Abstract
The impact of Bariatric Surgery (BS) on maternal and neonatal outcomes among pregnant women is not fully understood, especially in comparison to different weight categories. The primary aim of this study is to assess the factors associated to women who have undergone BS. The study also investigates the maternal and neonatal outcomes amongst this group in comparison to the three Body Mass Index (BMI) groups (women with obesity, overweight and normal weight). A 12-month population-based retrospective study was conducted using registry data from the PEARL-Peristat Study at the Women's Wellness and Research Center (WWRC) in Qatar from January 1, 2017, through December 31, 2017. Both univariate and multivariable regression analyses were employed to scrutinize risk factors and maternal and neonatal outcomes. The study included 6212 parturient women, of which 315 had a history of BS, while 5897 with no BS history. Qatari women, aged 35 and higher, with parity > 1, diabetes, and hypertension were more likely to be in the post-BS group. Women in the post-BS group were found to be more likely to have a cesarean delivery (37.5% vs. 24%, Adjusted Odds Ratio (aOR) = 1.59, CI 1.18–2.14), preterm babies (10% vs. 7%, aOR = 1.66, CI 1.06–2.59), and stillbirth (1.6% vs. 0.4%, aOR = 4.53, CI 1.33–15.50) compared to the normal weight women group. Moreover, post-BS women had a higher risk of low-birth-weight neonates than women with obesity (15% vs. 8%, aOR = 1.77, CI 1.153–2.73), overweight (15% vs. 7%, aOR = 1.63, CI 1.09–2.43), and normal weight (15% vs. 8%, aOR = 1.838, CI 1.23–2.75). Finally, women in the post-BS group were more likely to have low-birth-weight neonates amongst term babies than women with obesity and overweight. Pregnancies with post-BS should be considered a high-risk group for certain medical outcomes and should be monitored closely. These findings may guide the future clinical decisions of antenatal and postnatal follow-up for post-BS women.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Obesity is a major public health concern. In 2022, there were 2.5 billion overweight adults aged 18 and older, of whom more than 890 million were living with obesity. This means that 43% of the adult population, including 43% of men and 44% of women, were overweight. This marks a significant rise from 1990, when only 25% of adults were overweight, World obesity Atlas projections indicated that obesity will increase from 38% of the world’s population in 2020 to over 50% by 20351,2. In 2012, a survey of 2496 adults in Qatar revealed that 70.1% were overweight, including 71.8% of men and 68.3% of women. Of these, 41.4% were obese, with obesity affecting 39.5% of men and 43.2% of women3.
Obesity is associated with several comorbidities including hypertension, musculoskeletal disorders, cancer, and type 2 diabetes4,5. Women with obesity of childbearing age experience additional complications such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and infertility6,7,8. Pregnant women with obesity and overweight have a higher incidence of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia9, spontaneous miscarriage10, labor induction, anesthesia-related complications, primary cesarean section, and perioperative morbidity plus longer hospital stays11,12,13. This leads to a substantial increase in healthcare costs.
Moreover, neonates of pregnant women with obesity face a higher risk of pre- and post-term birth complications such as small and large for gestational age (SGA/LGA), congenital anomalies14, and perinatal mortality15,16,17. Offspring of women with obesity may also experience health complications later in life, such as hypertension, diabetes or cardiovascular diseases18.
Weight reduction approaches to lower the risk of obesity complications for both mothers and neonates is challenging15,16. Bariatric surgery (BS) is one of the preferred procedure in women with severe obesity, demonstrating good health outcomes19,20. BS procedures are continually on the rise. Globally over 800,000 BS procedures have been performed across 61 countries and 17 national registries between 2014 and 201921.
Qatar has been actively combating obesity. Since 2011, HMC has performed over 10,000 BS surgeries; of those, 703 took place in 2022. Notably, in 2012 a significant milestone was achieved when the first bariatric robotic surgery was performed22.
There are limited studies on perinatal outcomes other than the size for gestational age and preterm birth23,24,25. The primary aim of this study is to assess the medical risk factors, and pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of pregnant women who have undergone bariatric surgery in comparison to pregnant women without a history of BS in Qatar.
Methods
Study design and data collection
This study utilised a 12-month, population-based retrospective study, conducted from January to December 2017, based on electronic medical record registry data from the PEARL-Peristat Study at WWRC, Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC) in Qatar26,27,28,29,30,31,32. This population-based registry was designed using routinely collected hospital data for parturient women and their offspring.
The study consisted of all singleton live births at 24+0 weeks’ gestation and above.
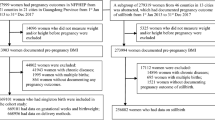
We excluded multiple-birth pregnancies due to their association with a higher occurrence of complications and variations in fetal growth. Out of 16,248 pregnancies, our study focused on 6212 singleton births with available data on post-bariatric surgery (BS) and body mass index (BMI). Among these, 315 were women had undergone BS. To form a comparison group, we included pregnancies in women without a history of BS, categorised as women with obesity (n = 1918), overweight (n = 1953), and normal weight controls (n = 2026). There were no exclusion criteria applied to any of the groups. This study complies with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki regarding for ethical research conduct and was approved by the Hamad Medical Corporation Institutional Review Board, with a waiver informed consent.
Maternal factors
The main outcome variable was Body mass index (BMI), which was examined and calculated as pre-pregnancy BMI or BMI during early pregnancy [i.e., at the first prenatal visit, depending on the availability of the relevant data: gestational age (< 13 weeks)] amongst all women. Early/pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) was calculated using the ratio of the pre-pregnancy or early booking weight (kg) divided by the measured height (m2). The derived early/pre-pregnancy BMI was grouped into four groups: underweight (≤ 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25 to 29.9 kg/m2), and women with obesity (≥ 30 kg/m2) following the NHLBI/WHO guidelines19,33. The women with obesity were then classified as women with a history of bariatric and women without a history of bariatric.
Accordingly, pregnant women were classified as having a normal weight, overweight, and women with obesity (with and without a history of bariatric surgery); underweight women were excluded as their inclusion was not relevant to the study's focus. Pregnancy outcomes were extracted as documented in the pregnant women notes or coding summaries.
Maternal demographic factors included age of the mother at delivery (< 35 years old vs. ≥ 35 years of age), and nationality (Qataris vs. other Arabs (based on the UNESCO list of Arab countries), and other nationalities). In addition, pregnancy factors included pregnancy mode (spontaneous vs. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) and Ovulation Induction (OI)), chronic/essential hypertension (yes vs. no) and if yes, pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH) (considered separately in the analyses), postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) (blood loss was defined as loss of ≥ 500 ml of blood for vaginal births or ≥ 1000 ml for caesarean delivery) and preeclampsia (PET); delivery mode (vaginal vs. caesarean) and if caesarean whether it was emergency vs. elective; and diabetes based on their glycemic status (none, overt diabetes mellitus (DM), and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)). For GDM analysis, women diagnosed with diabetes before pregnancy were excluded. In addition, the study included parity (nulliparous vs. parity 1–4 and parity ≥ 5). Parity classification was chosen to capture the specific demographic and clinical characteristics of our study population, which exhibits a high range of parity (0–11). Existing literature indicates that maternal and neonatal health outcomes vary significantly with parity levels. Higher parity (≥ 5) may be associated with increased risks of obstetric complications, and preterm birth, compared to lower parity (1–4). Additionally, high parity is linked with greater healthcare resource utilisation and different demographic characteristics, including maternal age and socioeconomic status. By using this classification, we ensure that our findings are comparable with other studies in the Middle East and reflective of the clinical realities in Qatar, providing relevant insights into maternal and neonatal health risks associated with varying parity levels34,35.
Neonatal factors
Neonatal factors included data about gestational age at time of delivery (Full term: = > 37 vs. extremely to very preterm: 24–31 weeks and moderate to late preterm: 32–36 weeks). Gestational age (GA) was based on the mother’s last menstrual period (LMP), early ultrasound scan (USS) and Ballard scoring19,33. The GA was classified in accordance with established international definitions20,36. In addition, the study included birth weight, which was classified into Low Birth Weight (LBW) (≤ 2499 g) and normal birth weight (≥ 2500 g) for the whole sample. Term births, those who were born at 37 weeks of gestational age or more, were also classified into LBW and normal birth weight, and included as a separate factor. Low Apgar scores at 1 and 5 min were defined as any score lower than 7. Finally, baby disposition, which was categorised into admission to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and stillbirth (fetal death at ≥ 22 completed weeks of gestation) was also included.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 28 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Categorical and binary variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, while interval variables were presented as means and standard deviations. Chi-square tests were employed to examine the associations between maternal and neonatal factors in one hand, and BMI categories versus post-bariatric surgery (post-BS) status on the other hand (post-BS women versus normal weight, overweight, and women with obesity). The same analytical approach was applied to compare BMI categories (normal weight, overweight, and women with obesity).
Risk Factors of post-BS: Univariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to assess the associations between maternal and neonatal factors (Independent Variables “IVs”) and post-BS status versus each BMI category as an outcome (Dependent Variable “DV”). Additionally, univariate logistic regressions were performed for the comparisons between BMI categories as outcomes. Crude odds ratios (cOR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated and reported.
Multiple logistic regression analyses were subsequently conducted, including variables that were significant at p < 0.05 in the univariate analyses as IVs, and post-BS status versus each BMI category as an outcome (DV). The same analytical approach was applied when the BMI comparisons as the outcomes. The final models reported adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95% CIs for the independent risk factors. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05 (two-tailed).
Outcomes of post-BS: On the other hand, the same approaches were employed to investigate the outcomes of BS when compared to BMI groups. Univariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to evaluate the associations between post-BS status and each BMI category (IVs) and various pregnancy outcomes (DVs). Additionally, univariate logistic regressions were performed to compare different BMI categories as risk factor of pregnancy outcomes. Crude odds ratios (cOR) with 95% CIs were calculated and reported. Subsequently, multiple logistic regression analyses were conducted, incorporating variables that were significant at p < 0.05 in the univariate analyses from the first stage (Risk factors of post-BS stage) as IVs, and the pregnancy outcomes as DVs. The final models reported adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95% CIs for the independent risk factors. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05 (two tailed).
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Hamad Medical Corporation Institutional Review Board.
Informed consent
The informed consent was waived by the Hamad Medical Corporation Institutional Review Board committee.
Results
Comparison analysis between the available data versus the missing data
A comparative analysis was conducted between cases with available data (n = 6212) and those with missing data on post-bariatric surgery (post-BS) and body mass index (BMI) (n = 10,036) concerning demographic and clinical variables. Significant differences were observed between these two groups. Data availability was higher among older mothers (≥ 35 years) compared to younger mothers (22.5% vs. 18.1%; p < 0.001). Additionally, essential hypertension was more prevalent amongst women who were included in the study (1.8% vs. 0.9%; p < 0.001). The mode of delivery also differed significantly, with cesarean delivery being more common among those with available data (32.5% vs. 28.4%; p < 0.001). Induced labor was more frequently reported in the data-available group (17.8% vs. 14.3%; p < 0.001), as was gestational diabetes mellitus (30.6% vs. 22.9%; p < 0.001). Elective Caesarean Section (CS) rates were higher among those with available data (52.5% vs. 48.3%; p < 0.01). Finally, the prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) was significantly greater in the data-available group (5.5% vs. 1.8%; p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in relation to the rest of the demographic and clinical factors.
Characteristics of the study population
A total of 6212 women who had singleton pregnancies from January 2017 to December 2017 comprising of post-BS (n = 315/6212; 5.07%) were included in the study. These were compared to women with obesity (n = 1918/6212; 30.87%), overweight (n = 1953/6212; 31.44%) and normal weight pregnant women (n = 2026/6212; 32.61%) with no history of weight loss surgeries.
The clinical characteristics and outcomes of the studied population are listed in Table 1. It shows general differences between post-BS, women with obesity, overweight, and normal groups of pregnant women in relation to demographic and clinical factors.
Pregnant women aged ≥ 35 years and Qataris are more likely to be in the post-BS group. They were also more likely to give birth to babies with low birth weight (< 2500 g) and have low Apgar score at 5 min. Women with obesity had a higher prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), chronic/essential hypertension, induction of labor, NICU admission and cesarean delivery compared to the other groups. Pregnant women with obesity are also more likely to be aged ≥ 35 years compared to the non-surgery BMI groups. Also, preterm birth was found to be more likely amongst women with obesity, overweight, and post-BS groups compared to normal.
Neonatal and maternal adverse events as risk factors for women in the post-bariatric surgery group compared to obesity, overweight, and normal weight groups
Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to assess the risk factors for post-BS, women with obesity and overweight in comparison to normal weight (Table 2). The results show that Qatari women, aged 35 years and above, DM, parity (higher than 1), and Essential Hypertension (EHTN) were significantly more likely to be from the obesity group in comparison to the normal weight group even after adjustment for other significant factors from the univariate analysis. The same results were found for the overweight pregnant women (except for EHTN) and post-BS (except for DM) (see Table 2).
When comparing post-BS with overweight pregnant women, it was found that that post-BS were significantly more likely to be Qataris and to have EHTN before and after adjustment. On the other hand, pregnant women with obesity in comparison to overweight were more likely to have multiple births (1–4 and > 5), DM, and EHTN even after adjustment for other significant factors from the univariate analysis. Finally, post-BS pregnant women were significantly more likely to be Qataris and less likely to be DM in comparison to pregnant women with obesity even after adjustment for other significant factors from the univariate analysis (see Table 3).
Outcomes for pregnant women post-BS, women with obesity, and overweight
Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to investigate outcomes in pregnant women with post-BS history and based on weight status (women with obesity, overweight, and normal weight) (Table 4).
The results indicated that all groups, including post-BS, obese, and overweight women, had significantly higher likelihoods of cesarean delivery compared to women with normal weight, even after adjusting for the significant risk factors from the univariate analysis at stage one.
Post-BS women were significantly more likely to have preterm, low birthweight (< 2500 g), or stillbirth babies compared to normal weight women, and were more likely to have low birthweight babies (including term low birth weight) compared to overweight and women with obesity, even after adjusting for the significant risk factors from the univariate analysis at stage one.
Pregnant women with obesity were also more likely to have PET and induced labor compared to women with normal weight, and induced labor was a significant outcome for obesity versus overweight women as well even after adjusting for the significant risk factors from the univariate analysis at stage one (Table 4).
Overweight women were more likely to have assisted births and extremely premature babies compared to women with obesity, even after adjusting for the significant risk factors from the univariate analysis at stage one. Both women with obesity and overweight had significantly higher odds of GDM compared to normal weight and post-BS women, with women with obesity being more likely to have GDM than overweight women even after adjusting for the significant risk factors from the univariate analysis at stage one (Table 4).
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the incidence of post-BS, and the factors associated with the post-BS group in comparison to other BMI weight status. In addition, we investigated the neonatal and maternal outcomes associated with obesity in parturient women, with a specific emphasis on those who conceived following BS. Unprecedented in Qatar, this research involved a classification of participants into four groups, leading to six unique comparisons. The study revealed that advanced maternal age, parity > 1, diabetes, and hypertension were significant risk factors, particularly in the context of post-BS.
Within three vital comparison groups (women with obesity vs. overweight, women with obesity vs. normal, and overweight vs. normal), our findings unequivocally demonstrated a heightened risk of maternal and neonatal adverse outcomes with increasing BMI index37. Noteworthy outcomes included gestational diabetes, caesarean deliveries, and labor induction, aligning seamlessly with extensive epidemiological studies and National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines for managing obesity in pregnancy38,39,40. Our findings contribute not only to the Qatari context but also provide a valuable benchmark for global discussions on the impact of obesity on pregnancy outcomes.
In the realm of post-BS comparison groups (BS vs. women with obesity, BS vs. overweight, BS vs. normal), a profound reduction in the risk of gestational diabetes among post-BS women stood out prominently. The significance of this reduction was stark when compared to both the women with obesity group with no history of BS and the overweight group with no history of BS. The findings also shed light on a significant reduction in assisted birth among post-BS women, an aspect that has been notably underexplored in existing literature.
Comparing our GDM reduction results with other meta-analyses revealed intriguing nuances. While our estimated reduction in the odds of GDM post-BS (aOR = 0.39, CI 0.29–0.54, P < 0.001) paralleled some studies, it also showcased variations compared to others23,25,41. This discrepancy emphasizes the importance of contextual factors and warrants further investigation into the underlying reasons for such variations. Notably, our study identified a paucity of epidemiological investigations on the five other comparison groups, signaling a critical gap in understanding the comprehensive spectrum of outcomes in post-BS women.
In addition, post-BS women showed a significant reduction in assisted birth compared to overweight (4% vs. 9%, aOR = 0.46, CI 0.21–0.99, P < 0.05). Numerous studies proved GDM risk reduction for women who conceived following BS23,25,37,38,41,42,43,44, however, a shortage of epidemiological studies concerning assisted birth specifically were identified45.
Despite the evident reduction in GDM risk, our study calls attention to the need for vigilant monitoring of post-BS women for potential complications inadequately mitigated by BS. Cesarean delivery and other risks, including term low birth weight, low birth weight, stillbirth, and preterm neonates, demand particular consideration. These results may be due to nutritional deficiency and rapid weight loss44.
Our findings concur with a substantial body of evidence indicating an increased risk of preterm deliveries, stillbirth, and low birth weight neonates among post-BS women12,16,23,25,33,42,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55. However, the scarcity of studies on low birth weight among term babies underscores the imperative for further investigation. Conflicting results on cesarean delivery42,56,57 highlight the multifaceted nature of this outcome among post-BS women, necessitating extended research to unravel its underlying complexities. These findings indicate the need for extended research on Caesarean Section (CS) and BS complications that are not fully understood and may be related to other factors, such as changes in maternal anatomy, fetal growth patterns, or other severe maternal complications.
The study provides valuable insights, though it is important to acknowledge a few areas for future improvement. The retrospective design introduces biases and limits causal inferences, and the use of 2017 data may not fully capture evolving trends or current clinical practices and healthcare advancements. While the study includes multinational and multi-ethnic groups, generalising findings beyond the Qatari population requires caution. The study also lacks detailed data on the specific types of bariatric surgery, weight gain during pregnancy, and the time between BS surgery and pregnancy; factors that could influence outcomes. Additionally, the absence of information on post-BS conditions like hypoglycemia or dumping syndrome in the context of alterations in maternal glucose metabolism may overlook important aspects of maternal and neonatal health. Furthermore, differences in data availability suggest skewness, particularly with older mothers and those with conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and caesarean deliveries. This overrepresentation may impact the applicability of results to younger or lower-risk populations. Future research with updated datasets and more detailed variables will strengthen these findings and expand their applicability. To improve generalisability, future studies should also aim for more representative samples and employ prospective, longitudinal designs to provide a dynamic understanding of obesity in pregnancy. Exploring the sophisticated factors contributing to the variability in GDM reduction across different studies is vital. In addition, investigating under-researched areas, such as assisted birth and the relationship between nutritional deficits and newborn weight, will further enrich our understanding of bariatric surgery's impact on pregnancy.
The strength of our study lies in its pioneering nature as the first in Qatar to comprehensively examine various risk factors in pregnant women post-BS compared to women with obesity, overweight, and normal-weight counterparts. The detailed examination of multiple comparison groups enriches the existing literature on obesity and pregnancy outcomes.
Conclusions
As obesity rates surge, our study highlights the inextricable link between obesity in women of childbearing age and adverse health conditions, particularly during pregnancy.
While BS proves instrumental in reducing obesity-related pregnancy complications, GDM, pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH), and macrosomia, it introduces potential risks that may result in adverse outcomes for both mothers and babies. These risks include nutritional deficiencies, anemia, changes in maternal glucose metabolism, and the possibility of having children who are small for gestational age58. These must be addressed proactively, ideally during preconception counselling. The identified gaps in literature call for further research to elucidate the correlation between nutritional deficits and newborn weight, thereby enhancing the holistic understanding of pregnancy outcomes in this unique demographic. Future studies should consider the interaction of genetic and environmental factors, utilising a precision medicine approach along with population health analyses59,60,61,62
Data availability
This is a research article and all data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article. All inquiries should be directed to Nader Al-Dewik: naldewik@hamad.qa.
Abbreviations
- OI:
-
Ovulation Induction
- WWRC:
-
Women's Wellness and Research Center
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
- BS:
-
Bariatric surgery
- CS:
-
Caesarean section
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- GDM:
-
Gestational diabetes mellitus
- HTN:
-
Hypertension
- EHTN:
-
Essential hypertension
- LBW:
-
Low birth weight
- NICU:
-
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- PPH:
-
Postpartum hemorrhage
- PIH:
-
Pregnancy-induced hypertension
- ART:
-
Assisted reproductive technology
- LBWT:
-
Low birth weight
- PET:
-
Pre-eclampsia
- PP obesity:
-
Postpartum obesity
References
Obesity and overweight. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesityand-overweight (World Health Organization, 2018).
World obesity. World Obesity Atlas 2023. (Accessed 17 June 2023) https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2023 (2024).
Mohideen, F. S. et al. Prevalence of multimorbidity among adults attending primary health care centres in Qatar: A retrospective cross-sectional study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 10(5), 1823 (2021).
Memish, Z. A. et al. Obesity and associated factors–Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2013. Prev. Chronic Dis. 11, E174 (2014).
Skubleny, D. et al. The impact of bariatric surgery on polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 26(1), 169–176 (2016).
Bateman, R. M. et al. 36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine: Brussels, Belgium, 15-18 March 2016. Crit. Care 20(Suppl 2), 94 (2016).
Christ, J. P. & Falcone, T. Bariatric surgery improves hyperandrogenism, menstrual irregularities, and metabolic dysfunction among women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Obes. Surg. 28(8), 2171–2177 (2018).
Sermondade, N. et al. Female obesity is negatively associated with live birth rate following IVF: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 25(4), 439–451 (2019).
Jeyabalan, A. Epidemiology of preeclampsia: Impact of obesity. Nutr. Rev. 71(Suppl 1), S18-25 (2013).
Boots, C. E., Bernardi, L. A. & Stephenson, M. D. Frequency of euploid miscarriage is increased in obese women with recurrent early pregnancy loss. Fertil. Steril. 102(2), 455–459 (2014).
Galtier-Dereure, F. et al. Weight excess before pregnancy: Complications and cost. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 19(7), 443–448 (1995).
Morin, K. H. Perinatal outcomes of obese women: A review of the literature. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 27(4), 431–440 (1998).
Ratner, R. E., Hamner, L. H. 3rd. & Isada, N. B. Effects of gestational weight gain in morbidly obese women: II: Fetal morbidity. Am. J. Perinatol. 7(4), 295–299 (1990).
Al-Dewik, N. et al. Prevalence, predictors, and outcomes of major congenital anomalies: A population-based register study. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 2198 (2023).
D’Souza, R. et al. Maternal body mass index and pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 1(4), 100041 (2019).
Fallatah, A. M. et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes among obese pregnant women in King Abdulaziz University Hospital: A retrospective single-center medical record review. Med. Arch. 73(6), 425–432 (2019).
Stothard, K. J. et al. Maternal overweight and obesity and the risk of congenital anomalies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 301(6), 636–650 (2009).
Patel, N., Pasupathy, D. & Poston, L. Determining the consequences of maternal obesity for offspring health. Exp. Physiol. 100(12), 1421–1428 (2015).
Harreiter, J. et al. Management of pregnant women after bariatric surgery. J. Obes. 2018, 4587064 (2018).
Pg Baharuddin, D. M. et al. Bariatric surgery and its impact on fertility, pregnancy and its outcome: A narrative review. Ann. Med. Surg. 72, 103038 (2021).
Akpinar, E. O. et al. National bariatric surgery registries: An international comparison. Obes. Surg. 31(7), 3031–3039 (2021).
Saleem, F. HMC performs rare robotic surgery, in The Peninsula. (2023).
Galazis, N. et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes in women undergoing bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 181, 45–53 (2014).
Kizy, S. et al. National trends in bariatric surgery 2012–2015: Demographics, procedure selection, readmissions, and cost. Obes. Surg. 27(11), 2933–2939 (2017).
Yi, X. Y. et al. A meta-analysis of maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancy after bariatric surgery. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 130(1), 3–9 (2015).
Ajmal, S. et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes associated with multiple repeat cesarean deliveries: A registry-based study from Qatar. Qatar Med. J. 2024(1), 3 (2024).
Lawand, G. et al. The impact of abnormal maternal body mass index during pregnancy on perinatal outcomes: A registry-based study from Qatar. J. Perinat. Med. 51(9), 1197–1205 (2023).
Minisha, F. et al. Perinatal outcomes in women with class IV obesity compared to women in the normal or overweight body mass index categories: A population-based cohort study in Qatar. Obes. Sci. Pract. 10(1), e698 (2024).
Vazhiyelethil, J. et al. Impact of bariatric surgery on maternal gestational weight gain and pregnancy outcomes in women with obesity: A population-based cohort study from Qatar. Qatar Med. J. 2024(1), 2 (2024).
Younes, S. et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of preterm and early term births: A population-based register study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18(11), 5865 (2021).
Younes, S. et al. Incidence, risk factors, and feto-maternal outcomes of inappropriate birth weight for gestational age among singleton live births in Qatar: A population-based study. PLoS ONE 16(10), e0258967 (2021).
Farrell, T. et al. A customised fetal growth and birthweight standard for Qatar: a population-based cohort study. J. Perinat. Med. 52, 878–885. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpm-2024-0060 (2024).
González, I. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery: Improving outcomes for mother and child. Int. J. Womens Health 8, 721–729 (2016).
Hosseini-Chavoshi, M. et al. The health of older women after high parity in TAFT, Iran. Asian Popul. Stud. 7(3), 263–274 (2011).
Al-Shaikh, G. K. et al. Grand multiparity and the possible risk of adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes: A dilemma to be deciphered. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 17, 1–7 (2017).
Ballard, J. L. et al. New Ballard Score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. J. Pediatr. 119(3), 417–423 (1991).
Lutsiv, O. et al. The effects of morbid obesity on maternal and neonatal health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Obes. Rev. 16(7), 531–546 (2015).
Angeliki, A., Dimitrios, P. & Chara, T. Maternal obesity and its association with the mode of delivery and the neonatal outcome in induced labour: Implications for midwifery practice. Eur. J. Midwifery 2, 4 (2020).
Yazdani, S. et al. Effect of maternal body mass index on pregnancy outcome and newborn weight. BMC Res. Notes 5, 34 (2012).
Haseeb, Y. A. Obstetric outcome in obese Saudi pregnant women: A cohort prospective study at a teaching hospital. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 5(2), 142–144 (2017).
Kwong, W., Tomlinson, G. & Feig, D. S. Maternal and neonatal outcomes after bariatric surgery; a systematic review and meta-analysis: Do the benefits outweigh the risks?. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 218(6), 573–580 (2018).
Getahun, D. et al. Perinatal outcomes after bariatric surgery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 226(1), 121.e1-121.e16 (2022).
Boller, M. J. et al. Perinatal outcomes after bariatric surgery compared with a matched control group. Obstet. Gynecol. 141(3), 583–591 (2023).
Akhter, Z. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery and adverse perinatal outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 16(8), e1002866 (2019).
Stephansson, O. et al. Delivery outcomes in term births after bariatric surgery: Population-based matched cohort study. PLoS Med. 15(9), e1002656 (2018).
Carreau, A. M. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery: Balancing risks and benefits. Can. J. Diabetes 41(4), 432–438 (2017).
Cedergren, M. I. Maternal morbid obesity and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcome. Obstet. Gynecol. 103(2), 219–224 (2004).
Chevrot, A. et al. Impact of bariatric surgery on fetal growth restriction: Experience of a perinatal and bariatric surgery center. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 214(5), 655.e1–7 (2016).
Josefsson, A. et al. Bariatric surgery in a national cohort of women: Sociodemographics and obstetric outcomes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 205(3), 206.e1–8 (2011).
Kjaer, M. M. & Nilas, L. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery—a review of benefits and risks. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 92(3), 264–271 (2013).
Maggard, M. A. et al. Pregnancy and fertility following bariatric surgery: A systematic review. JAMA 300(19), 2286–2296 (2008).
Ovesen, P., Rasmussen, S. & Kesmodel, U. Effect of prepregnancy maternal overweight and obesity on pregnancy outcome. Obstet. Gynecol. 118(2 Pt 1), 305–312 (2011).
Pallasmaa, N. et al. Cesarean delivery in Finland: Maternal complications and obstetric risk factors. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 89(7), 896–902 (2010).
Yu, Y. & Groth, S. W. Risk factors of lower birth weight, small-for-gestational-age infants, and preterm birth in pregnancies following bariatric surgery: A scoping review. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 307(2), 343–378 (2023).
Hazan, D. et al. Maternal and neonatal outcome of women before vs. after bariatric surgery: A single tertiary center experience. Am. J. Surg. 224(5), 1252–1255 (2022).
Sheiner, E. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery is not associated with adverse perinatal outcome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol 190(5), 1335–1340 (2004).
Magdaleno, R. Jr. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery: A current view of maternal, obstetrical and perinatal challenges. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 285(3), 559–566 (2012).
Falcone, V. et al. Pregnancy after bariatric surgery: A narrative literature review and discussion of impact on pregnancy management and outcome. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 18(1), 507 (2018).
Al-Dewik, N. et al. Precision medicine activities and opportunities for shaping maternal and neonatal health in Qatar. Pers. Med. 30, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/17410541.2024.2394397 (2024).
Al-Dewik, N. I., Younes, S. N., Essa, M. M., Pathak, S. & Qoronfleh, M. W. Making Biomarkers Relevant to Healthcare Innovation and Precision Medicine. Processes 10, 1107 https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061107 (2022).
A. L.-Dewik, N. I. & Qoronfleh, M. W. Genomics and Precision Medicine: Molecular Diagnostics Innovations Shaping the Future of Healthcare in Qatar. Advances in Public Health 2019, 3807032. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3807032 (2019).
Zhai, K., Yousef, M. S., Mohammed, S., Al-Dewik, N. I. & Qoronfleh, M. W. Optimizing Clinical Workflow Using Precision Medicine and Advanced Data Analytics. Processes 11, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030939 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Qatar National Research Fund (Grant no NPRP 6-238-3-059) and was sponsored by the Medical Research Centre, Hamad Medical Corporation. The authors want to thank QNRF and HMC for their funding as well as their respective institutions for their continued support. The publication of this article is funded by the Medical Research Center, HMC, Doha, Qatar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and study design: [NA-D, MS] formulated the research goals and aims, designed the methodology for the study, and defined the overall research strategy. Data collection and analysis: [*AM, *AA-D, SA*, YS, SH, AA, LM, HAK, RS, MS] were responsible for data curation, including collection, validation, and analysis. They applied statistical techniques and interpreted the data. Writing—original draft preparation: [TO, HAK, AA-N, MN-D,] took the lead in writing the manuscript, and drafting the initial version, including the abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Writing—review and editing: [NA-D, MS, MQ, TF, PVA, MA-Qi, A.R] critically reviewed and revised the manuscript, contributing to the refinement of the study's narrative, argumentation, and overall presentation. Supervision and project administration: [SA-O, MA-I, UA, JS, BT, GN, NR, HA-R] provided oversight, coordinated the research activities, and managed the execution of the project. Funding acquisition: [NA-D, HA-R] was involved in acquiring the financial support for the project and leading the grant application process. *These authors contributed equally to this work and shared the third authorship of this article. l authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Dewik, N.I., Samara, M., Mahmah, A. et al. Maternal and neonatal risks and outcomes after bariatric surgery: a comparative population based study across BMI categories in Qatar. Sci Rep 14, 27107 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69845-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69845-y
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes following metabolic bariatric surgery in the United Arab Emirates
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2025)