Abstract
Background
Angiogenesis is essential for colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. The role of serine/threonine kinase STK32C in this process remains unclear.
Methods
STK32C expression was examined in CRC tissues and correlated with patient prognosis. In vitro assays evaluated endothelial proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Mechanisms were studied using immunoprecipitation, western blotting, and gene set enrichment analysis. In vivo, xenograft and Matrigel plug assays assessed tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Results
STK32C was markedly overexpressed in CRC and associated with poor outcomes. Overexpression promoted endothelial angiogenic behaviors, while knockout suppressed them. Mechanistically, STK32C directly phosphorylated STAT3 at Thr196, enhancing its binding to JAK2 and activating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. In vivo, STK32C depletion reduced tumor growth, VEGF-A expression, and microvessel density, confirming its pro-angiogenic function. STK32C-mediated tumor angiogenesis relied on STAT3 Thr196 phosphorylation.
Conclusions
STK32C acts as a pro-angiogenic driver in CRC by activating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling via STAT3 Thr196 phosphorylation. Its strong association with poor prognosis highlights STK32C as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in anti-angiogenic therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Angiogenesis is a key enabler of cancer growth and metastasis, primarily regulated by VEGF, a family that includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and placental growth factor (PLGF) [1]. VEGF-A is the most prominent driver of tumour angiogenesis [2, 3]. Inhibitors like bevacizumab effectively curb angiogenesis and tumour progression and are recommended as first-line treatment for colorectal cancer with liver metastasis [4, 5]. However, resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy remains inevitable. Understanding the molecular basis of tumour angiogenesis can aid in the identification of predictive biomarkers, allowing for more personalised therapeutic approaches.
The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway plays a critical role in the development and progression of various human cancers. In cancer pathogenesis, elevated IL-6 levels drive the hyperactivation of JAK/STAT3 signalling, which is frequently linked to unfavourable patient outcomes [6,7,8,9]. The majority of cancers exhibit hyperactive STAT3 signalling, and this is often associated with poor prognosis, which may be influenced by signals from other growth factors and their receptors, activation by non-receptor tyrosine kinases such as SRC and BCR-ABL1, or loss-of-function mutations in negative regulators of STAT3 [10,11,12,13,14]. This cytokine directly influences tumour cells by activating the expression of STAT3 target genes, which encode proteins that promote tumour proliferation, such as cyclin D1, and enhance cell survival, such as BCL2-like protein 1 (BCL-xL). Additionally, STAT3’s role in facilitating IL-6 gene expression generates a feedforward autocrine feedback loop [15]. Moreover, STAT3 regulates the expression of multiple factors that contribute to various tumorigenic processes, including angiogenesis (e.g., VEGF), invasiveness and metastasis (e.g., matrix metalloproteinases, or MMPs), and immunosuppression (e.g., IL-10 and TGFβ, alongside VEGF and IL-6) [13, 16, 17]. This multifaceted action of STAT3 highlights its importance in cancer progression and the complexity of the tumour microenvironment.
Serine/threonine kinase 32C (STK32C), a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase subgroup within the AGC superfamily, has functions that remain largely unexplored. Studies have revealed that STK32C is overexpressed in brain tissues and is associated with adolescent depression, evidenced by DNA methylation differences observed in monozygotic twins [18]. Additionally, analyses from various studies indicate that alterations in STK32C gene expression are correlated with the activity of CD4+ regulatory T cells and lung inflammation [19, 20]. Moreover, tumour gene expression profiles suggest that STK32C may be upregulated in several malignancies, including prostate cancer [21]. This finding indicates a potential involvement of STK32C in tumour progression.
In this study, we uncovered that STK32C was highly expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) and aimed to clarify its contribution to angiogenesis. Through both in vitro experiments and animal models, we found that STK32C actively drove the formation of new blood vessels. Diving deeper into the molecular mechanisms, we explored how STK32C elevated VEGF-A expression, a key factor in angiogenesis. Our results showed that this regulation hinged on the phosphorylation of STAT3 at the T196 site. Together, these findings emphasised STK32C’s pivotal role in orchestrating angiogenesis within tumours and highlighted its potential as a promising target for anti-angiogenic therapies in CRC.
Methods
Reagents and antibodies
Antibodies for CD31 (Cat #77699), STAT3 (Cat#9139), p-STAT3(Y705) (Cat #9145), JAK2 (Cat #3230), p-JAK2 (Cat #3771), β-Action (Cat #4967), HA (Cat #3724), Flag (Cat #14793), were obtained from Cell Signalling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). STK32C (Proteintech #11434) pan Phospho-Serine/Threonine antibody (Abclonal, AP1067) was commercially bought. Antibodies for VEGF-A (ab1316) were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA). The human VEGF-A ELISA Kit (EK0539) was obtained from BOSTER Biological Technology (Wuhan, China). MK2206 from Sigma (Burlington, MA, USA). Growth factor-reduced Matrigel was purchased from BD Bioscience (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Primers used in this study were synthesised by TSINGKE Biological Technology (Beijing, China).
Cell culture and treatment
All cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. The CRC cell lines LOVO, HCT116 were cultured at 37 °C in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured in EBM-2 endothelial cell basal medium at 37 °C using the SingleQuot kit (Lonza, Walkersville, MD, USA). The cell lines were authenticated by STR profiling and routinely tested for mycoplasma contamination.
Preparation of conditioned medium (CM)
Briefly, stably transfected STK32C-overexpressing or STK32C knockout CRC cells were seeded at a density of 5 × 105 cells/ml in six-well plates. One day later, the cells were washed three times in PBS, then incubated in DMEM without foetal bovine serum. After 24 h of incubation, CM was collected with a cell density of approximately 90%. Subsequently, CM was used for cell experiments or stored at −80 °C.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
VEGF-A levels in CM were quantified using the human VEGF-A ELISA Kit according to its instructions. The absorbance of the microplate reader was set to 450 nm, and the OD values in the sample were detected.
Cell viability assay
Approximately 1–3 × 103 HUVECs were cultured in 96-well plates for 24 h, then the medium was replaced with various CMs and various CMs were added to the wells. After 48 h, the 100 μl CM was supplemented with 10 μl CCK8, which should avoid light, then the plates were incubated for 2 h. Afterwards, absorbance at 450 nm was measured to obtain the OD value.
In vitro angiogenesis assay
In vitro angiogenesis was measured by tube formation. Briefly, the Matrigel with reduced growth factor was thawed on ice, plated in a 96-well plate with 100 μl per well, and placed in a 37 °C incubator for 30 min to form a gel. Approximately 2 - 4 × 104 HUVECs were added to each well and incubated in CM for 24 h. Endothelial tubes were detected under a microscope every 4 h, the number of branches in the formed HUVEC tubes was assessed.
Tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry (IHC)
A human colorectal tissue of colorectal cancer/adjacent tissue was a kind gift from Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. This tissue was used to detect the expression of STK32C. For the tissue of nude mice, immunohistochemistry, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues were cut into 4-μm sections. Then, paraffin-embedded tissues were serially sectioned into 4 mm and incubated with primary antibodies of STK32C, VEGF-A and CD31, respectively. Microvascular density (MVD) was determined according to the method described by Weidner. Two experienced pathologists evaluated immunostaining results. The expression level was calculated by multiplying a proportion score and an intensity score, and was categorised as low expression (IHC score 0–7), high expression (IHC score greater than 7). The proportion score reflected the fraction of positive-stained cells (0, none; 1, ≤10%; 2, 10% to ≥25%; 3, >25% to 50%; 4, >50%), the intensity score revealed the staining intensity (0, no staining; 1, weak; 2, intermediate; 3, strong). Outcome assessments were performed in a blinded manner by independent pathologists.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) and reverse transcription was performed using an RT–PCR kit (TaKaRa). Quantitative PCR was performed using the ABI 7300 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems). The fold-change in gene expression was calculated using the 2-△△CT method using GAPDH as a control. The qPCR primer sequences of STK32C, VEGF-A, and GAPDH are listed in Table S1.
Western blot
Total cell protein was extracted using NP40 lysates with protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to 0.45 μm PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad). After blocking 1 h, blots were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. The next day, blots were incubated with the homologous HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Immunoreactive bands were detected with ECL reagents (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Luciferase reporter assay
Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and co-transfected with a firefly luciferase reporter plasmid driven by STAT3-responsive elements (pSTAT3-Luc) and a Renilla luciferase plasmid (pRL-TK) as an internal control. Luciferase activity was measured using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Firefly luciferase activity was normalised to Renilla luciferase activity to determine relative STAT3 transcriptional activity.
In vitro kinase assay
Recombinant STK32C protein was incubated with recombinant STAT3 in kinase reaction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl₂, 1 mM DTT, and 100 μM ATP in a total volume of 30 μL. The reaction was carried out at 30 °C for 30 minutes. The reaction was stopped by adding SDS loading buffer and boiling at 95 °C for 5 minutes. Samples were then subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using pan phospho-serine/threonine antibodies to detect substrate phosphorylation.
Co-IP
Cell extracts with protein A/G beads were performed before incubating with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. Protein A/G beads were added and further incubated for 2 h. The beads were washed with PBS five times, and 25 µl of 2 × SDS loading buffer was then added and the samples were boiled at 95–100 °C for 5 min.
Trans-well assays
Trans-well migration assays, approximately 2–4 × 104 HUVECs suspended in mediums, were seeded in the upper chamber membranes of 24-well plates. Then, 600 μl CMs was added to the lower chamber. 24 h later, the membrane was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min, then stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Gently wipe the inside of the membrane with a cotton swab and quantify the number of cells with a microscope.
Mouse xenograft tumour assay
Mice were housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) facility under controlled temperature and humidity with a 12 h light/dark cycle and ad libitum access to food and water. Humane endpoints were set, and mice were euthanized if their health deteriorated. The mouse experiment of this study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. Six-week-old male Balb/c nude mice were obtained from Beijing Huafukang Bioscience Company. Mice were randomly assigned to experimental and control groups. We resuspended LoVo cells, mixed the cells with Matrigel in a 1:1 ratio. A total of 1 × 106 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank of each mouse. Cells were planted in the left flank of each mouse. After mice developed a visible tumour mass, Tumour volume was calculated by the formula: Volume = (length×width2)/2. Tumour volumes were calculated every 3 days. Tumour volume measurement and outcome assessments were performed in a blinded manner. At the end of the experiment, mice were sacrificed. All the tumour xenografts were removed from the mice and immediately weighed. Finally, the xenografts were cut in half, half of the tumours were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for IHC analysis and the other half was used for Western blot analysis.
To assess angiogenesis in immune-competent mice, we performed a Matrigel plug assay: serum-free conditioned media (16 h) from MC38 shnc or shSTK32C cells were mixed with growth factor–reduced Matrigel to a final 50% CM (v/v) (heparin 20 U/mL); 500 μL/plug were injected subcutaneously into the dorsal region of 8-week C57BL/6 mice under randomisation and blinding. On day 7, plugs were excised, photographed and weighed, homogenised, and haemoglobin was quantified with Drabkin’s reagent (D5941, Sigma); data were expressed as mg/dL and analysed statistically. Animal numbers were chosen to ensure adequate power for detecting the expected effects while minimising animal use in line with ethical guidelines.
Statistical analysis
All data were analysed using SPSS 20.0 software. The expression levels of STK32C and clinicopathological features were compared using the Chi-square test. A Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to obtain the survival curves, and differences were assessed with the log-rank test. The differences between groups in cell experiments were analysed using Student’s t-test when data were normally distributed with equal variances; otherwise, the Mann–Whitney U test was applied. The differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results
STK32C was a pro-angiogenesis factor and associated with poor prognosis in cancer
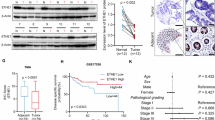
To clarify the biological function of STK32C in tumour angiogenesis, we analysed 78 cases of colorectal cancer samples using IHC assays. This analysis revealed a positive correlation between STK32C expression levels and both VEGF-A expression levels and the number of CD31-positive micro-vessels, suggesting a link between STK32C and tumour angiogenesis (Fig. 1a–c). Additionally, we performed Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) on colorectal cancer using multiple datasets, revealing that angiogenesis signalling was significantly activated in tumour with high STK32C expression (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. 1a). Also, a similar correlation between STK32C and VEGF-A was observed in other cancer types, including thyroid carcinoma, tenosynovial giant cell tumour, adrenal carcinoma, and pancreatic cancer (Supplementary Fig. 1b). Using the TCGA database, we compared STK32C transcript levels in colorectal cancer and normal tissues, finding that STK32C was significantly elevated in cancer tissues (Fig. 1e, f). Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis demonstrated enhanced ability to differentiate colorectal cancer from normal tissues (Fig. 1g). In our analysis of 78 pairs of clinical samples, STK32C protein expression was markedly higher in cancer tissues compared to normal samples (Fig. 1H), with significant differences in IHC scores (Fig. 1i, j). Immunohistochemical staining of samples at various clinical stages showed that STK32C levels were significantly elevated in stage III and IV tumour specimens compared to stages I and II (Fig. 1k). Similarly, in the TNM staging system, T3 and T4 groups exhibited greater STK32C expression than T1 and T2 groups (Fig. 1l), indicating a potential role for STK32C in tumour progression and patient prognosis. Further analysis through protein blotting of seven paired clinical samples (normal and tumour) confirmed STK32C upregulation in all tumour samples (Supplementary Fig. 2a). TCGA data analysis indicated that STK32C expression was consistently higher in cancer tissues across most cancer types (Supplementary Fig. 2b). Survival analysis demonstrated that in colon and rectal adenocarcinomas, patients with low STK32C expression had significantly better survival rates than those with high STK32C expression (Fig. 1m, n), with similar trends observed in other cancer types (Supplementary Fig. 2c). Next, we added the IHC scores of STK32C and VEGFA for each tumour sample to generate a combined expression score. Patients were then stratified into two groups based on the total score: low expression (score 0–14) and high expression (score >14). Survival analysis revealed that patients in the high expression group had significantly worse overall survival compared to those in the low expression group, indicating that the co-expression of STK32C and VEGFA is associated with poor prognosis (Fig. 1o).
a–c Representative IHC staining of STK32C, VEGF-A and CD31 in the two tumours was presented. b, c was scatter diagram. d Gene set enrichment analysis of TCGA-COAD and GSE17536 datasets. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalised enrichment score. e, f Comparison of STK32C expression levels between colorectal tumour and normal tissues using TCGA database. g ROC curve analysis for differential diagnosis of cancer, AUC is the area under the curve, CI is the confidence interval. h–l Representative IHC staining of STK32C in the two tumours were presented. The histograms i–l showed the IHC score of STK32C in the two groups. m The overall survival (OS) curves for STK32C-low and STK32C-high patients with CRC according to the Kaplan-Meier analysis using TCGA database. n The OS curves for STK32C-low and STK32C-high patients with CRC according to the Kaplan-Meier analysis. o The OS curves for STK32C/VEGFA-low and STK32C/VEGFA-high patients with CRC according to the Kaplan-Meier analysis.
STK32C positively promoted tumour angiogenesis in vitro
To further reveal the pro-angiogenesis function of STK32C, we first conducted western blot analysis using LoVo and HCT116 cells stably expressing vector or Flag-STK32C. Results revealed an increase in VEGF-A protein levels in the STK32C-overexpression cells (Fig. S3a). Consistent results were obtained using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which measured VEGF-A levels in the cell supernatants of both groups (Fig. S3b). Subsequently, RNA was extracted from both groups, and quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis demonstrated that the mRNA levels of VEGF-A were significantly elevated in the STK32C overexpression group compared to the control (Fig. S3c). Next, we cultured HUVECs with CMs from both groups, and CCK8 analysis revealed that CMs from STK32-overexpressing cell significantly promoted HUVECs proliferation (Fig. S3d). Additionally, the migration ability of HUVECs cultured with CMs from STK32-overexpressing cells were markedly higher than those observed in the control group (Fig. S3e, f). Furthermore, the angiogenesis ability in HUVECs cultured with CMs from STK32-overexpressing cell was also enhanced in the STK32C high-expression group compared to controls (Fig. S3g,h).
To further elucidate the role of STK32C in tumour angiogenesis, we knocked out STK32C in LoVo and HCT116 cells. Immunoblotting revealed that VEGF-A expression was significantly downregulated in sgSTK32C cells compared to sgnc controls (Fig. 2a).We also assessed RNA levels across the three groups, finding that mRNA levels of VEGFA were reduced in sgSTK32 C cells (Fig. 2b). Correspondingly, the VEGF-A concentration in the cell supernatants was lower in the STK32C knockout group (Fig. 2c). Also, CCK8 analysis revealed that CMs from sgSTK32 cells significantly inhibited HUVECs proliferation (Fig. 2d). CMs form sgSTK32C cells lead to a slower migration and angiogenesis ability of HUVECs (Fig. 2e–h).
a Western Blot analysis of VEGF-A and STK32C protein expression in these cells. b qPCR analysis of VEGF-A mRNA expression in these different treated cells. c Elisa analysis of VEGF-A protein expression in these cells. d CCK8 assays to detect the proliferation ability of HUVECs cultured with different CMs. e, f Trans-well assays to examine the migration ability of HUVECs cultured with different CMs. g, h Tube formation assay to detect the tube formation ability of HUVECs cultured with different CMs. All experiments are examined and analysed in triplicates.
STK32C positively promoted the activation of the STAT3 signalling pathway in CRC
To further investigate how STK32C affect tumour angiogenesis, we firstly conducted GSEA analysis using multiple datasets, and results showed that IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway was significantly activated in tumours with high STK32C expression (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Fig. 4a). Subsequently, immunoblotting demonstrated that phosphorylated JAK2 and STAT3 levels were significantly reduced in sgSTK32C cells compared to controls (Fig. 3b). Also, phosphorylated STAT3 levels were elevated in the high STK32C expression group (Supplementary Fig. 4b). We further showed that IL-6 activated STAT3 in LoVo cells, while STK32C knockout diminished this activation (Fig. 3c). Notably, STK32C overexpression enhanced IL-6-mediated phosphorylated STAT3 upregulated, while STK32C D216A (an enzyme activity deficient mutant) had no this effect (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 4c). This indicates that the phosphokinase activity of STK32C was essential for it-mediated IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling activation. JAK2 firstly bound to STAT3 and then phosphorylated STAT3, hence, we detected whether STK32C could affect the interaction between JAK2 and STAT3. Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis revealed that the interaction between JAK2 and STAT3 was weakened in the STK32C knockout group (Fig. 3e). Consistently, increased STK32C expression enhanced JAK2’s binding to STAT3 (Supplementary Fig. 4d). The overexpression of STK32C WT, but not STK32C D216A mutant, further promoted IL-6-mediated JAK2/STAT3 interaction (Fig. 3f and Supplementary Fig. 4e). Meanwhile, Analysis of the relationship between STK32C and p-STAT3 in colorectal tumour tissues indicated a positive correlation between STK32C levels and p-STAT3 (Fig. 3g and Supplementary Fig. 4f). Next, we performed additional qPCR analyses to evaluate the expression of MMP2, MMP9, IL8, VEGFB, VEGFC and TGFB1, which were the downstream genes of IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signalling. Our results demonstrated that STK32C silencing downregulated, and STK32C overexpression upregulated, the expression of these STAT3-regulated genes (Fig. 3h and Supplementary Fig. 4g), suggesting that STK32C did not solely affect VEGFA, but more broadly modulates the STAT3-driven transcriptional programme.
a Gene set enrichment analysis of TCGA-COAD, GSE17536 and GSE17538. b Western Blot analysis of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, p-STAT3 and STK32C protein expression in these different treated cells. c Western Blot analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3 and STK32C protein expression in these different treated cells. d Western Blot analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3 and STK32C protein expression in these different treated cells. e, f Immunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction of STAT3 and JAK2 in these different treated cells. h qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression level of STAT3-driven genes in these different treated cells. g The scatter diagram were presented to show the IHC score of STK32C and p-STAT3 in colorectal cancer tissues. All experiments are examined and analysed in triplicates.
STK32C regulated IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway via phosphorylating STAT3 at threonine 196
To elucidate the mechanism by which STK32C activated IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway, we firstly conducted endogenous immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments that confirmed a binding interaction between STK32C and STAT3 (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Fig. 5a). Considering that STK32C was a serine/threonine protein kinase, we assumed that STK32 might phosphorylated STAT3. Pan phospho-serine/threonine antibody was used to detect the level of serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3. Of note, following the overexpression of STK32C, level of serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3 was found to increase (Supplementary Fig. 5b). Interestingly, IL-6 application could also up-regulated the level of serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3, and STK32C WT (not STK32C D216A) further enhanced this effect, while knockout of STK32C had the opposite effect (Figs. 4b, c and Supplementary Fig. 5c). Next, we conducted additional experiments in the MSS-type cell line SW620, and found that knockout of STK32C similarly led to reduced phosphorylation of STAT3, consistent with our observations in MSI-H models (LoVo and HCT116) (Supplementary Fig. 5d). To identify the specific phosphorylation site on STAT3, we designed plasmids with various deletions of STAT3 fragments and performed IP analysis. We found that deleting the amino acids between positions 2 and 200 of STAT3 significantly impaired its ability to bind to STK32C, suggesting that this region was important for their interaction. (Fig. 4d). Based on this, we hypothesised that STK32C might phosphorylate STAT3 within this region. To test this possibility, we examined potential serine/threonine phosphorylation sites using the Phosphosite database and identified that there were three potential phosphorylation sites of STAT3 (S181, S194 and T196). Then, we separately replace these amino acids with alanine. Immunoblotting analysis indicated that T196A mutant impaired STK32C-mediated serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3 upregulation (Fig. 4e and Supplementary Fig. 5e). Next, we constructed LoVo cells stably expressing STAT3 WT or STAT3 T196A mutant (Supplementary Fig. 5f). Immunoblotting analysis further proved that STAT3 T196A mutant inhibited the IL-6/STK32C-induced STAT3 serine/threonine phosphorylation in both LoVo (human) and MC38 (murine) colorectal cancer cell lines (Figs. 4f, g and Supplementary Fig. 5G). Additionally, the T196A mutation counteracted the enhancement of JAK2 binding to STAT3 induced by IL-6 (Fig. 4h). Conservation analysis of the threonine residue at position 196 in STAT3 across different species demonstrated a high degree of conservation in the adjacent peptide sequences (Fig. 4I), indicating the functional importance of this region for the protein’s activity. Next, we performed an in vitro kinase assay using purified recombinant proteins to directly assess the kinase–substrate specificity of STK32C. The results demonstrated that STK32C was able to phosphorylate wild-type STAT3, but fails to phosphorylate the STAT3 T196A mutant, indicating that T196 is a critical phosphorylation site directly targeted by STK32C in vitro (Fig. 4j). Subsequently, we further evaluated the transcriptional consequence of T196 phosphorylation using a luciferase-based STAT3 reporter assay. Results showed that the T196A mutation significantly impaired STAT3-driven transcriptional activity (Supplementary Fig. 5h, 5i). Also, knockout of STK32C inhibited STAT3-driven transcriptional activity (Supplementary Fig. 5j), supporting the notion that T196 phosphorylation contributes to full STAT3 transcriptional function.
a Endogenous Co-IP analysis of STAT3 and STK32C. b, c Western Blot analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3 and STK32C protein expression in these different treated cells. d Co-IP assays of different STAT3 fragments and STK32C. e Western Blot analysis of serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3 level in these different treated cells. f Western Blot analysis of serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3 level in in these different treated cells. g Western Blot analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3, serine/threonine phosphorylated STAT3 and STK32C level in these different treated cells. h Co-IP analysis of the interaction of STAT3 and JAK2 in these different treated cells. i The threonine residue at position 196 in STAT3 across different species. j In vitro kinase assay using purified recombinant proteins, followed by Western Blot. All experiments are examined and analysed in triplicates.
STAT3 T196 phosphorylation was essential factor for STK32C-mediated tumour angiogenesis
To further explore the correlation of the STAT3 T196 phosphorylation and STK32C on angiogenesis, we performed immunoblotting on LoVo cell lines stably expressing STAT3 T196A, comparing them with control groups. A marked downregulation of VEGFA expression was observed in the mutant cells, which did not change even in the presence of elevated STK32C levels (Fig. 5a). Moreover, quantitative PCR (qPCR) and ELISA analyses conducted across four sample groups demonstrated that while STK32C significantly enhanced VEGF expression in wild-type cells, this effect was absent in the mutant cells (Fig. 5b). The proliferation ability of HUVECs in the mutant group remained unaffected by STK32C (Fig. 5c), consistent with results from tumour cell invasion assays (Fig. 5d, e). Importantly, in the T196A mutant group, STK32C was unable to boost the angiogenic capacity of HUVECs (Fig. 5f, g). Furthermore, qPCR results demonstrated that STK32C overexpression upregulated the expression of these STAT3-regulated genes in STAT3 WT cells, but not in STAT3 T196A cells (Supplementary Fig. 5k). To further substantiate our findings, we conducted immunoblotting on LoVo cell lines with STK32C knockout. This knockdown did not change VEGFA expression in the mutant group (Fig. 5h). Additionally, qPCR and ELISA analyses indicated that in wild-type cell lines with STK32C knockout, both intracellular and extracellular VEGF levels decreased; however, this reduction was not seen in the mutant group (Fig. 5i). Similarly, the ability of HUVEC proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis were unaffected by STK32C knockout in the T196A mutant cells (Fig. 5j–n).
a, h Western Blot analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3 and VEGFA protein expression in these different treated cells. b, i The histogram showed qPCR and ELISA analysis of VEGF-A expression level in the four different treated cells. (c, j) CCK8 assays to detect the proliferation ability of HUVECs cultured with different CMs. d, e, k, l Trans-well assays to examine the migration ability of HUVECs treated with different CMs from the four groups. f, g, m, n Tube formation assays to detect the tube formation ability of HUVECs treated with different CMs from the four groups. All experiments are examined and analysed in triplicates.
Knockout of STK32C inhibited tumour growth and angiogenesis in vivo
To further elucidate the role of STK32C in tumour growth and angiogenesis, we injected LoVo cells stably expressing sgSTK32C and sgnc subcutaneously into nude mice. The results indicated that sgnc LoVo cells exhibited accelerated growth compared to sgSTK32C LoVo cells in vivo (Fig. 6a). Moreover, the xenograft tumours derived from sgnc cells were larger and heavier than those from sgSTK32C cells (Fig. 6b, c). Additionally, mice harbouring sgSTK32C cells demonstrated improved survival rates compared to those with sgnc LoVo cells (Fig. 6d). To evaluate the angiogenic status within the grafted tumours, immunohistochemical staining was performed to assess the expression levels of p-STAT3, VEGF-A, and the number of CD31-positive micro-vessels. The analysis revealed that the levels of p-STAT3, VEGF-A, and the number of microvessels were significantly reduced in the sgSTK32C group (Fig. 6e, f). Consistent with these observations, immunoblotting confirmed that both VEGF-A and p-STAT3 levels were markedly lower in the sgSTK32C group compared to the sgnc group (Fig. 6g).
a sgnc cells or sgSTK32C cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. After 16 days, mice were sacrificed, representative tumour images at the end of the experiment were presented. b The tumour volume growth curves from days 1–16 were presented. c The tumour weights were examined. d The survival (OS) curves for these group mice. e, f Representative IHC staining of STK32C, p-STAT3, VEGF-A and CD31 in the three groups. The right histogram (f) showed number of micro-vessels. g Western blot revealed the expression level of STK32C, p-STAT3 and VEGF-A expression in xenograft tumour. h The indentified cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. After 13 days, mice were sacrificed, representative tumour images at the end of the experiment were presented. i The tumour volume growth curves from days 1-13 were presented. j The right histogram showed number of micro-vessels. k Schematic representation of the molecular mechanism by which STK32C regulated the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway.
To detect the correlation between STK32C and STAT3 T196 phosphorylation in tumour angiogenesis, we performed additional in vivo experiments in which STK32C was overexpressed in STAT3-WT and STAT3-T196A mutant tumour cells, respectively. These cells were then implanted into immunodeficient mice to assess tumour progression and angiogenesis. Our results showed that overexpression of STK32C in STAT3-WT cells significantly enhanced tumour growth and angiogenesis. However, the same STK32C overexpression failed to promote angiogenesis in STAT3-T196A mutant cells. Also, The STAT3 T196A mutation suppresses STK32C overexpression-induced tumour growth and angiogenesis (Fig. 6h–j and Supplementary Fig. 5l, 5m). To further confirm the function of STK32C in immune-competent mice, we performed a Matrigel plug assay. Results showed that haemoglobin content was significantly reduced in the shSTK32C group, indicating diminished angiogenesis in immune-competent settings (Supplementary Fig. 5n, 5o).
Discussion
This study provided the first comprehensive investigation of the role of serine/threonine kinase STK32C in colorectal cancer, demonstrating its contribution to tumour angiogenesis [22, 23] via activation of the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Our results revealed that STK32C was significantly overexpressed in CRC tissues and correlated with poor clinical outcomes, suggesting its potential as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target [24, 25].
Several serine/threonine kinases had been shown to modulate STAT3 activity via Ser727 phosphorylation, potentially influencing the STAT3–JAK2 complex. PKCδ enhanced both Ser727 and Tyr705 phosphorylation of STAT3, promoting its transcriptional activity. In contrast, ERK2 phosphorylated STAT3 on serine residues while suppressing its tyrosine phosphorylation and JAK2-mediated activation. CDK5 also phosphorylated STAT3 at Ser727 and increased its DNA-binding ability [26,27,28]. Our findings showed that STK32C promoted angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF-A expression through STAT3 phosphorylation at threonine 196. This post-translational modification of STAT3 was essential, as it enhanced phosphorylation at the Y705 site, which was necessary for the activation of downstream signalling involved in cell survival and angiogenesis. Notably, although IL-6 is a well-established activator of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, our data suggest that STK32C is not a downstream target of IL-6 signalling, but rather a constitutively active serine/threonine kinase that enhances the responsiveness of this pathway. Specifically, STK32C interacts directly with STAT3 and phosphorylates it at threonine 196, which facilitates the recruitment of JAK2 and potentiates STAT3 activation in response to IL-6. This effect is dependent on the kinase activity of STK32C, as the D216A catalytic mutant fails to enhance IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation or JAK2–STAT3 interaction. Furthermore, loss of STK32C impairs IL-6-mediated STAT3 activation. These findings indicate that STK32C functions as a signal amplifier within the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 cascade rather than being activated by IL-6 itself. This provides a novel mechanistic insight into how serine/threonine kinases can modulate canonical cytokine pathways and contribute to tumour angiogenesis.
The IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway was widely recognised for its involvement in cancer progression and immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment. Our research confirmed that STK32C functioned as a critical modulator of this pathway in CRC. Specifically, our immunoprecipitation assays revealed that STK32C strengthened the binding interaction between JAK2 and STAT3, facilitating subsequent STAT3 activation and enhancing VEGF-A expression. Notably, mutation of the threonine 196 residue in STAT3 abrogated STK32C’s ability to stimulate VEGF-A production and JAK2/STAT3 binding, further underscoring the specificity of this phosphorylation event in driving angiogenic signalling.
The in vivo effects of STK32C on tumour progression were consistent with our in vitro findings. In a nude mouse xenograft model, silencing STK32C reduced tumour volume, VEGF-A expression, and micro-vessel density. These findings aligned with previous research on the role of serine/threonine kinases in cancer, particularly regarding their regulation of angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and metastatic potential. As such, STK32C represented a viable target for anti-angiogenic therapies, potentially in combination with existing treatments that inhibited the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 axis. While anti-VEGF therapies such as bevacizumab have demonstrated clinical benefit in various cancer types, their efficacy is often compromised by intrinsic or acquired resistance, transient responses, and activation of compensatory pro-angiogenic pathways [29, 30]. These limitations highlight the need for upstream targets that regulate VEGFA as well as broader tumour-promoting programmes. Our findings position STK32C as a promising upstream regulator of tumour angiogenesis through STAT3 T196 phosphorylation. Unlike direct VEGFA blockade, targeting STK32C has the potential to simultaneously suppress multiple angiogenic and pro-invasive genes regulated by STAT3, including VEGFA, MMP9, and IL8. This broader transcriptional impact suggests that STK32C-targeted strategies may not only reduce VEGFA production but also interfere with parallel mechanisms of tumour vascularisation and progression. Although our current study does not include direct clinical data linking STK32C expression to bevacizumab response, this hypothesis warrants further investigation. If confirmed, STK32C may serve not only as a pro-angiogenic driver but also as a potential predictive biomarker to guide anti-VEGF therapy selection in CRC. Future studies involving stratification of patients by STK32C expression and analysis of clinical treatment response will be necessary to validate this possibility. Moreover, given that STK32C is a kinase-like protein, it may be more amenable to small-molecule inhibition compared to secreted ligands like VEGFA. Collectively, these findings support the rationale for pursuing STK32C as a novel therapeutic target that could overcome the limitations of current anti-VEGF therapies and provide more durable suppression of tumour angiogenesis and growth.
Given that STAT3 is a central mediator of immunosuppressive signalling through downstream targets such as IL-10, TGF-β, and VEGF, it is plausible that STK32C may influence the tumour immune microenvironment via modulation of this axis. IL-6/STAT3 signalling is well known to drive the expression of these factors, promoting the recruitment of regulatory immune cells and suppression of anti-tumour immunity. While the direct immunological role of STK32C has not been fully elucidated, our findings suggest it may potentiate STAT3 activity, implying a possible contribution to immune evasion mechanisms. Future studies exploring cytokine profiles and immune cell composition in STK32C-deficient models will be important to clarify this relationship.
In conclusion, our study proposed a model in which STK32C enhanced IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signalling, thereby upregulating VEGF-A and promoting angiogenesis in CRC (Fig. 6k). Given its role in supporting tumour growth and its association with poor prognosis, STK32C offered a promising target for therapeutic intervention. Future studies should explore the clinical potential of STK32C inhibitors in CRC treatment, potentially as an adjunct to existing therapies targeting angiogenesis and immune evasion pathways.
Data availability
The datasets and materials utilised in this research are fully provided within the manuscript.
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Pandey AK, Singhi EK, Arroyo JP, Ikizler TA, Gould ER, Brown J, et al. Mechanisms of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Inhibitor-associated Hypertension And Vascular Disease. Hypertension. 2018;71:e1–e8.
Saltz LB. Bevacizumab in colorectal cancer: it should have worked. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1469–70.
Smeets D, Miller IS, O’Connor DP, Das S, Moran B, Boeckx B, et al. Copy number load predicts outcome of metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving bevacizumab combination therapy. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4112.
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, et al. Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:1445–51.
Chen Y, Wang J, Wang X, Liu X, Li H, Lv Q, et al. STAT3, a Poor Survival Predicator, Is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis from Breast Cancer. J breast cancer. 2013;16:40–9.
Macha MA, Matta A, Kaur J, Chauhan SS, Thakar A, Shukla NK, et al. Prognostic significance of nuclear pSTAT3 in oral cancer. Head Neck. 2011;33:482–9.
Ludwig H, Nachbaur DM, Fritz E, Krainer M, Huber H. Interleukin-6 is a prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood. 1991;77:2794–5.
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A, Bhatt AN. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol : J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2016;37:11553–72.
Nozawa H, Chiu C, Hanahan D. Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:12493–8.
Nagasaki T, Hara M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi H, Sato M, Takeyama H. Interleukin-6 released by colon cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis: anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and inhibited tumour-stroma interaction. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:469–78.
Bournazou E, Bromberg J. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: JAK-STAT3 signaling. Jak-stat. 2013;2:e23828.
Walter M, Liang S, Ghosh S, Hornsby PJ, Li R. Interleukin 6 secreted from adipose stromal cells promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2009;28:2745–55.
Chang Q, Bournazou E, Sansone P, Berishaj M, Gao SP, Daly L, et al. The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and metastasis. Neoplasia. 2013;15:848–62.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer-new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:97–105.
Dempster EL, Wong CC, Lester KJ, Burrage J, Gregory AM, Mill J, et al. Genome-wide methylomic analysis of monozygotic twins discordant for adolescent depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;76:977–83.
Qin H, Wang Z, Du W, Lee WH, Wu X, Riggs AD, et al. Killer cell Ig-like receptor (KIR) 3DL1 down-regulation enhances inhibition of type 1 diabetes by autoantigen-specific regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:2016–21.
Kang DD, Lin Y, Moreno JR, Randall TD, Khader SA. Profiling early lung immune responses in the mouse model of tuberculosis. PloS one. 2011;6:e16161.
Beaver LM, Buchanan A, Sokolowski EI, Riscoe AN, Wong CP, Chang JH, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals a dynamic and differential transcriptional response to sulforaphane in normal and prostate cancer cells and suggests a role for Sp1 in chemoprevention. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014;58:2001–13.
Antal CE, Hudson AM, Kang E, Zanca C, Wirth C, Stephenson NL, et al. Cancer-associated protein kinase C mutations reveal kinase’s role as tumor suppressor. Cell. 2015;160:489–502.
Qian X, Li X, Lu Z. Protein kinase activity of the glycolytic enzyme PGK1 regulates autophagy to promote tumorigenesis. Autophagy. 2017;13:1246–7.
Buschbeck M. Strategies to overcome resistance to targeted protein kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Drugs RD. 2006;7:73–86.
Cohen P. Protein kinases-the major drug targets of the twenty-first century?. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:309–15.
Wallerstedt E, Smith U, Andersson CX. Protein kinase C-delta is involved in the inflammatory effect of IL-6 in mouse adipose cells. Diabetologia. 2010;53:946–54.
Jain N, Zhang T, Fong SL, Lim CP, Cao X. Repression of Stat3 activity by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Oncogene. 1998;17:3157–67.
Fu AK, Fu WY, Ng AK, Chien WW, Ng YP, Wang JH, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 phosphorylates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and regulates its transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:6728–33.
Le X, Nilsson M, Goldman J, Reck M, Nakagawa K, Kato T, et al. Dual EGFR-VEGF Pathway Inhibition: A Promising Strategy for Patients With EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16:205–15.
Perez-Gutierrez L, Ferrara N. Biology and therapeutic targeting of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:816–34.
Acknowledgements
No additional acknowledgements to report.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. R2022MH194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZX and CC conceptualised the study and prepared the manuscript draft. ZX and JMX carried out the experiments and performed data analysis. CYL contributed to data acquisition and analysis. LFJ and QH oversaw the project and provided guidance.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Qilu Hospital, Shandong University (Approval No. KYLL-2021(ZM)-209). Informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study. This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed and agreed upon the final version of the manuscript for submission and publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Jin, M., Chu, Y. et al. STK32C activated IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling and promoted tumor angiogenesis. Br J Cancer 134, 60–71 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03245-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03245-5