Abstract
Ruthenium dioxide has attracted extensive attention as a promising catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in acid. However, the over-oxidation of RuO2 into soluble H2RuO5 species results in a poor durability, which hinders the practical application of RuO2 in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Here, we report a confinement strategy by enriching a high local concentration of in-situ formed H2RuO5 species, which can effectively suppress the RuO2 degradation by shifting the redox equilibrium away from the RuO2 over-oxidation, greatly boosting its durability during acidic oxygen evolution. Therefore, the confined RuO2 catalyst can continuously operate at 10 mA cm–2 for over 400 h with negligible attenuation, and has a 14.8 times higher stability number than the unconfined RuO2 catalyst. An electrolyzer cell using the confined RuO2 catalyst as anode displays a notable durability of 300 h at 500 mA cm–2 and at 60 °C. This work demonstrates a promising design strategy for durable oxygen evolution reaction catalysts in acid via confinement engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE) has been commercialized as an important technology for producing green hydrogen via electrocatalytic water splitting, as it could offer many prominent advantages, such as high current density, compact device design, high H2 purity, and fast current response1,2,3,4. In PEMWE, the anodic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) as the bottleneck reaction suffers from a sluggish four-electron transfer process. The strongly acidic and highly oxidative environment at the anode further puts stringent requirements on the design of efficient OER catalysts1,5,6. At the current stage, the acidic OER catalysts in PEMWE rely highly on the use of iridium (Ir)-based catalysts on account of their good stability7,8,9. However, the low abundance and high cost of Ir metal limit the wide application of PEMWE. Ruthenium dioxide (RuO2), with relatively low cost and high activity, has attracted broad attention as a promising acidic OER catalyst10,11,12,13,14. Yet still, the long-term durability of RuO2 remains a major challenge in acidic electrolyte.
According to the prior experimental results and calculated Pourbaix diagram15,16,17,18, the over-oxidation of RuO2 into soluble high-valence H2RuO5 species (RuO52– ion) at high anodic potentials has been widely recognized as the primary mechanism of RuO2 degradation. Currently, there are generally two classes of strategies to extend the operating life of RuO2. One aims at improving the OER activity to lower the required overpotential for the catalyst at a specific current density; a diverse range of methods, such as strain engineering11,19,20,21, defect engineering22,23,24,25, doping engineering9,14,26,27,28,29,30,31, and heterostructure engineering32,33,34, have been explored to optimize the adsorption energy between the modified RuO2 and oxygenated intermediates, thus improving the OER activity. Another strategy is to introduce electron-donating dopants to lower the Ru oxidation state and suppress the dissolution12,31,35,36,37,38. For example, Qiao et al. reported a dynamic electron accepting–donating process on Re-doped RuO2 catalyst, in which the Re dopant could accept electrons to activate the Ru site at low potentials, and then donate electrons back to prevent RuO2 from over-oxidation at high potentials35. However, the introduction of additional elements into RuO2 lattice increases the risk of forming coordinatively unsaturated Ru sites, leading to the demetallation of surface Ru sites and thus the deteriorated stability39,40,41. Therefore, it is highly desired to develop new strategies to improve the durability of Ru-based OER catalysts.
Some previous reports have revealed that hollow catalysts with a prominent confinement effect could enrich reaction intermediates in the hollow cavities during electrocatalytic CO2 reduction42,43. We infer that a high local concentration of in-situ formed H2RuO5 species could suppress RuO2 degradation by shifting the thermodynamic redox equilibrium away from RuO2 over-oxidation. To validate this inference, we designed a composite catalyst featuring RuO2 nanoparticles spatially confined within honeycomb-like antimony-doped tin dioxide (ATO) support (denoted as h-ATO/RuO2). Compared with ATO-supported unconfined RuO2 catalyst, the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst exhibited a similar OER activity but much more enhanced OER stability, running stably for over 400 h at 10 mA cm–2 with negligible degradation in acidic electrolytes. Multiple characterizations revealed that the confinement effect endows h-ATO/RuO2 with a higher resistance against oxidation and dissolution in acidic OER, which could be attributed to the enriched local concentration of dissolved high-valence Ru species. Furthermore, when used as the anode in a PEMWE device, the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst demonstrated a good durability of 300 h at a water-splitting current density of 500 mA cm–2 and at 60 °C.
Results
Synthesis and characterization of catalysts
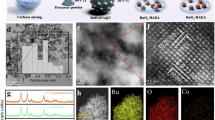
The confinement strategy was achieved by growing RuO2 particles on honeycomb-like ATO (h-ATO) support. We selected ATO as the oxide support on account of its good stability and electrical conductivity under acidic OER conditions44,45. The preparation process for the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst is illustrated in Fig. 1a (see the “Methods” section for details). We first synthesized polystyrene (PS) spheres as the templates, which were impregnated with tin salt and antimony salt precursors. Then the h-ATO support was obtained through heating the mixture in air at 500 °C to remove the PS template and simultaneously crystallize the ATO. Subsequently, RuO2 nanoparticles were in-situ grown on the pore walls of h-ATO support via a vacuum degassing process followed by hydrothermal and annealing treatments, eventually forming the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst (Fig. 1a).
As shown in the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Figs. 1,2), the PS template has an average size of ~230 nm and the h-ATO support shows a honeycomb-like architecture with interconnected macropores (~180 nm in diameter). The macroporous structure did not affect the mass transport in the electrocatalytic reaction46,47,48. After RuO2 deposition, the resulting h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst well inherits the architecture of h-ATO (Fig. 1c and Supplementary Fig. 3), indicating that the deposition process did not impair the porosity of h-ATO. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed that small RuO2 nanoparticles with sizes of 5 ~ 10 nm are evenly distributed on the wall of h-ATO support (Fig. 1d, e and Supplementary Fig. 3). Inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) measurement of h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst gave a molar ratio of 41:15:1 for Ru:Sn:Sb and a corresponding mass fraction of ~70 wt% for RuO2, close to the initial feed ratio in catalyst synthesis. X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern for h-ATO support (Supplementary Fig. 4) displayed the characteristic peaks of SnO2 phase (JCPDS no. 41-1445). For h-ATO/RuO2 (Supplementary Fig. 4), the XRD peaks except for SnO2 could be attributed to the rutile RuO2 phase (JCPDS no. 41-1445). High-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst revealed the clear lattice spacings for RuO2(110) and SnO2(110) planes (Fig. 1f). Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) elemental mapping (Fig. 1g and Supplementary Fig. 5) further confirmed the spatial confinement of RuO2 nanoparticles within the pores of h-ATO support for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst.
We also prepared a comparison sample without the confinement effect, in which RuO2 nanoparticles were grown on the surface of spherical-like ATO (denoted as s-ATO/RuO2, Supplementary Figs. 6,7). Furthermore, RuO2 without ATO support (denoted as RuO2) was also synthesized, and we noticed some agglomeration of the RuO2 nanoparticles in this sample (Supplementary Fig. 8). We then compared with the chemical states of Ru and Sn elements for different samples using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and no electronic transfer was observed between the RuO2 and ATO support (Supplementary Fig. 9).
Electrocatalytic OER in acidic electrolytes
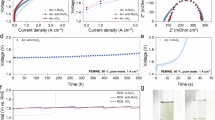
We first assessed the acidic OER performance in 0.5 M H2SO4 electrolyte using a conventional three-electrode system. Figure 2a and Supplementary Fig. 10 shows the linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves for different catalysts. To reach a current density of 10 mA cm–2, our as-prepared RuO2 required an overpotential of 255 ± 5 mV with iR-correction, lower than that for commercial RuO2 (Com-RuO2, 327 ± 10 mV). For the two ATO-supported RuO2 samples, i.e. h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2, the overpotentials at 10 mA cm–2 were 216 ± 4 mV and 220 ± 3 mV, respectively. The ATO support was catalytically inert for OER and delivered no OER current within the measured voltage range (Supplementary Fig. 11). Compared with RuO2, the improved OER activity for ATO-supported RuO2 samples could be attributed to the effective distribution of RuO2 nanoparticles on ATO support. In addition, h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 exhibited a similar OER activity (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. 12), indicating that the difference in ATO morphology has little effect on their OER activities.
a LSV curves for different catalysts with 100% iR correction (R: 6 ± 0.3 Ω). Scan rate: 5 mV s–1. Electrolyte: O2–saturated 0.5 M H2SO4. Active RuO2 mass loading: 0.18 mg cm–2. Temperature: room temperature. b Tafel plots and c EIS Nyquist plots for different catalysts. d, e Accelerated degradation tests for h-ATO/RuO2 (d) and s-ATO/RuO2 (e). f Comparison of overpotentials for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 at 10 mA cm–2 for different cycles. g Chronopotentiometry curves for different catalysts at 10 mA cm–2. h Stability number (S-number) for different catalysts.
Tafel analysis (Fig. 2b) revealed that all samples have the Tafel slopes of ~60 mV dec-1 at low overpotential region, suggesting the similar OER catalytic mechanism behind them49,50. The Tafel slopes are also consistent with many reported values for RuO2-based catalysts13,50. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) recorded at 1.45 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) showed that the ATO-supported RuO2 samples had small charge transfer resistances (Fig. 2c). We further performed the electrochemical double-layer capacitance tests (Supplementary Fig. 13) to determine the electrochemically active surface area (ECSA). The ECSA values for h-ATO/RuO2, s-ATO/RuO2, RuO2, and Com-RuO2 were 133, 121, 51, and 34 cm2, respectively. The ECSA-normalized OER kinetic current density demonstrated the similar intrinsic OER activities for the h-ATO/RuO2, s-ATO/RuO2, and RuO2 samples (Supplementary Fig. 14), suggesting the enhanced geometric OER activity for ATO-supported RuO2 catalysts in Fig. 2a arising from the high surface area exposure. In addition, the lowest intrinsic OER activity for Com-RuO2 (Supplementary Fig. 14) could be attributed to the different synthesis methods between as-prepared RuO2 and Com-RuO2.
These results above revealed that h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2, despite their different ATO morphologies, have the comparable geometric and intrinsic OER activities (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. 14). On the basis of it, we went on to compare the two samples in stability. We first evaluated the stability using the accelerated degradation tests (ADT). After 4000 cycles, the LSV curves for h-ATO/RuO2 were unchanged (Fig. 2d). By comparison, the OER activity for s-ATO/RuO2 declined substantially, with the overpotential at 10 mA cm–2 increased by ~100 mV (Fig. 2e, f), indicating the superior stability for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst. Then the long-term stability was further evaluated via chronopotentiometry method at a constant current density of 10 mA cm–2 (Fig. 2g). The OER activity for Com-RuO2 degraded within several hours, consistent with the results reported previously4,12,30. RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 both showed a moderately improved stability for ~100 h. Most impressively, h-ATO/RuO2 could extend the durability time to 400 h with a very small voltage increase of ~40 mV. The degradation rate for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst was as low as 100 μV h-1, much lower than that for s-ATO/RuO2 (544 μV h-1, Supplementary Fig. 15). We further determined the metal dissolution via ICP-MS test, and found a small dissolution of ~2.8% for Ru in h-ATO/RuO2 after 400 h (Supplementary Fig. 16 and Supplementary Table 1). Accordingly, the stability number (S-number, defined by Cherevko et al.51) was determined to be 2.64×105 for h-ATO/RuO2, which is 14.8-fold, 22-fold, and 334-fold higher than that for s-ATO/RuO2, RuO2, and Com-RuO2 catalysts (Fig. 2h and Supplementary Table 1). These results qualify h-ATO/RuO2 as one of the most stable Ru-based electrocatalysts reported thus far for acidic OER (Supplementary Table 2).
Understanding the enhanced stability on h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst
Multiple characterizations were performed to investigate the structural changes of the catalysts toward acidic OER process. The initial crystalline phase and surface morphology of h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst were still well retained after OER tests (Supplementary Figs. 17, 18). To uncover the origin of the resistance against oxidation and dissolution for h-ATO/RuO2, we carried out the ex-situ XPS to probe the chemical state changes of Ru and O elements before and after OER tests. The catalyst after OER tests was obtained by performing at 1.45 V versus RHE for 24 h. For the Ru 3p spectra (Fig. 3a), h-ATO/RuO2 exhibited an unchanged peak position after OER, whereas the peak position for the spent s-ATO/RuO2 was positively shifted by about 0.5 eV with respect to its pristine state (Fig. 3a), indicative of the increased Ru valence state for s-ATO/RuO2 after stability tests4,38,52. This implies that h-ATO/RuO2 could effectively prevent Ru from over-oxidation, which was also confirmed by the O 1 s spectra. The O 1 s spectra for the initial samples could be deconvoluted into three peaks at 529.3, 530.9, and 532.3 eV (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 19), corresponding to the lattice oxygen (O2–), hydroxyl groups (OH–), and adsorbed water (H2O), respectively10,53,54. For h-ATO/RuO2, the O2– proportion before and after the stability test decreased from 21.6% to 10.5% but still remained prominent, and the H2O proportion increased from 18.0% to 28.5% (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Fig. 20), indicative of the inevitable adsorption of water after OER, consistent with the previous reports4,36. In contrast, the initial O2– peak with a proportion of 21.1% for s-ATO/RuO2 became totally absent after OER test (Fig. 3b,c). Meanwhile, RuO2 and Com-RuO2 samples exhibited the similar lattice oxygen loss with s-ATO/RuO2 (Supplementary Figs. 19 and 20), which are different from h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst, indicating the stable structure for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst.
a, b High-resolution XPS spectra of Ru 3p (a) and O 1 s (b) for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 before and after OER. c The Ru 3p peak position and the O2– proportion for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 catalysts. d, e In situ ATR-SEIRAS spectra for h-ATO/RuO2 (d) and s-ATO/RuO2 (e) at potentials from 1.3 to 1.6 V versus RHE. f Area ratios of v(OH)s/v(OH)w for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 catalysts.
To monitor the dynamic structural evolution during OER, we further performed in situ attenuated total reflection surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy (ATR-SEIRAS) on the catalysts at different anodic potentials (Supplementary Fig. 21). For all ATR-SEIRAS spectra (Fig. 3d, e and Supplementary Fig. 22), the broad peaks at wavenumbers from ~3100 to ~3700 cm–1 were assigned to the O–H stretching mode of interfacial water. The O–H stretching peaks could be divided into three components using Gaussian fitting4,55,56, including ice-like water with strong O–H bonds (v(OH)s at ~3200 cm–1), liquid-like water with relatively weak O–H bonds (v(OH)w at ~3400 cm–1), and free water with isolated O–H bonds (v(OH)i at ~3600 cm–1). Accordingly, v(OH)s could be attributed to the strong binding of O–H groups with unsaturated Ru sites, and v(OH)w is related to the combination of lattice oxygen with water via H bonds4,57. The summary in Fig. 3f shows that as the anodic potential increased from 1.3 to 1.6 V, the area ratio of v(OH)s/v(OH)w for h-ATO/RuO2 kept nearly unchanged, whereas the ratio for s-ATO/RuO2 increased from 46.7% to 91.7%. Meanwhile, we also observed the similar increase of v(OH)s/v(OH)w area ratios for RuO2 and Com-RuO2 with the increased applied potential (Supplementary Fig. 22). This suggests the increased amounts of unsaturated Ru sites for s-ATO/RuO2, RuO2, and Com-RuO2 during OER, which is mainly caused by the loss of lattice oxygen, consistent with the XPS data above. These observations indicate that h-ATO/RuO2 with confinement effect exhibits a higher resistance against oxidation and dissolution than s-ATO/RuO2, which could suppress the Ru over-oxidation and lattice oxygen loss toward stable OER in acidic media.
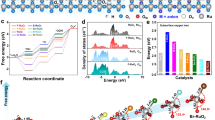
To further confirm the confinement effect on h-ATO/RuO2, we carried out the following experiment to estimate the local concentration of in-situ generated RuO52– ions near the catalyst surface. As shown in Fig. 4a, the experiment was performed in an H-type cell and the working electrode with the catalyst was first performed at 1.45 V versus RHE for 20 h tests, and then was took out from the solution. After removing the applied voltage, the electrode was rinsed in pure water, and the resulting solution was tested via ICP-MS. The results showed that the local Ru ions normalized by ECSA for h-ATO/RuO2 is 2.5 times higher in concentration than that for s-ATO/RuO2 catalyst (Fig. 4b), indicating the enriched RuO52– ions near the catalyst surface for h-ATO/RuO2. Meanwhile, we also measured the bulk Ru dissolved in the anolyte after 20 h tests and found that the Ru loss of 0.65% for h-ATO/RuO2 is much lower than that of 2.47% for s-ATO/RuO2 (Fig. 4c). It accords with the long-term stability result that h-ATO/RuO2 exhibited a very low Ru dissolution rate compared with s-ATO/RuO2 (Supplementary Table 1). These observations further confirm that the high local Ru concentration for h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst can suppress the Ru dissolution due to its confinement effect.
a Schematic illustration of the test process of local Ru concentration near the catalyst surface and bulk Ru dissolved in the anolyte. b Local Ru concentration near the catalyst surface normalized by ECSA for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 catalysts. c Bulk Ru dissolved in the anolyte after 20 h tests for h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 catalysts. The error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent measurements.
Furthermore, we conducted a finite-element analysis to simulate how a nanocavity structure helps to enrich the local concentration of in-situ formed species. We constructed a hollow hemispherical ATO shell with a RuO2 layer at the interior wall (as the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst), and a spherical ATO shell with a RuO2 layer at the exterior wall (as the s-ATO/RuO2 catalyst). Some effect factors, such as the surface charge and local pH, are not considered for a simplified simulation. As shown in Supplementary Fig. 23, it can be seen that the electric field for h-ATO/RuO2 is concentrated at the interior cavity, significantly stronger than that for s-ATO/RuO2. With the effects of the charge and mass transfer, we found that the cavity could obstruct the outward transport of in-situ formed RuO52– species, resulting in a higher RuO52– concentration locally within the cavity (Supplementary Fig. 24). These results from experiments and simulation indicate that the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst we designed here could help to enrich the high local concentration of RuO52– species via confinement effect, which could in turn shift the thermodynamic redox equilibrium away from the RuO2 over-oxidation, thereby conferring exceptional durability.
PEMWE performance study
Encouraged by the good stability of h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst, we further explored its potential application in a PEMWE device. The electrolyzer was constructed with h-ATO/RuO2 as the anode catalyst, commercial Pt/C as the cathode catalyst, and Nafion 115 as the membrane (Fig. 5a). The current–voltage curves in Fig. 5b show that the h-ATO/RuO2-based electrolyzer required cell voltages of only 1.60 and 1.73 V (without iR correction) to deliver water-splitting current densities of 500 and 1000 mA cm–2 at 60 °C, respectively, much lower than those for Com-RuO2-based counterpart (1.83 and 2.15 V). Moreover, the h-ATO/RuO2 could operate stably at 500 mA cm–2 for 300 h with a small voltage increase (Fig. 5c). The summary on the performances of previously documented PEMWE devices (Supplementary Table 3) reveals that h-ATO/RuO2 exhibits the good stability among these Ru-based OER anode catalysts.
a Schematic illustration of PEMWE device. b The I-V curves of PEMWE device using h-ATO/RuO2 or Com-RuO2 as the anode catalyst at 60 °C. c Chronopotentiometry curve of PEMWE device using h-ATO/RuO2 as anode catalyst operated at 500 mA cm–2 and at 60 °C. The cell voltages were reported here without iR correction.
Discussion
In conclusion, we developed a confinement strategy on h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst that exhibited a robust OER stability for 400 h at 10 mA cm–2 in acidic media, with stability number 14.8 times higher than for unconfined s-ATO/RuO2 catalyst. Multiple characterizations revealed that h-ATO/RuO2 displayed a higher resistance against oxidation and dissolution during acidic OER, which could be attributed to the enriched local concentration of dissolved Ru ions via confinement effect, shifting the thermodynamic redox equilibrium away from RuO2 over-oxidation. Furthermore, the assembled PEMWE cell based on h-ATO/RuO2 anode catalyst achieved a notable durability of 300 h at 500 mA cm–2 and at 60 °C. This work demonstrates an effective and feasible strategy via confinement engineering for developing low-cost and high-efficiency OER catalysts for practical PEMWE application.
Methods
Catalyst preparation
Chemicals
Styrene (99%), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP, 99%), K2S2O8 (99%), SnCl4 (99.9%), Sb(CH3COO)3 (98%), RuCl3 (99%), and H2SO4 (98%) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd. All of chemicals were used as received without further purification treatment.
Synthesis of PS
We first synthesized the polystyrene (PS) template by a microemulsion polymerization method58. Briefly, 32.5 mL of styrene was mixed with 250 mL of H2O containing 1.25 g of PVP with magnetic stirring at 94 °C for 30 min under nitrogen protection. Then 25 mL of K2S2O8 (0.5 g) aqueous solution was added into the above solution to induce the polymerization. After keeping stirring at 94 °C for 24 h, the resulting mixture was washed and dried for the subsequent use.
Synthesis of h-ATO/RuO2
The PS powder (280 mg) was dispersed in a mixed solution of SnCl4 (0.19 mmol) and Sb(CH3COO)3 (0.01 mmol) solution, which was slowly heated to evaporate the solvent. The molar ratio of Sb/(Sb + Sn) was chosen to be 5% on account of the high conductivity45. The resulting mixture was annealed at 500 °C for 1 h in air to remove the PS template and obtain the honeycomb-like ATO (h-ATO) support. Subsequently, h-ATO powder (10 mg) was dispersed in an aqueous solution (20 ml) containing RuCl3 (32 mg), and the solution pH value was adjusted to about 7. The above solution was treated with vacuum degassing to make the h-ATO support filled with RuCl3 solution. After a hydrothermal reaction at 120 °C for 6 h, the product was centrifuged, washed, and dried, which was further annealed at 250 °C for 2 h in air to obtain the h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst.
Synthesis of s-ATO/RuO2 and RuO2
The synthesis of s-ATO/RuO2 is similar with that of h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst except for replacing the pristine PS with the sulfonated PS template. In brief, PS powder (300 mg) was mixed with 12 mL concentrated H2SO4, which was heated at 40 °C for 6 h to prepare the sulfonated PS template59. The sulfonation treatment could introduce the negative charge on the PS surface and the Sn/Sb cations can be uniformly adsorbed by electrostatic force, thus resulting in the formation of ATO with hollow spherical-like morphology (not a honeycomb-like morphology). The synthesis of RuO2 is similar with that of h-ATO/RuO2 catalyst but without adding the h-ATO support.
Characterizations
XRD patterns were carried out using a Rigaku SmartLab 9 kW equipped with Cu-Kα radiation (λ, 1.5418 Å). SEM images were recorded on an FEI Verios 460 L scanning electron microscope. TEM and HRTEM images were taken on an FEI Talos F200X transmission electron microscope. XPS measurements were performed on a Thermo Scientific ESCALAB250Xi photoelectron spectrometer equipped with Al Kα (1486.6 eV) as the X-ray source. ICP-MS results were obtained from a Thermo Scientific iCAP RQ instrument. Raman spectra were collected on a LabRAM HR Evolution Confocal Raman Microscope equipped with an aberration-corrected Czerny Turner total reflection spectrometer (HORIBA JY). In situ ATR-IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet iS50 FT-IR spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) equipped with MCT-A detector at different applied potentials.
Electrochemical measurements in a three-electrode system
The OER electrochemical measurements were conducted in O2-saturated 0.5 M H2SO4 electrolyte (pH, 0.4 ± 0.03) on CHI 760E electrochemical workstation. For the electrolyte preparation, 5.56 mL of H2SO4 was diluted to 200 mL aqueous solution, which was directly used for electrochemical tests without storage. The standard three-electrode cell included a glassy carbon electrode with area of 0.196 cm2, an Ag/AgCl (3.5 M KCl) electrode, and a platinum plate as the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, respectively. The reported potentials with respect to RHE scale were calculated from the following equation: ERHE = EAg/AgCl + 0.059 pH + 0.196 V. The catalyst ink was prepared by dispersing catalyst powder (5 mg) in 0.96 mL ethanol and 0.04 mL Nafion solution (5 wt%) via ultrasonication. We kept the same mass loading of active RuO2 component for different catalysts. For h-ATO/RuO2 and s-ATO/RuO2 catalysts, 10 μL ink was coated on glassy carbon electrode, yield a loading of ~0.25 mg cm–2 for total mass and ~0.18 mg cm–2 for active RuO2 component. For RuO2 and Com-RuO2 (Adamas beta, 99%) catalysts, 7 μL ink was coated on glassy carbon electrode, yield a loading of ~0.18 mg cm–2 for RuO2.
The OER polarization curves were recorded between 1.0 V and 1.7 V versus RHE at a scan rate of 5 mV s–1 with a rotation rate of 1600 rpm. The EIS test was carried out in a frequency range from 100 kHz to 0.1 Hz at 1.45 V versus RHE with a voltage amplitude of 5 mV. The long-term stability was assessed via a chronopotentiometry test at a fixed current density of 10 mA cm–2. Carbon cloth-supported catalysts (area: 1 cm2) with active RuO2 loading of 0.7 mg cm–2 was used as the working electrode. The working electrode was separated from the counter electrode by Nafion 117 (183 μm) membrane in an H-type cell to avoid the re-deposition of dissolved Ru on the counter electrode for the accurate determination of dissolved Ru amounts. All potentials reported here were corrected by iR compensation in the three-electrode system, where R was 6 ± 0.3 Ω from the EIS test.
The ECSA was determined by: ECSA = Cdl/Cs, where Cdl is the double-layer capacitance of sample and Cs is the specific capacitance. A typical value of 0.035 mF cm–2 was widely used for Cs according to the previous reports10,60,61, and the Cdl was obtained from the ECSA tests (Supplementary Figs. 13 and 14). The S-number51 was determined by: S = nO2 / nRu, where nO2 is the total molar number of evolved oxygen and nRu is the total dissolved Ru obtained from ICP-MS measurement.
Electrochemical measurements in a PEMWE device
Ru-based materials and commercial Pt/C (20 wt%) were used as the anode and cathode catalysts, respectively. To prepare the anode or cathode catalyst ink, the catalyst powder was dispersed in a mixture of isopropanol and water (3:1) solvent and Nafion solution (5 wt%) with amount of 30 wt% was added as the binder. The mass loadings of anode and cathode catalysts were controlled to be about 2 mgRuO2 cm–2 and 1 mgPt/C cm–2, respectively. The membrane electrode assembly (MEA) was prepared through a decal transfer process. The catalyst was first coated onto a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) substrate, and then the PTFE-supported anode catalyst, Nafion 115 (127 μm) membrane, and PTFE-supported cathode catalyst were fixed together using a hot pressing treatment (130 °C, 2 min, 5 MPa). The catalyst-coated membrane was obtained after peeling off the PTFE substrate. A Pt-coated Ti felt (0.4 mm thick Ti felt with 0.5 μm Pt coating) and a carbon paper were used as anode and cathode porous transport layers, respectively. Finally, MEA, porous transport layer, and gasket were assembled into an electrolyzer.
The PEMWE electrolyzer was operated at 60 °C, and the anode chamber was fed with pure deionized water by a peristaltic pump. The I-V curves were recorded under the steady-state conditions by fixing the currents for 10 min and then recording the required voltages. The stability was evaluated via a chronopotentiometry test at 500 mA cm–2. All cell voltages in the PEMWE electrolyzer were reported without iR correction.
Finite-element analysis
The models for finite-element analysis were constructed in COMSOL Multiphysics 6.1 as three-dimensional models. For models, a mesh comprising tetrahedral elements was used, and a quadratic shape function was used to discretize the concentration field and the electric potential field. The modules of “transport of dilute species” and “electric current” were used. The electrolyte (0.5 M H2SO4) was assumed to have an electric conductivity of 19.8 S m–1, and a relative permittivity of 80. The diffusivity of RuO52– species in the electrolyte was set as 1.98 × 10–9 m2 s–1. A separated solver was employed. For the solution within the diffusion layer, convective mass transport was neglected, and only the effects of diffusion and electromigration were taken into consideration. The governing equations for steady-state mass transport and electric current in this specific study read:
in which C stands for the RuO52– species concentration, D for the diffusivity, φ for the electric potential, σ for the electric conductivity of the electrolyte, and z, F, R, T for their respective conventional meanings.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the paper and Supplementary Information files. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Chong, L. et al. La- and Mn-doped cobalt spinel oxygen evolution catalyst for proton exchange membrane electrolysis. Science 380, 609–616 (2023).
Ram, R. et al. Water-hydroxide trapping in cobalt tungstate for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Science 384, 1373–1380 (2024).
Spoeri, C., Kwan, J. T. H., Bonakdarpour, A., Wilkinson, D. & Strasser, P. The stability challenges of oxygen evolving electrocatalysts: towards a common fundamental understanding and mitigation of catalyst degradation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 5994–6021 (2017).
Xue, Y. et al. Stabilizing ruthenium dioxide with cation-anchored sulfate for durable oxygen evolution in proton-exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Nat. Commun. 14, 8093 (2023).
Li, L., Wang, P., Shao, Q. & Huang, X. Recent progress in advanced electrocatalyst design for acidic oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004243 (2021).
Seitz, L. C. et al. A highly active and stable IrOx/SrIrO3 catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Science 353, 1011–1014 (2016).
Zheng, Y.-R. et al. Monitoring oxygen production on mass-selected iridium–tantalum oxide electrocatalysts. Nat. Energy 7, 55–64 (2021).
Li, A. et al. Atomically dispersed hexavalent iridium oxide from MnO2 reduction for oxygen evolution catalysis. Science 384, 666–670 (2024).
Hao, S. et al. Dopants fixation of ruthenium for boosting acidic oxygen evolution stability and activity. Nat. Commun. 11, 5368 (2020).
Wu, Z.-Y. et al. Non-iridium-based electrocatalyst for durable acidic oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Nat. Mater. 22, 100–108 (2023).
Yao, Y. et al. Engineering the electronic structure of single atom Ru sites via compressive strain boosts acidic water oxidation electrocatalysis. Nat. Catal. 2, 304–313 (2019).
Sun, P. et al. Designing 3d transition metal cation-doped MRuOx as durable acidic oxygen evolution electrocatalysts for PEM water electrolyzers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 15515–15524 (2024).
Rao, R. R. et al. Operando identification of site-dependent water oxidation activity on ruthenium dioxide single-crystal surfaces. Nat. Catal. 3, 516–525 (2020).
Li, L. et al. Lanthanide-regulating Ru-O covalency optimizes acidic oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 15, 4974 (2024).
Iwakura, C., Hirao, K. & Tamura, H. Anodic evolution of oxygen on ruthenium in acidic solutions. Electrochim. Acta 22, 329–334 (1977).
Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. & Heitbaum, J. Oxygen evolution on Ru and RuO2 electrodes studied using isotope labelling and on-line mass spectrometry. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 237, 251–260 (1987).
Rard, J. A. Chemistry and thermodynamics of ruthenium and some of its inorganic compounds and aqueous species. Chem. Rev. 85, 1–39 (1985).
Wang, Z., Guo, X., Montoya, J. & Nørskov, J. K. Predicting aqueous stability of solid with computed Pourbaix diagram using SCAN functional. NPJ Comput. Mater. 6, 160 (2020).
Qin, Y. et al. RuO2 electronic structure and lattice strain dual engineering for enhanced acidic oxygen evolution reaction performance. Nat. Commun. 13, 3784 (2022).
Xu, Y. et al. Strain-modulated Ru-O Covalency in Ru-Sn oxide enabling efficient and stable water oxidation in acidic solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202316029 (2024).
He, W. et al. Grain-boundary-Rich RuO2 porous nanosheet for efficient and stable acidic water oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202405798 (2024).
Zhang, L. et al. Sodium-decorated amorphous/crystalline RuO2 with rich oxygen vacancies: a robust ph-universal oxygen evolution electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 18821–18829 (2021).
Ge, R. et al. Ultrafine defective RuO2 electrocatayst integrated on carbon cloth for robust water oxidation in acidic media. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1901313 (2019).
Zhao, Z. L. et al. Boosting the oxygen evolution reaction using defect-rich ultra-thin ruthenium oxide nanosheets in acidic media. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 5143–5151 (2020).
Yan, H., Jiang, Z., Deng, B., Wang, Y. & Jiang, Z.-J. Ultrathin carbon coating and defect engineering promote RuO2 as an efficient catalyst for acidic oxygen evolution reaction with super-high durability. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2300152 (2023).
Chen, S. et al. Mn-doped RuO2 nanocrystals as highly active electrocatalysts for enhanced oxygen evolution in acidic media. ACS Catal. 10, 1152–1160 (2020).
Wang, Y. et al. Unraveling oxygen vacancy site mechanism of Rh-doped RuO2 catalyst for long-lasting acidic water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 14, 1412 (2023).
Jianwei, S. et al. Assembling ultrasmall copper‐doped ruthenium oxide nanocrystals into hollow porous polyhedra: highly robust electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution in acidic media. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801351 (2018).
Wang, J. et al. Single-site Pt-doped RuO2 hollow nanospheres with interstitial C for high-performance acidic overall water splitting. Sci. Adv. 8, eabl9271 (2022).
Ping, X. et al. Locking the lattice oxygen in RuO2 to stabilize highly active Ru sites in acidic water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 15, 2501 (2024).
Liu, H. et al. Eliminating over-oxidation of ruthenium oxides by niobium for highly stable electrocatalytic oxygen evolution in acidic media. Joule 7, 558–573 (2023).
Sun, S.-C. et al. Bifunctional WC-supported RuO2 nanoparticles for robust water splitting in acidic media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202202519 (2022).
Zhou, L. et al. Stabilizing non-iridium active sites by non-stoichiometric oxide for acidic water oxidation at high current density. Nat. Commun. 14, 7644 (2023).
Hao, Y. et al. Polarized ultrathin BN induced dynamic electron interactions for enhancing acidic oxygen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202402018 (2024).
Jin, H. et al. Dynamic rhenium dopant boosts ruthenium oxide for durable oxygen evolution. Nat. Commun. 14, 354 (2023).
Zhang, D. et al. Construction of Zn-doped RuO2 nanowires for efficient and stable water oxidation in acidic media. Nat. Commun. 14, 2517 (2023).
He, J., Li, W., Xu, P. & Sun, J. Tuning electron correlations of RuO2 by co-doping of Mo and Ce for boosting electrocatalytic water oxidation in acidic media. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 298, 120528 (2021).
Shi, Z. et al. Customized reaction route for ruthenium oxide towards stabilized water oxidation in high-performance PEM electrolyzers. Nat. Commun. 14, 843 (2023).
Zagalskaya, A. & Alexandrov, V. Role of defects in the interplay between adsorbate evolving and lattice oxygen mechanisms of the oxygen evolution reaction in RuO2 and IrO2. ACS Catal. 10, 3650–3657 (2020).
Dickens, C. F. & Nørskov, J. K. A theoretical investigation into the role of surface defects for oxygen evolution on RuO2. J. Phys. Chem. C. 121, 18516–18524 (2017).
Klyukin, K., Zagalskaya, A. & Alexandrov, V. Role of dissolution intermediates in promoting oxygen evolution reaction at RuO2(110) surface. J. Phys. Chem. C. 123, 22151–22157 (2019).
Zhuang, T.-T. et al. Copper nanocavities confine intermediates for efficient electrosynthesis of C3 alcohol fuels from carbon monoxide. Nat. Catal. 1, 946–951 (2018).
Yang, P.-P. et al. Protecting copper oxidation state via intermediate confinement for selective CO2 electroreduction to C2+ fuels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 6400–6408 (2020).
Han, B. et al. Screening oxide support materials for OER catalysts in acid. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, F813 (2018).
Xu, J. et al. Antimony doped tin oxides and their composites with tin pyrophosphates as catalyst supports for oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 18629–18640 (2012).
Qi, J., Zhang, W. & Cao, R. Porous materials as highly efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. ChemCatChem 10, 1206–1220 (2018).
Li, Q. et al. Recent progress of hollow structure platform in assisting oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 452, 139232 (2023).
Wu, Z.-Y. et al. A general synthesis of single atom catalysts with controllable atomic and mesoporous structures. Nat. Synth. 1, 658–667 (2022).
Dickens, C. F., Kirk, C. & Nørskov, J. K. Insights into the electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction with ab initio calculations and microkinetic modeling: beyond the limiting potential volcano. J. Phys. Chem. C. 123, 18960–18977 (2019).
Shen, Y. et al. Cr dopant mediates hydroxyl spillover on RuO2 for high-efficiency proton exchange membrane electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 15, 7861 (2024).
Geiger, S. et al. The stability number as a metric for electrocatalyst stability benchmarking. Nat. Catal. 1, 508–515 (2018).
Zhu, W. et al. Stable and oxidative charged Ru enhance the acidic oxygen evolution reaction activity in two-dimensional ruthenium-iridium oxide. Nat. Commun. 14, 5365 (2023).
Rochefort, D., Dabo, P., Guay, D. & Sherwood, P. M. A. XPS investigations of thermally prepared RuO2 electrodes in reductive conditions. Electrochim. Acta 48, 4245–4252 (2003).
Foelske, A., Barbieri, O., Hahn, M. & Kötz, R. An x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of hydrous ruthenium oxide powders with various water contents for supercapacitors. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 9, A268 (2006).
Álvarez-Malmagro, J., Prieto, F., Rueda, M. & Rodes, A. In situ Fourier transform infrared reflection absortion spectroscopy study of adenine adsorption on gold electrodes in basic media. Electrochim. Acta 140, 476–481 (2014).
Chen, D.-J., Xu, B., Sun, S.-G. & Tong, Y. J. Electroless deposition of ultrathin Au film for surface enhanced in situ spectroelectrochemisrty and reaction-driven surface reconstruction for oxygen reduction reaction. Catal. Today 182, 46–53 (2012).
Lobo, A. & Conrad, H. Interaction of H2O with the RuO2(110) surface studied by HREELS and TDS. Surf. Sci. 523, 279–286 (2003).
Shen, K. et al. Ordered macro-microporous metal-organic framework single crystals. Science 359, 206–210 (2018).
Ren, S. et al. Hollow SnO2 microspheres and their carbon-coated composites for supercapacitors. Colloids Surf. A 444, 26–32 (2014).
McCrory, C. C. L., Jung, S., Peters, J. C. & Jaramillo, T. F. Benchmarking heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 16977–16987 (2013).
Lin, Y. et al. Chromium-ruthenium oxide solid solution electrocatalyst for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media. Nat. Commun. 10, 162 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFA1502902, T.-B.L.), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (21931007, T.-B.L.; 22375146 and 22109149, Z.-Y.Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.-Y.Y. conceived and designed the project. W.-X.Z. and X.-X.C. performed the experiments, collected and analyzed the data. P.-P.C. and C.Z. carried out the finite-element method simulations. L.-L.W., Y.D., G.-J.F., X.-R.W., and J.-J.L. provided the help to analyze the results. Z.-Y.Y. and T.-B.L. wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Iryna Zenyuk and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, WX., Cheng, XX., Chen, PP. et al. Boosting the durability of RuO2 via confinement effect for proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Nat Commun 16, 337 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55747-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55747-0