed to offset tropical deforestation. Such geographic disparities highlight the complex interplay between regional land-use practices and biome-specific drivers of land cover modification.
Global NEP change patterns driven by LCC
LCC exerted substantial and spatially heterogeneous impacts on global terrestrial carbon sequestration (Fig. 2a). During 1981–2019, 31.3% of global land areas experienced LCC-induced increases in NEP, with pronounced spatial clustering in Europe, central-southern China, the southeastern United States, northern Russia, and India. Conversely, 26.8% of terrestrial regions exhibited NEP reductions attributable to LCC, predominantly concentrated in southern hemisphere tropics and humid zones, including Brazil, Indonesia, and southeastern Australia. Spatiotemporal analysis revealed that 36.9% of global lands underwent moderate LCC-induced NEP changes (±30 g C m⁻² yr⁻¹), while over 9.3% exhibited substantial changes exceeding ±100 g C m⁻² yr⁻¹. Although multiple drivers—including climate change, CO₂ fertilization, and nitrogen deposition—modulate terrestrial carbon fluxes17,20, LCC independently exerted significant influence on NEP dynamics (Fig. 2b). Notably, LCC contributed >10% of total NEP changes across 25.7% of global lands (14.1% exhibiting positive impacts; 11.6% negative impacts), with 12.1% of areas showing >40% LCC-induced NEP changes (6.7% positive; 5.4% negative).
a Maps the spatial distribution of LCC-induced NEP changes, while b illustrates the proportional contribution of LCC to total NEP variations. The histogram denotes area proportion; c statistically resolves interannual trends, with solid blue and red curves representing annual and accumulative LCC-induced NEP changes, respectively, complemented by dashed polynomial regression line characterizing decadal-scale trajectories.
Temporal analysis delineates a dynamic LCC-NEP relationship characterized by phase transitions (Fig. 2c). Initial LCC impacts (1980s–2000s) predominantly reduced NEP, with interannual compensation between carbon gains and losses yielding minimal accumulative effects. Subsequent decades witnessed a progressive shift toward net NEP enhancement, potentially linked to expanding spatial extents of land cover conversions and large-scale afforestation initiatives in northern hemisphere temperate zones21. However, given the persistent global net forest decline with no abrupt forest area variations (Fig. 1a), we hypothesize that newly established forests gradually offset carbon losses from degraded older forests. The observed temporal transition likely reflects accelerated carbon sequestration capacity in maturing regenerated forests, which eventually surpassed legacy carbon losses by old destroyed forests. Detailed analyses of these compensatory dynamics will be elaborated in the Discussion section.
Regional and categorical variations in LCC-induced NEP changes
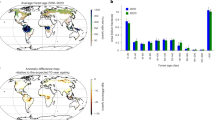
Given the spatial heterogeneity of LCC patterns (Figs. S1–S2), a comprehensive analysis was conducted to quantify LCC-induced NEP changes at national/regional scales and across land conversion types (Fig. 3 and Fig. S3). Globally, accumulative absolute NEP changes attributable to LCC during 1981–2019 amounted to 4061 Tg C, comprising a 2145 Tg C increase and a 1916 Tg C decrease, yielding a net terrestrial carbon sequestration gain of 229 Tg C. Forest-related conversions emerged as the dominant driver, accounting for 81% of total NEP reductions induced by all conversions of LCC. Specifically, conversions of forest to cropland, pasture, and grass/shrubland decreased carbon sequestration by 402 Tg C, 595 Tg C, and 429 Tg C, respectively. Conversely, afforestation/reforestation activities which constituted 72.7% of total NEP gains, enhanced carbon sequestration by 452 Tg C (cropland-to-forest), 736 Tg C (pasture-to-forest), and 360 Tg C (grass/shrubland-to-forest). Notably, cropland-to-grass/shrubland conversions also contributed significantly, increasing NEP by 230 Tg C, underscoring the importance of non-forest vegetation conversions in regional carbon budget dynamics.
Deforestation (conversions from forests to other lands) exerted pronounced negative impacts on NEP in tropical rainforest regions, particularly across southeast Asia and south America (Fig. 3 and Fig. S3). Indonesia exhibited the most severe LCC-induced NEP decline, losing 278 Tg C during 1981–2019 due to extensive deforestation activities such as large-scale deforestation including coastal peatland drainage, montane rainforest logging, and agricultural expansion22,23. These activities precipitated forest-to-grass/shrubland (–101 Tg C) and forest-to-cropland (–73 Tg C) conversions, with urban sprawl24 further reducing NEP by 67 Tg C. Brazil ranked second in carbon sequestration losses (–157 Tg C), predominantly due to Amazonian forest-to-pasture conversion (-109 Tg C)—a consequence of synergistic pressures from fossil fuel extraction logging25, agricultural expansion26, and infrastructure development27. Similarly, the Democratic Republic of Congo also experienced substantial NEP reductions (–120 Tg C) linked to persistent deforestation.
Conversely, northern temperate zones demonstrated robust LCC-induced NEP enhancements, with Europe (+310 Tg C), the United States (+220 Tg C), China (+215 Tg C), Russia (+143 Tg C), and India (+135 Tg C) emerging as primary beneficiaries (Fig. 3). Afforestation/reforestation (conversions from other lands to forests) notably pasture-to-forest conversions—accounted for 64.5%, 63.7%, and 30.5% of national NEP gains in China, the U.S., and Europe, respectively. Recent studies confirmed that the carbon sequestration during the 2000s was partially due to afforestation and forest regrowth in East Asia and Europe28,29. European cropland/pasture-to-grass/shrubland conversions further contributed 24.9% of regional NEP increases. Russia’s gains stemmed predominantly from grass/shrubland-to-forest (56.7%) and cropland-to-forest (40.1%) conversions, which is likely a result of the shift from a state command to a market-driven economy after 1990, leading to widespread abandonment of agricultural land, including both cultivated areas and grasslands30,31. India’s NEP improvement derived largely from policy-driven cropland-to-forest and cropland-to-grass/shrubland conversions under afforestation and agricultural intensification initiatives32.
Globally, forest dynamics dominated LCC-induced NEP variations, characterized by contrasting hemispheric patterns: northern afforestation/reforestation versus tropical deforestation. Newly established forests increased accumulative NEP by 1559 Tg C (38.4% of total LCC-driven absolute change), while deforestation reduced accumulative NEP by 1544 Tg C (38.0% of total LCC-driven absolute change). Crucially, carbon sequestration gains from afforestation/reforestation effectively offset 97.8% of deforestation-induced losses. These findings underscore the pivotal role of forest transition pathways in mediating terrestrial carbon budget responses to anthropogenic land use. Our national-scale analysis of linkages between net area changes in four primary land categories (forest, cropland, pasture, and grass/shrubland) and accumulative LCC-induced net NEP changes (Fig. S4) revealed distinct patterns: young forest area increase exhibited a strong positive correlation with carbon sequestration (r = 0.71, P < 0.01), while cropland area conversions correlated negatively with NEP changes (r = –0.65, P < 0.01). Conversely, no statistically significant relationships emerged between LCC- induced carbon sequestration dynamics and area changes in pasture or grass/shrubland (P > 0.05). These results collectively demonstrate that terrestrial carbon flux responses to LCC at the national scale are predominantly mediated by forest and cropland conversion, with marginal contributions from pasture or grass/shrubland conversions.
Discussion
Comparison with TRENDY ensemble simulations
To assess the capability of land surface models in reproducing fine-resolution NEP variations driven by LCC, we performed a systematic comparison of outputs from 17 dynamic global vegetation models (DGVMs) within the TRENDYv10 ensemble. Our analysis revealed substantial inter-model variability among TRENDY simulations, with only 10 of 17 models successfully capturing the globally positive LCC effects (Fig. S7). Although the multi-model mean demonstrated an overall positive LCC influence, the aggregated accumulative LCC-induced NEP changes (76 Tag C) were markedly lower than those simulated by the BEPS model (229 tag C). This discrepancy is particularly noteworthy given that TRENDY ensemble results from the primary basis for the Global Carbon Budget estimates, which exhibit considerable uncertainties in quantifying LCC-related carbon fluxes33. The observed divergence between TRENDY and BEPS simulations may stem from fundamental differences in model structural frameworks, or implementation of LCC effects - where TRENDY models incorporate both land-use change and management practices, while BEPS specifically focuses on land cover modifications. Furthermore, the BEPS model integrates satellite-observed vegetation leaf area index data, enabling more realistic representation of vegetation dynamics through parameters such as forest age. This critical factor, which has been empirically demonstrated to significantly influence carbon sink capacity, remains unaccounted for in current TRENDY model parameterizations. Our findings highlight a substantial uncertainty source in global carbon balance assessments, particularly regarding the quantification of LCC impacts on terrestrial carbon fluxes. This methodological discrepancy warrants urgent attention in future model development and carbon budget estimations, as current DGVM ensembles may systematically underestimate LCC-induced carbon dynamics through inadequate representation of key ecological processes.
Newly established forests predominantly drove LCC-induced NEP changes
This study employed the remote sensing-driven BEPS carbon model and HILDA+ land cover dataset to investigate the impacts of LCC on NEP at global and regional scales from 1981 to 2019. Despite a global decline in forest area during this period (Fig. 1), LCC exerted an overall positive contribution to global NEP changes (Fig. 3). Afforestation/reforestation induced an accumulative carbon sequestration increase of 1559 Tg C, which surpassed deforestation-driven carbon losses (1544 Tg C). We hypothesize that this net gain arises from the enhanced carbon sequestration capacity of newly established forests outweighing the losses from older forest degradation, highlighting the critical role of forest age dynamics. Forest age is a pivotal intrinsic factor governing carbon sequestration rates and storage34, primarily through its regulation of maximum light-use efficiency35. For instance, a study found that NPP in temperate and boreal forests exhibits an age-dependent trajectory following stand-replacing disturbances: NPP initially rises, peaks at maturity, and subsequently declines with aging36. Furthermore, unmanaged old-growth forests may even transition into carbon sources37. To investigate whether our conclusions were similarly attributable to forest age, we analyzed the relationship between changes in NEP resulting from forest changes and forest age.
Spatial analysis revealed that newly established forests predominantly occur in northern temperate regions, where forests are relatively young (mostly <90 years; Fig. S5), whereas forest losses concentrate in tropical zones with older forests (often >210 years). Statistically, the mean forest age in afforested areas (73 years) was substantially lower than in deforested regions (160 years; Fig. 4a). Quantitatively, forest gain elevated accumulative NEP by 281 g C/m² during 1981–2019, while forest loss reduced it by 192 g C/m² (Fig. 4b). This disparity underscores the superior carbon sequestration efficiency of younger forests compared to older ones, consistent with established forest age–carbon flux relationships36,37,38. Temporal analysis of annual NEP changes induced by forest gain/loss (Fig. S6) demonstrated that carbon gains from afforestation were initially outweighed by deforestation losses before around 2010s, after which afforestation benefits dominated. This temporal pattern mirrors the documented parabolic relationship between forest age and carbon sequestration. Specifically, studies indicate that afforestation initially yields near-neutral NEP values, reflecting ecosystems acting as weak carbon sources or sinks during early stages. NEP then escalates to a peak within 10–20 years post-afforestation38, consistent with our findings (Fig. S6). This explains the delayed emergence of net LCC-induced NEP increases around the 2010s (Fig. 2c). Collectively, our results indicate that the carbon sequestration advantage of younger forests, despite their smaller spatial extent, compensates for the larger-scale loss of older, less efficient carbon sinks. These findings provide macro-scale validation of prior research on carbon flux–forest age relationships.
Currently, approximately one-third of forests are under 20 years old, including extensive woody regrowth in post-abandonment European lands39 and large-scale afforestation initiatives in China and India32. These young forests, if sustainably managed, hold significant potential to amplify global carbon sequestration in the coming decades. Their ongoing maturation could counterbalance carbon losses from aging forests, particularly in tropical regions, emphasizing the need for age-informed forest conservation and restoration strategies to optimize climate mitigation outcomes.
Implications for boosting terrestrial carbon sequestration
According to the 2023 Global Carbon Neutrality Annual Progress Report, over 130 countries worldwide have made commitments to carbon neutrality (http://cntracker.jafly.net/report). To achieve carbon neutrality goals, diverse strategies such as harnessing renewable energy resources40, transforming food systems41, and implementing carbon capture and storage42, have been explored or implemented. Land-based carbon sequestration, particularly through afforestation/reforestation to enhance terrestrial carbon sinks, is considered a reliable and cost-effective approach43 and plays a pivotal role in this effort44. However, based on HILDA+ data, recent land cover conversion patterns, marked by continuous forest loss and urban/cropland expansion, appear to contradict this objective. Given the critical importance of carbon neutrality for ecological civilization and human development, nations must urgently adopt effective land-use strategies to reverse this trend.
Our findings reveal that conversions between forests and other land types during 1982–2019 dominated global LCC-induced NEP changes. Although afforestation/reforestation contributed to a substantial accumulative carbon sequestration gain (1,559 Tg C), this was nearly offset by deforestation-driven losses (−1,544 Tg C), indicating that destructive ecological exploitation persists in many regions despite proactive carbon sink policies elsewhere. If these regions implement climate action measures, terrestrial carbon sink capacity could significantly improve. Tropical rainforest nations, such as Indonesia, Brazil, and Colombia, which face the highest deforestation rates, must prioritize forest restoration through natural regeneration, native/commercial forest plantations45,46, and protected area establishment25. Local policies such as granting indigenous land rights or incentivizing sustainable logging in restored forests are critical46. While moderate logging can enhance old forest productivity by increasing structural complexity47, severe destruction must be prevented, as it sharply reduces ecosystem productivity and prolongs recovery48. Additionally, unmanaged old-growth forests may transition into carbon sources37, but their clearance reduces carbon stocks, which may re-enter the atmosphere as CO249. Thus, old forest harvesting must be carefully regulated, considering local ecological resilience and socioeconomic conditions. For newly afforested stands, rapid carbon sequestration growth suggests timber harvests should occur post-maturity to maximize benefits. Further research is needed to refine region-specific carbon flux–forest age relationships for optimal management.
Our results also highlight the national-level significance of cropland area changes in LCC-induced NEP changes (Fig. S4). Global agricultural expansion has driven substantial deforestation (Fig. S1). Although only a small fraction of cropland-absorbed carbon remains stored post-harvest50, enhancing productivity within existing croplands can mitigate ecological losses from expansion. Intensified agricultural management is key, endorsed by researchers and policymakers for its potential to reduce cropland area51,52. For instance, Brazil’s focus on soybean expansion in existing livestock areas could prevent deforestation while achieving 162 Mt production53, and India’s agricultural intensification has significantly boosted cropland greenery32. Practices like improved field management, crop rotation, reduced tillage, straw returning, and organic fertilization further enhance cropland carbon sequestration54,55.
Uncertainties
While our study provides a spatially explicit assessment of LCC-induced NEP changes using a high-resolution, satellite-constrained carbon flux dataset, it does not quantify uncertainty ranges, as the analysis is based on a single set of model outputs and land cover trajectories. As such, the reported values should be interpreted as deterministic estimates conditional on the input data. Future research incorporating multiple LCC scenarios, ensemble simulations, or observational constraints would help to further evaluate the robustness of these estimates.
This study isolated LCC-induced NEP changes by designing two scenarios with either fixed or dynamic land cover data relative to the initial year. We explored the results from the forest age perspective, analyzing why carbon sequestration gains from smaller areas of newly established forests outweigh losses caused by old forest depletion. Although forest age is not directly parameterized in the model, we contend that age-dependent effects are implicitly captured through remote sensing-derived leaf area index (LAI) data. Since LAI is intrinsically linked to forest developmental stages (and thus age), its integration into the BEPS model indirectly accounts for age-related physiological and structural changes. Hense, by leveraging LAI, the model inherently reflects forest age dynamics, albeit through proxy mechanisms. We therefore posit that the BEPS framework, grounded in remote sensing observations, can reasonably capture age-driven variations in carbon sequestration capacity, even in the absence of explicit age parameterization. Future studies could prioritize integrating forest age parameters into the BEPS model to comprehensively evaluate age effects on carbon sequestration, which warrants further investigation.
Methods
BEPS model overview
The Biosphere-atmosphere Exchange Process Simulator (BEPS) was renamed from the Boreal Ecosystem Productivity Similator, which was initially developed for boreal ecosystems56,57, but was subsequently expanded to all ecosystems of the globe58. BEPS is a process-based diagnostic model driven by climate, remotely sensed vegetation parameters (LAI), clumping index, land cover, and soil data. BEPS adopts the sunlit-shaded leaf stratification strategy in modeling canopy-level photosynthesis. It includes a photosynthesis module56, a land surface scheme for the computations of energy and water balance59, and a soil biogeochemical module for soil carbon, nitrogen, and heterotrophic respiration calculations based on a modified Century model60. NEP is calculated as the difference between photosynthesis and respiration:
where \({GPP}\) is the gross primary productivity, \({AR}\) and \({HR}\) are autotrophic respiration and heterotrophic respiration, respectively. For the calculation of GPP, BEPS uses a two-leaf canopy photosynthesis model56:
where \({{GPP}}_{{sun}}\) and \({{GPP}}_{{shaded}}\) are the \({GPP}\) per unit area of sunlit and shaded leaves, respectively. \({{LAI}}_{{sun}}\) and \({{LAI}}_{{shaded}}\) are the \({LAI}\) of sunlit and shaded leaves respectively, and are calculated as:
where \(\varOmega\) is the clumping index and \(\theta\) is the daily mean solar zenith angle. GPP values of sunlit and shaded leaves are calculated using Farquhar’s leaf biochemical model. This model can be combined with a physical model describing the CO2 flow from the free air to the inside of the stomatal cavity for sunlit and shaded leaves separately56,61. The simulated annual NEP by BEPS closely follows the trend and interannual variability of the residual land sequestration estimated by the Global Carbon Project17. Figure S8 illustrates the comparison between the simulated land sequestration from the BEPS model and that from 17 Trendy models, which demonstrates a substantial concordance in interannual variability between the BEPS and Trendy models simulation.
Carbon cycle modeling methods
BEPS includes modules to calculate AR and HR62, the biomass carbon stock is stratified into four pools (leaf, stem, root, and fine root pools), and the soil carbon stock into nine pools (surface structural litter, surface metabolic litter, soil structural litter, soil metabolic litter, coarse woody litter, surface microbe, soil microbe, slow, and passive carbon pools). These carbon pools are initially determined for the year 1901 by solving a set of equations describing the dynamics of carbon pools under the assumption that the carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystems was in dynamic equilibrium at that time63. Then, for the period from 1901 to 1980, we run the model using historical data on climate, LAI, CO2 concentration, and nitrogen deposition. Due to a lack of data, we assumed that LAI in 1982–1986 represented that in 1901–1981. Simulations suggest that the impact of LAI changes prior to 1981 on the role of LAI after 1981 was just within a few percent17. In this model, AR is divided into maintenance respiration and growth respiration. Maintenance respiration depends on foliage, stem and root biomass, and temperature, whereas growth respiration is calculated as 25% of GPP. HR is computed as the sum of C released to the atmosphere during the decomposition of five litter (surface structural litter, surface metabolic litter, soil structural litter, soil metabolic litter, and coarse woody litter) and four soil C (surface microbe, soil microbe, slow, and passive) pools, i.e.
where \({{\rm{\tau }}}_{{\rm{j}}}\) is a respiration efficiency equal to the percentage of decomposed \({\rm{C}}\) released from pool j to the atmosphere, \({{\rm{k}}}_{{\rm{j}}}\) the decomposition rate of \({\rm{C}}\) pool j and \({{\rm{C}}}_{{\rm{j}}}\) is the size of pool j and is updated at each time step.
Input data for the BEPS model
The input data include LAI, meteorological data, soil data, nitrogen deposition, and CO2 data. LAI data were from GIMMS LAI4g product64. The spatial resolution of the LAI series was 0.0833° × 0.0833°. Meteorological data included daily maximum and minimum temperatures, downward solar radiation, relative humidity, and precipitation, which were interpolated from the 0.5° × 0.5° CRUNCEP V8.0 dataset. Except for relative humidity, which is calculated from temperatures, specific humidity, and pressure, other meteorological data are directly retrieved from the CRUNCEP V8.0 dataset. The soil data are fractions of clay, silt, and sand, and were retrieved from the harmonized global soil database (http://www.fao.org/nr/lman/abst/lman_080701_en.htm). Nitrogen deposition data were estimated from tropospheric NO2 column density retrieved from the Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment and Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer65.
Land cover data
We used HILDA+ land cover data with 1 km resolution to investigate the impact of LCC on NEP. Compared to higher-resolution remote sensing datasets such as Hansen Global Forest Change (GFC; 2000–2020), ESA Climate Change Initiative (CCI; 1992–2020), and MODIS (2001–present), HILDA+ offers an extended temporal coverage (1960–2019), which critically supports our long-term carbon sequestration analysis spanning 1981–2019. The dataset was generated by integrating remote sensing, land use reconstructions, and statistics, and has been confirmed to be reliable. Since HILDA + is built on multiple heterogeneous datasets, errors inherent in single datasets are attenuated during the change allocation procedure18. HILDA+ land cover categories include urban, cropland, pasture, other forest, evergreen coniferous forest, deciduous coniferous forest, evergreen broad-leaved forest, deciduous broad-leaved forest, mixed forest, grass/shrubland, and other land. In order to match the plant function types of NEP in the BEPS simulation, we consider other forest in HILDA+ as mixed forest and grass/shrubland as sparse shrubland. For the analysis of annual global land cover dynamics, we generated land conversion matrices (1982–2019 relative to 1981) at a spatial resolution of 0.073°. These matrices quantify pixel-level conversion probabilities between distinct land cover types from the baseline year (1981) to each subsequent year, enabling systematic tracking of interannual conversion patterns.
Calculation of BEPS NEP changes caused by LCC
We employed the BEPS model to estimate of annual NEP associated across13 plant function types (evergreen coniferous forest, deciduous coniferous forest, evergreen broad-leaved forest, deciduous broad-leaved forest, mixed forest, wooden savanna, savanna, closed shrubland, sparse shrubland, grassland, cropland, and other vegetation). To isolate NEP changes driven by LCC, we conducted two simulations, S1, which fixed land cover at the 1981 baseline while allowing other variables (e.g., climate, CO₂) to vary temporally, and S2, which incorporated both dynamic drivers and land cover conversions. The LCC-induced NEP changes were quantified as the difference between S2 and S1 outputs. To attribute NEP responses to specific land cover conversions, we first derived annual land conversion matrices (1982–2019 relative to 1981) at a 0.073° spatial resolution, calculating pixel-level conversion percentages \({{Trans}}_{{year},\,i\to j}\) between land cover types from \({{LC}}_{i}\) to \({{LC}}_{j}\) between the initial year 1981 and dynamic year. For each grid cell, the annual NEP change associated with a specific conversion (\({{LC}}_{i}\to {{LC}}_{j}\)) was computed as:
where \({S1}_{{year},i}\) and \({S2}_{{year},\,j}\) represent NEP estimates for \({{LC}}_{i}\) and \({{LC}}_{j}\) under their respective simulations. Cumulative cell-level NEP changes over the study period were aggregated as:
Regional LCC-induced NEP changes were then scaled spatially by summing grid-cell contributions weighted by their areas:
where \({A}_{{cell}}\) is the latitude-adjusted grid cell area, calculated to account for earth’s curvature using:
where \(R\) is the Earth radius, \({{lat}}_{2}\), \({{lat}}_{1}\), \({{lon}}_{2}\) and \({{lon}}_{1}\) are the values of the boundary of the grid \({A}_{{cell}}\).
Simulations of Trendy models. To evaluate the capacity of DGVMs in replicating fine-resolution LCC-driven NEP changes identified through our analysis, we conduct a comparative analysis of outputs from 17 DGVMs (TRENDYv10)66. The evaluated DGVM ensemble comprises CABLE-POP, CLASSIC, CLASSIC-N, CLM5.0, DLEM, IBIS, ISAM, ISBA-CTRIP, JSBACH, LPJ-GUESS, LPJ, OCN, ORCHIDEE, ORCHIDEEv3, SDGVM, VISIT, and YIBs. These models principally utilize the HYDEv3.3 historical land-use dataset67, offering global-scale annual agricultural extent mapping with enhanced spatial allocation of farming systems. Supplementary implementations in six models (CABLE-POP, CLM5.0, JSBACH, LPJ-GUESS, LPJ, and VISIT) incorporate the LUH2-GCB2021 harmonized transition dataset68, which resolves sub-grid land conversion dynamics. The method derives LCC-specific NEP responses through differential analysis of two simulation scenarios: S3 (incorporating transient CO2, climate, and land use forcings) and S2 (maintaining static land use with transient CO2/climate conditions). Modeled NEP values were computed as the difference between net primary productivity (NPP) and heterotrophic respiration (Rh) outputs. All simulations were conducted at 1° spatial resolution. Given that TRENDY protocols integrate both land-use modifications and management practices across stable land cover regions - factors beyond the scope of our HILDA + -based LCC analysis, our evaluation was constrained to areas exhibiting detectable LCC in the HILDA + . To address resolution inconsistencies between the original 0.073° HILDA+ and the 1° DGVM outputs, we implemented a modal aggregation that resamples HILDA+ to 1° spatial resolution using majority-voting cell assignment.
Forest age map
This investigation employed a globally gridded forest age dataset (circa 2010 reference year), synthesized through multivariate integration of national forest inventories, aboveground biomass observations, and bioclimatic parameters69. This dataset offers a comprehensive estimation of global forest age at a resolution of 1 km, with a notable precision of 0.81 and 0.99 for distinguishing between old-growth and non-old-growth forests, respectively. To reconstruct annual forest age dynamics from 1982 to 2019, we implemented annual temporal adjustments through linear extrapolation of the 2010 baseline values. Specifically, forest age estimates were calculated using temporal offsets relative to the reference year:
where positive temporal offsets (t > 2010) represent additive adjustments and negative offsets (t < 2010) denote subtractive corrections. Resultant negative age values were constrained to zero. Spatial harmonization with BEPS model outputs was achieved through bilinear interpolation resampling.
Data availability
The HILDA+ dataset, providing global land cover information, is available at https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.921846. The global forest age map can be accessed from https://www.bgc-jena.mpg.de/geodb/projects/Data.php. The TRENDYv10 ensemble carbon sink simulations are available at https://zenodo.org/records/6884342. The BEPS model-derived NEP estimates, along with reanalysis outputs, have been deposited in Zenodo and are publicly accessible at https://zenodo.org/records/15760904.
Code availability
The primary data analysis code used in this study is available on Zenodo (https://zenodo.org/records/15760904). The BEPS model code is not publicly available due to development constraints; however, interested researchers may contact the corresponding author to discuss potential access.
References
Lonngren, K. E. & Bai, E.-W. On the global warming problem due to carbon dioxide. Energy Policy 36, 1567–1568 (2008).
Le Quéré, C. et al. Global carbon budget 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 10, 2141–2194 (2018).
Pan, Y. et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 333, 988–993 (2011).
Yang, Y. et al. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 861–895 (2022).
Houghton, R. & Hackler, J. Emissions of carbon from forestry and land-use change in tropical Asia. Glob. Change Biol. 5, 481–492 (1999).
Rohatyn, S., Rotenberg, E., Tatarinov, F., Carmel, Y. & Yakir, D. Large variations in afforestation-related climate cooling and warming effects across short distances. Commun. Earth Environ. 4, 18 (2023).
Arneth, A., Kelliher, F., McSeveny, T. & Byers, J. Net ecosystem productivity, net primary productivity and ecosystem carbon sequestration in a Pinus radiata plantation subject to soil water deficit. Tree Physiol. 18, 785–793 (1998).
Zhao, J., Ma, J. & Zhu, Y. Evaluating impacts of climate change on net ecosystem productivity (NEP) of global different forest types based on an individual tree-based model FORCCHN and remote sensing. Glob. Planet. Change 182, 103010 (2019).
Houghton, R. A. & Nassikas, A. A. Global and regional fluxes of carbon from land use and land cover change 1850–2015. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 31, 456–472 (2017).
Baccini, A. et al. Estimated carbon dioxide emissions from tropical deforestation improved by carbon-density maps. Nat. Clim. Change 2, 182–185 (2012).
Arneth, A. et al. Historical carbon dioxide emissions caused by land-use changes are possibly larger than assumed. Nat. Geosci. 10, 79–84 (2017).
Pugh, T. et al. Simulated carbon emissions from land-use change are substantially enhanced by accounting for agricultural management. Environ. Res. Lett. 10, 124008 (2015).
Song, C. et al. Ecological characterization of vegetation using multi-sensor remote sensing in the solar reflective spectrum. In Remote Sensing Handbook, Volume IV (ed. Thenkabail, P. S.) 533–575 (CRC Press, 2024).
Zhang, Y. et al. Land cover change-induced decline in terrestrial gross primary production over the conterminous United States from 2001 to 2016. Agric. Meteorol. 308, 108609 (2021).
Tu, H. et al. Effects of Land Cover Change on Vegetation Carbon Source/Sink in Arid Terrestrial Ecosystems of Northwest China, 2001–2018. Remote Sens. 15, 2471 (2023).
Kolby Smith, W. et al. Large divergence of satellite and Earth system model estimates of global terrestrial CO2 fertilization. Nat. Clim. Change 6, 306–310 (2016).
Chen, J. M. et al. Vegetation structural change since 1981 significantly enhanced the terrestrial carbon sink. Nat. Commun. 10, 4259 (2019).
Winkler, K., Fuchs, R., Rounsevell, M. & Herold, M. Global land use changes are four times greater than previously estimated. Nat. Commun. 12, 2501 (2021).
MacDicken, K. G. Global forest resources assessment 2015: What, why and how? Ecol. Manag. 352, 3–8 (2015).
Piao, S. et al. Changes in climate and land use have a larger direct impact than rising CO2 on global river runoff trends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104, 15242–15247 (2007).
Piao, S. et al. Lower land-use emissions responsible for increased net land carbon sink during the slow warming period. Nat. Geosci. 11, 739–743 (2018).
Paradis, E. Forest gains and losses in Southeast Asia over 27 years: The slow convergence towards reforestation. Policy Econ. 122, 102332 (2021).
Margono, B. A., Potapov, P. V., Turubanova, S., Stolle, F. & Hansen, M. C. Primary forest cover loss in Indonesia over 2000–2012. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 730–735 (2014).
Liu, X. et al. Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity. Nat. Commun. 10, 5558 (2019).
Asner, G. P. et al. Targeted carbon conservation at national scales with high-resolution monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, E5016–E5022 (2014).
Song, X.-P. et al. Massive soybean expansion in South America since 2000 and implications for conservation. Nat. Sustainability 4, 784–792 (2021).
Asner, G. P. et al. Selective logging in the Brazilian Amazon. Science 310, 480–482 (2005).
Pugh, T. A. et al. Role of forest regrowth in global carbon sink dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 4382–4387 (2019).
Kondo, M. et al. Plant regrowth as a driver of recent enhancement of terrestrial CO2 uptake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 4820–4830 (2018).
Hostert, P. et al. Rapid land use change after socio-economic disturbances: the collapse of the Soviet Unionversus Chernobyl. Environ. Res. Lett. 6, 045201 (2011).
Matasov, V., Prishchepov, A. V., Jepsen, M. R. & Müller, D. Spatial determinants and underlying drivers of land-use transitions in European Russia from 1770 to 2010. J. Land Use Sci. 14, 362–377 (2019).
Chen, C. et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2, 122–129 (2019).
Friedlingstein, P. et al. Global carbon budget 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 11, 1783–1838 (2019).
Du, E. Uncertain effects of nutrient availability on global forest carbon balance. Nat. Clim. Change 5, 958–959 (2015).
Li, Z. & Zhou, T. Optimization of forest age-dependent light-use efficiency and its implications on climate-vegetation interactions in china. Int. Arch. Photogramm., Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 40, 449–454 (2015).
Tang, J., Luyssaert, S., Richardson, A. D., Kutsch, W. & Janssens, I. A. Steeper declines in forest photosynthesis than respiration explain age-driven decreases in forest growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 8856–8860 (2014).
Gundersen, P. et al. Old-growth forest carbon sinks overestimated. Nature 591, E21–E23 (2021).
Chen, Z., Yu, G. & Wang, Q. Effects of climate and forest age on the ecosystem carbon exchange of afforestation. J. Forestry Res. 31, 365–374 (2020).
Buitenwerf, R., Sandel, B., Normand, S., Mimet, A. & Svenning, J. C. Land surface greening suggests vigorous woody regrowth throughout European semi-natural vegetation. Glob. Change Biol. 24, 5789–5801 (2018).
Ellabban, O., Abu-Rub, H. & Blaabjerg, F. Renewable energy resources: Current status, future prospects and their enabling technology. Renew. Sustain. energy Rev. 39, 748–764 (2014).
Caron, P. et al. Food systems for sustainable development: proposals for a profound four-part transformation. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 38, 1–12 (2018).
Fuss, S. et al. Betting on negative emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 850–853 (2014).
Chen, J. M. Carbon neutrality: Toward a sustainable future. The Innovation 2, (2021).
Griscom, B. W. et al. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 11645–11650 (2017).
Forster, E. J., Healey, J. R., Dymond, C. & Styles, D. Commercial afforestation can deliver effective climate change mitigation under multiple decarbonisation pathways. Nat. Commun. 12, 3831 (2021).
Lewis, S. L., Wheeler, C. E., Mitchard, E. T. & Koch, A. Regenerate natural forests to store carbon. Nature 568, 25–28 (2019).
Meigs, G. W. & Keeton, W. S. Intermediate-severity wind disturbance in mature temperate forests: legacy structure, carbon storage, and stand dynamics. Ecol. Appl. 28, 798–815 (2018).
Fu, Z. et al. Recovery time and state change of terrestrial carbon cycle after disturbance. Environ. Res. Lett. 12, 104004 (2017).
Grieco, E., Vangi, E., Chiti, T. & Collalti, A. Impacts of deforestation and land use/land cover change on carbon stock dynamics in Jomoro District, Ghana. J. Environ. Manag. 367, 121993 (2024).
Piao, S. et al. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 1, 14–27 (2020).
Bashaasha, B., Kraybill, D. S. & Southgate, D. D. Land use impacts of agricultural intensification and fuelwood taxation in Uganda. Land Econ. 77, 241–249 (2001).
Ewers, R. M., Scharlemann, J. P., Balmford, A. & Green, R. E. Do increases in agricultural yield spare land for nature?. Glob. Change Biol. 15, 1716–1726 (2009).
Marin, F. R. et al. Protecting the Amazon forest and reducing global warming via agricultural intensification. Nat. Sustain. 5, 1018–1026 (2022).
Sun, W., Huang, Y., Zhang, W. & Yu, Y. Carbon sequestration and its potential in agricultural soils of China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 24, GB3001 (2010).
Xie, Z. et al. CO2 mitigation potential in farmland of China by altering current organic matter amendment pattern. Sci. China Earth Sci. 53, 1351–1357 (2010).
Chen, J., Liu, J., Cihlar, J. & Goulden, M. Daily canopy photosynthesis model through temporal and spatial scaling for remote sensing applications. Ecol. Model. 124, 99–119 (1999).
Liu, J., Chen, J., Cihlar, J. & Park, W. A process-based boreal ecosystem productivity simulator using remote sensing inputs. Remote Sens. Environ. 62, 158–175 (1997).
Chen, J. M. et al. Effects of foliage clumping on the estimation of global terrestrial gross primary productivity. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 26, GB1019 (2012).
Chen, B., Chen, J. M. & Ju, W. Remote sensing-based ecosystem–atmosphere simulation scheme (EASS)—Model formulation and test with multiple-year data. Ecol. Model. 209, 277–300 (2007).
Parton, W. et al. Observations and modeling of biomass and soil organic matter dynamics for the grassland biome worldwide. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 7, 785–809 (1993).
Leuning, R. Modelling stomatal behaviour and and photosynthesis of Eucalyptus grandis. Funct. Plant Biol. 17, 159–175 (1990).
Ju, W. et al. Modelling multi-year coupled carbon and water fluxes in a boreal aspen forest. Agric. Meteorol. 140, 136–151 (2006).
Chen, J. M. et al. Spatial distribution of carbon sources and sinks in Canada’s forests. Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 55, 622–641 (2003).
Cao, S. et al. Spatiotemporally consistent global dataset of the GIMMS leaf area index (GIMMS LAI4g) from 1982 to 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 15, 4877–4899 (2023).
Lu, X. et al. Estimated global nitrogen deposition using NO2 column density. Int. J. remote Sens. 34, 8893–8906 (2013).
O’sullivan, M. et al. Process-oriented analysis of dominant sources of uncertainty in the land carbon sink. Nat. Commun. 13, 4781 (2022).
Klein Goldewijk, K., Beusen, A., Doelman, J. & Stehfest, E. Anthropogenic land use estimates for the Holocene–HYDE 3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 9, 927–953 (2017).
Pierre, F. et al. Global carbon budget 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 14, 1917–2005 (2022).
Besnard, S. et al. Mapping global forest age from forest inventories, biomass and climate data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 13, 4881–4896 (2021).
Acknowledgements
Bing Zhang acknowledges support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.42030111), Dailiang Peng acknowledges supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42471372), the National Key R&D Program of China(Grant No. 2023YFE0207900), and the Science and Disruptive Technology Program, AIRCAS (Grant No. 2024-AIRCAS-SDPT-15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.B. (Zhang) designed and performed this research. P.D.L. and Z.S.J. performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. J.W.M. and C.J.M. helped with the simulation of NEP using BEPS model. C.P. help with the assessment of land cover conversions effects on net ecosystem productivity and provided constructive comments on the manuscript. G.H.D., and H.A.R. provided constructive comments on the manuscript. P.Y.H., Y.L., X.Y.D., Z.B. (Zhao), B.J.A., S.Z., H.Y.M., L.L.Y., C.F., S.M.G., H.L. and Z.X.Y. contributed to writing and revising the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Liyin He and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, D., Zhang, B., Zheng, S. et al. Newly established forests dominated global carbon sequestration change induced by land cover conversions. Nat Commun 16, 6570 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61956-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61956-y