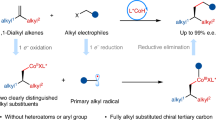
Abstract
The tunable enantioselective functionalization of alkene feedstocks represents a highly desirable yet predominantly unresolved tactic for generating high-value scaffolds. Herein, we report a tunable enantioselective electrolytic system for dehydrogenative allylation, dehydrogenative alkenylation, and hydroalkylation reactions with identical substrates to afford structurally diverse products. This success hinges on the rational design of the stereoselective coupling of an electrogenerated nickel-bound α-carbonyl radical species that can trap unactivated alkenes and engage in various subsequent radical termination processes to enable the intermolecular functionalization of unactivated alkenes. The mild reaction conditions and sustainable electrocatalytic radical platform guarantee excellent functional group tolerance and substrate compatibility with unactivated alkenes (63 examples, up to 98% e.e.), and the process evolves H₂ without the need for external chemical oxidants. The utility of this enantioselective electrolytic strategy is demonstrated by its application in the stereoselective formal synthesis of (S)-SYK inhibitor, signifying substantial progress in synthetic methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The catalytic intermolecular functionalization of alkenes is a fundamental and essential transformation to construct basic organic frameworks in organic synthesis, which have important applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, catalysts, and materials1. A typical carbon−carbon bond-forming reaction, renowned as the Michael reaction2, is the addition of carbanions or their catalytic equivalents to activated alkenes bearing electron-withdrawing groups, such as α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. The catalytic functionalization of unactivated alkenes is an appealing strategy for creating structurally diverse motifs and performing late-stage derivatization of medicinally relevant molecules3,4,5. However, the low electrophilicity of unactivated alkenes makes it challenging to achieve rapid, straightforward, and stereoselective intermolecular additions with HOMO-raised nucleophiles, particularly in a tunable manner6. This requires alternative synthetic strategies to achieve divergent synthesis and excellent enantioselectivity7,8. We rationalized that radical functionalization of alkene feedstocks, such as abundant and inexpensive hexene to undergo the initial radical addition event, followed by tunable radical termination steps to achieve multiple transformations, represents a viable strategy for enantioselective divergent alkene transformation (Fig. 1a)9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17.
Organic electrosynthesis stands out as a sustainable synthetic avenue that enables the controlled occurrence of single electron transfer (SET) and facilitates the generation of radical intermediates from bench-stable substrates under mild conditions, eliminating the need for exogenous chemical oxidants18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29. However, the stereocontrolled functionalization of unactivated alkenes remains a formidable challenge. Although electrochemical oxidative allylation has been demonstrated—as exemplified by the work of the Xu group10,12—achieving analogous dehydrogenative alkenylation and hydroalkylation under electrolytic conditions continues to pose significant hurdles. More broadly, the development of electrochemical radical addition platforms capable of divergently accessing dehydrogenative allylation, alkenylation, and hydroalkylation from identical precursors with high chemoselectivity and stereocontrol represents a major unmet goal in synthetic chemistry. The integration of electrosynthesis and asymmetric catalysis has emerged as a highly potent and versatile synthetic approach for developing unconventional reaction pathways to generate reactive stereocontrollable radical intermediates for streamlined access to valuable chemical building blocks30,31,32,33,34,35,36, offering rational and predictable means for C−C bond formation from a common precursor in synthetic chemistry37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49.
From the outset, the endeavor to achieve tunable enantioselective functionalization of unactivated alkenes has been met with the challenge of controlling selectivity in radical addition50,51,52,53,54 and termination owing to the anticipated multiple side reactions. To address this issue, we devised a catalytic cycle with a chiral Lewis acid-coupled electron transfer (LCET) process and introduced a powerful electrocatalytic platform for the enantioselective α-functionalization of carbonyl compounds (Fig. 1b)34,35. A vital design criterion is the nickel-bound enolate species, which are more prone to anodic oxidation, selectively generate chirals, thus effectively controlling the stereochemistry of subsequent radical addition reactions and circumventing noncatalytic racemic background reactions arising from direct oxidation of the carbonyl substrate. Upon radical addition, we propose that the chiral electrocatalyst-mediated alkene functionalization proceeds through three competing radical termination pathways, each generating distinct products. The introduction of a secondary cobalt catalyst facilitates hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) to form dehydrogenative allylation products14,15,16. Alternatively, further oxidation of the alkyl radical enables a radical-polar crossover process to form oxidative alkenylation products13, whereas direct hydrogen atom transfer leads to hydroalkylation products36. In this work, we report a general and enantioselective electrocatalytic system for the divergent functionalization of unactivated alkenes. This strategy enables dehydrogenative allylation, alkenylation, and hydroalkylation from a chiral nickel-bound radical intermediate with high stereoselectivity, broad functional group tolerance, and compatibility with diverse carbon nucleophiles (Fig. 1c). The asymmetric catalytic system provides a unified platform to systematically investigate competitive radical termination pathways under mild electrochemical conditions.
Results
Reaction development
To validate our hypothesis, we initiated the reactions of racemic benzoxazolyl acetate (1a) and hexene (2a) in an undivided cell equipped with a carbon felt (CF) anode and a platinum (Pt) cathode under a constant current of 2.0 mA at 25 °C (Table 1a). Encouragingly, with ferrocenemethylamine A1 functioning as the mediator and Pybox L1 acting as the chiral ligand, the alkenylated product 4a could be obtained in 11% yield and 60% enantiomeric excess (e.e.). A subsequent ligand screening (L2-L5) revealed that the use of a Box ligand with a cyclopentyl group (L5), resulted in 4a in 72% yield and 92% e.e. A subsequent evaluation of additives indicated that the chemoselectivity of the reaction is strongly dependent on additive selection, even when identical substrates are employed. Using the salen-Co additive A2, the alkenylated and allylated products were obtained with a chemoselectivity of 1:1. The similar stereoselectivities observed for both products (see Supplementary Table S2) further support that they share a common stereocontrol mode in terms of quaternary carbon center formation, whereas divergent radical termination pathways account for their structural differences. The effects of different substituted salen-Co additives on the reaction chemoselectivity were examined (A2-A5), and trifluoromethyl-substituted salen-Co A5 selectively gave rise to allylated product 3a (74% yield, 92% e.e.). The differential chemoselectivity among Co catalysts (A2–A5) correlates with their Co–H bond dissociation energies (BDE), where the higher BDE of A5 enhances HAT efficiency and favors allylation product formation (see Supplementary Table S3). Notably, employing (TMS)₃Si-H (BDE = 79 kcal/mol) as a radical-terminating HAT reagent enabled the synthesis of hydroalkylated product 5a in 60% yield and 93% e.e. Remarkably, all three reaction variants delivered exceptional enantioselectivity (3a-5a), underscoring the generality of this Ni-electrocatalytic approach.
Additional control experiments were carried out to elucidate the process of electricity-driven Ni/Co dual-catalyzed dehydrogenative allylation reactions (Table 1b). The absence of a chiral Lewis acid catalyst (entry 2), additive A5 (entry 3), or electric current (entry 4) completely inhibited the generation of 3a, thus ruling out competing racemic scenarios and highlighting the criticality of these conditions for the process. Chemical oxidation with Ag₂O resulted in a loss of stereocontrol, delivering racemic 3a in 22% yield (entry 5). Additional studies revealed that product 3a forms even without the chiral Ni catalyst (entry 6), indicating that Ag₂O serves a dual function as both an oxidant and a Lewis acid, thereby promoting a competing racemic pathway. The controlled electrochemical delivery of electrons ensures a clean transformation under mild redox conditions while suppressing the racemic background reactions observed with chemical oxidants (entry 1 vs 5). These results highlight the unique advantages of electrochemistry for the catalytic asymmetric transformations reported here in terms of the cleanness of conversion and enantioselectivity.
Substrate scope
With the optimal reaction conditions established, we investigated the versatility of this electricity-enabled enantioselective dehydrogenative allylation reaction (Fig. 2). Initially, the functional group tolerance of various unactivated alkenes was tested (3a-3w). Simple alkenes bearing potentially reactive functionalities such as chloride (3b), bromide (3c), hydroxyl (3d), protected hydroxyl groups (3e-3j), phthalimide (3k), and amide (3l) were well accommodated in this protocol, delivering the expected products effectively. Alkene substrates bearing carbon chains of different lengths were transformed to the corresponding products in good yields, with excellent chemo- and enantioselectivities (3m-3t). The absolute configuration of 3t was confirmed via X-ray diffraction, and the others were assigned analogously. Encouraged by the broad functional group tolerance under mild electrolytic reaction conditions, we explored the generality of the present protocol for complex molecules. Alkenes derived from (R)-carvone (3u) and pregnenolone (3v) were suitable substrates. The reaction with cyclic alkene also proceeded smoothly to afford product 3w in 70% yield. These results demonstrate that the Ni/Co dual electrocatalytic system has a wide substrate scope for unactivated alkenes with high functional group tolerance.
Reactions were performed by using 1 (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.5 mmol), Ni(OAc)2·4H2O (10 mol%), L5 (11 mol%), A5 (20 mol%), morpholine (0.1 mmol), and nBu4NBF4 (0.1 M) in THF/TFE under constant-current conditions (1.5 mA) in an undivided cell, 4.5 F/mol. Isolated yields after chromatography are shown. a2 (1.2 mmol). b10 °C. cA2 (10 mol%), 2 (1.5 mmol) and without base. d-10 °C. eA4 (10 mol%), 2 (1.5 mmol), and 2,6-Lutidine (0.1 mmol) in MeOH/TFE. fA3 (20 mol%), L2 (11 mol%), and 2 (2 mmol), without base in DCE/TFE. gL3 (11 mol%), 2,6-Lutidine (0.1 mmol).
Further investigation with substituted racemic benzoxazolyl acetate 1 revealed that variations in the benzoxazole moiety had little effect on the reaction outcomes (3x-3ab). Variation of the ester group of racemic benzoxazolyl acetates had no noticeable effect on the reaction outcomes (3ac-3af). Racemic 1 bearing various substituents at the α-position of the carbonyl group also performed efficiently in enantioselective electrocatalytic reactions (3ag-3aj). Remarkably, the reaction also proved adaptable to 1,2-benzisoxazol-3-ylacetate, consistently delivering 3ak in high yield and enantioselectivity (69% yield, 88% e.e.).
Upon research on electrochemically promoted asymmetric anodic allylation reactions, we demonstrate that the reaction chemoselectivity can be precisely controlled by medium engineering, where ferrocene-based A1 selectively promotes dehydrogenative alkenylation over competing allylation pathways. Under the optimized reaction conditions, a broad range of unactivated alkenes were investigated (Fig. 3). Heteroatom-substituted alkenes proceeded smoothly under standard conditions, delivering alkenylation products with comparable yields and excellent chemoselectivities (4a-4l). Notably, the electrocatalytic dehydrogenative alkenylation approach demonstrated its practical utility for large-scale applications by effectively scaling the reaction to 6 mmol, consistently producing product 4a in a high yield and excellent enantioselectivity. Alkenes with aryl (4 m and 4n) or long-chain (4o) alkane substituents can effectively participate in this reaction to afford excellent enantioselectivity. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the R configuration of 4l. Furthermore, 1,2-benzisoxazol-3-ylacetate was also compatible with the desired product in 64% yield and 92% e.e. (4p).
Reactions were performed by using 1 (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.5 mmol), Ni(OAc)2·4H2O (10 mol%), L5 (11 mol%), A1 (10 mol%), 2,6-Lutidine (0.1 mmol), nBu4NPF6 (0.1 M) and DCE/TFE under constant-current conditions in an undivided cell, 4.5 F/mol. Isolated yields after chromatography are shown. aL3 (11 mol%), 2 (2 mmol) at 40 °C.
Hydroalkylation via tandem radical reactions efficiently results in the formation of quaternary carbon centers in complex molecular frameworks from simple precursors. This prompted us to investigate alternative hydrogen transfer reagents as third coupling partners to effectively trap the key alkyl radical intermediate. Having optimized the reaction conditions with (TMS)3Si-H as a hydrogen transfer reagent, we investigated the generality of this asymmetric multicomponent electrochemical difunctionalization of alkenes (Fig. 4). Notably, both unactivated alkenes and diversely substituted benzoxazolyl acetates were well tolerated, consistently affording the desired products (5a-5h) in high yields with excellent enantioselectivities.
Reactions were performed by using 1 (0.1 mmol), 2 (2 mmol), Ni(OAc)2·4H2O (10 mol%), L5 (11 mol%), A1 (10 mol%), (TMS)3Si-H (0.5 mmol), 2,6-Lutidine (0.1 mmol), nBu4NPF6 (0.1 M) and MeOH/TFE under constant-current conditions in an undivided cell, 6.0 F/mol. Isolated yields after chromatography are shown. aL2 (11 mol%) in DCE/TFE.
Synthetic applications
The Ni/Co electrocatalyzed asymmetric dehydrogenative allylation reaction is also applicable to propylene gas (Fig. 5a). The alkene moiety in enantioenriched product 3a provides a versatile synthetic handle for further transformations to afford alkane 6 and alcohol 7 (Fig. 5b). The reduction of the ester group of 3a followed by hydrogenation of the alkene afforded corresponding alcohol 8 in 66% yield and 92% e.e. Moreover, the benzoxazole moiety in enantioenriched product 3x was readily converted to an aldehyde group in 9 and ketone groups in 10 and 11, enabling access to diverse chiral architectures while preserving enantiopurity.
Our enantioselective methodology was further verified via the asymmetric formal synthesis of (S)-SYK inhibitor (Fig. 5c)55. Following the reduction of enantioenriched hydroalkylation product 5d, subsequent O-mesylation cleanly afforded corresponding dimesylate 12 while maintaining the original stereochemistry. Treatment of dimesylate 12 with benzylamine provided cyclic amine 13, which underwent smooth N-deprotection followed by Boc protection to deliver N-Boc product 14 in 92% yield with complete retention of enantiopurity. Subsequent removal of the benzoxazole group generated an aldehyde that was reduced to afford enantioenriched alcohol 15, a versatile intermediate for (S)-SYK inhibitor synthesis55.
Mechanistic investigations
A range of experiments was conducted to explore the mechanism of asymmetric electrolytic transformation (Fig. 6). Initially, cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments were run on the reaction components. Upon addition of the chiral nickel catalyst, the oxidative peak of benzoxazolyl propanoate 1b shifted negatively (Fig. 6a, left) and exhibited a concurrent increase in current with higher concentrations of 1b (Fig. 6a, middle), supporting the facile oxidation of a nickel-bound enolate intermediate. Critically, while the substrate alone with ferrocenemethylamine A1 showed no significant current response, the addition of the chiral nickel catalyst led to a substantial increase in the oxidative current with attenuation of the reduction peak. This clear contrast provides evidence for efficient electron transfer between A1 and the Ni-bound enolate intermediate (Fig. 6a, right).
To unequivocally verify the hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) mechanism in the hydroalkylation reaction, we conducted a deuterium-labeling experiment by replacing (TMS)₃Si–H with (TMS)₃Si-D (Fig. 6b). The reaction exclusively afforded deuterated product 16 with 98% D-incorporation, providing direct evidence for HAT-mediated C–H bond formation and the radical nature of the key intermediate. Radical clock experiments provide further support for the formation of the α-keto radical intermediate in the enantioselective electrochemically tunable protocol (Fig. 6c). The β-pinene 17 was treated under our electrochemical conditions, and ring-opening product 18 was obtained in 90% yield, 9:1 d.r., and 88% e.e. Furthermore, we investigated the electrochemical reaction of 1a with cyclopropane-containing alkene 19. Notably, both additives (A1 and A5) efficiently promoted the cyclopropyl ring-opening process, delivering product 20 with excellent enantioselectivity. As supported by the data in Fig. 6, these results strongly corroborate our proposed mechanism involving nickel-bound radical intermediates in the asymmetric electrochemical functionalization of alkenes.
To unravel the origin of enantioselectivity in the Ni/Co dual electrocatalytic synthesis of allylated product 3, we performed comprehensive DFT calculations (Fig. 7a). The computational studies systematically examined the reaction’s dual selectivity that controls enantioselectivity in the radical addition step and product chemoselectivity during radical termination. Initially, the chiral nickel-bound α-carbonyl radical (INT3q) undergoes Giese addition (via TS2-Siq) to generate the alkyl radical INT4q. The transition-state structures controlling the stereochemistry are shown in Fig. 7b. TS2-Siq leads to the experimentally preferred stereoisomer (R)−3a, whereas TS2-Req produces the minor enantiomer (S)−3a. The difference in the free energy of activation (ΔΔG‡) was 1.8 kcal/mol, which is consistent with the experimentally observed selectivity of 92% e.e. (Table 1). The enantioselectivity primarily stems from distinct coordination modes of the benzoxazolyl ester substrate. These different coordination modes lead to opposing facial selectivities, as illustrated in Supplementary Fig. S9. Further energy decomposition analysis (Supplementary Fig. S8) indicates that the variation in coordination geometry arises mainly from steric repulsion between the phenyl ring of the substrate and the BOX ligand. We subsequently investigated the radical termination process promoted by cobalt as an HAT catalyst in the synergistic catalytic system. Radical intermediate INT5d undergoes facile β-hydrogen atom transfer (β-HAT) when activated by CoII species. TS3-3as(BS) leads to the formation of dehydrogenative allylation product 3a, whereas TS3-4as(BS) generates dehydrogenative alkenylation product 4a. DFT calculations reveal a 2.2 kcal/mol lower free energy barrier for HAT at the favored position (TS3-3as(BS)) compared to the alternative site (TS3-4as(BS)) (Fig. 7c), rationalizing the observed chemoselectivity in dehydrogenative allylation.
All calculations described here use the wB97X-D/def2-TZVP/SMD(THF:TFE = 1:5)//B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-31 G(d)-SDD level of theory. a Gibbs free energy profile of asymmetric Ni/Co dual-electrocatalyzed dehydrogenative allylation. The lightning symbol represents the anodic oxidation process, performed at +0.26 V vs. SCE corresponding to the experimentally determined onset potential of the nickel-bound enolate. Spin states are annotated as superscripts: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), and BS (broken symmetry). b Transition states of Ni-catalyzed asymmetric radical addition. c Transition states of Co-catalyzed HAT. For clarity, hydrogen atoms were omitted (except for H in HAT). The black numbers represent the key bond lengths in the transition states. Color scheme: C, gray; O, red; N, blue; H, white; F, bright green; Ni, light green; Co, pink. d Proposed catalytic cycles.
Taking into account the combined results of the mechanistic studies and DFT calculations, a plausible catalytic mechanism based on electric-triggered asymmetric catalysis is outlined in Fig. 7d. The asymmetric electrochemical catalysis is initiated by the condensation of 1 with the nickel catalyst, resulting in the formation of a nickel-bound enolate intermediate (I). Anodic oxidation of I through an anodic SET pathway was proposed to form a nickel-coordinated radical intermediate (II). This radical species undergoes stereoselective interception by unactivated alkenes to establish a stereogenic center, forming alkyl radical III, a key step that governs asymmetric induction in these tunable catalytic cycles. Critically, the divergence between the dehydrogenative allylation, dehydrogenative alkenylation, and hydroalkylation pathways is governed by distinct radical termination processes. Under Ni/Co dual electrocatalytic conditions, in situ-generated alkyl radical III undergoes a sterically controlled HAT process via the cobalt catalyst, preferentially forming dehydrogenative allylation products 3 at the less hindered site. Alternatively, the introduction of (TMS)3Si-H as the group-transfer reagent selectively traps radical III to deliver hydroalkylation products 5. Conversely, the use of additive A1 in the absence of additional termination reagents promotes single-electron oxidation of alkyl radical intermediate III to form carbocationic species V. This intermediate is stabilized by 2,6-lutidine and undergoes base-promoted β-hydride elimination preferentially from the more acidic proximal carbon, ultimately furnishing enantioenriched dehydrogenative alkenylation products 4.
We have developed a versatile nickel-electrocatalytic system that enables tunable enantioselective transformations of identical substrates to access three distinct product classes—dehydrogenative allylation, dehydrogenative alkenylation, and hydroalkylation—all with excellent enantioselectivity (up to 98% e.e.). The key to this success is the stereocontrolled coupling of electrogenerated nickel-bound α-carbonyl radicals with unactivated alkenes, where selective radical termination pathways dictate chemoselectivity. This sustainable electrocatalytic platform operates under mild conditions without external oxidants, demonstrating exceptional functional group tolerance and a broad substrate scope (63 examples). The synthetic utility of this approach is highlighted through a streamlined formal synthesis of the (S)-SYK inhibitor, indicating a significant advance in electrochemical asymmetric synthesis.
Methods
General procedure for the enantioselective Ni/Co dual-electrocatalytic functionalization of unactivated alkenes
A 10 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stir bar was charged with 1 (0.1 mmol), 2 (0.5 mmol), Ni(OAc)2·4H2O (0.01 mmol), L5 (0.011 mmol), A5 (0.02 mmol), morpholine (0.1 mmol), nBu4NBF4 (0.3 mmol), THF (0.5 mL) and TFE (2.5 mL) under an argon atmosphere. The flask was equipped with a carbon felt (1.5 cm × 1.5 cm × 3 mm) as the anode and a platinum plate (1.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 0.2 mm) as the cathode. Constant current (1.5 mA) electrolysis was carried out at 25 °C until complete consumption of the starting material (monitored by TLC). The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel chromatography to afford the desired product 3.
Data availability
Crystallographic data for the structures reported in this article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, under deposition numbers CCDC 2430133 (3t) and CCDC 2430132 (4l). Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. All other data supporting the findings of this study, including experimental procedures and compound characterization, NMR, and HPLC are available within the Article and its Supplementary Information or from the corresponding authors. The authors declare that all other data supporting the findings of this study are available within this Article and its Supplementary Information. Source Data are provided with this paper. NMR data in a Mnova file format and HPLC traces are available at Zenodo at https://zenodo.org/records/17364427, under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
McDonald, R. I., Liu, G. & Stahl, S. S. Palladium(II)-catalyzed alkene functionalization via nucleopalladation: stereochemical pathways and enantioselective catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 111, 2981–3019 (2011).
Zheng, K., Liu, X. & Feng, X. Recent advances in metal-catalyzed asymmetric 1,4-conjugate addition (ACA) of nonorganometallic nucleophiles. Chem. Rev. 118, 7586–7656 (2018).
Song, L. et al. Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed remote difunctionalizing carboxylation of unactivated alkenes with CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 21121–21128 (2020).
Gnaim, S. et al. Cobalt-electrocatalytic HAT for functionalization of unsaturated C–C bonds. Nature 605, 687–695 (2022).
Zhou, X.-S. et al. Direct asymmetric α-alkylation of β-ketocarbonyl compounds with simple olefins by photoredox-nickel-hydrogen atom transfer triple catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202424915 (2025).
Zhan, G., Du, W. & Chen, Y.-C. Switchable divergent asymmetric synthesis via organocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 1675–1692 (2017).
Dénès, F., Pérez-Luna, A. & Chemla, F. Addition of metal enolate derivatives to unactivated carbon−carbon multiple bonds. Chem. Rev. 110, 2366–2447 (2010).
Mondal, S. et al. Enantioselective radical reactions using chiral catalysts. Chem. Rev. 122, 5842–5976 (2022).
Zhu, L. et al. Electrocatalytic generation of amidyl radicals for olefin hydroamidation: use of solvent effects to enable anilide oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 2226–2229 (2016).
Cai, C.-Y. et al. Tailored cobalt-salen complexes enable electrocatalytic intramolecular allylic C–H functionalizations. Nat. Commun. 12, 3745 (2021).
Lei, G., Xu, M., Chang, R., Funes-Ardoiz, I. & Ye, J. Hydroalkylation of unactivated olefins via visible-light-driven dual hydrogen atom transfer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 11251–11261 (2021).
Chen, M., Wu, Z.-J., Song, J. & Xu, H.-C. Electrocatalytic allylic C−H alkylation enabled by a dual-function cobalt catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202115954 (2022).
Liang, K., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Nickel-catalyzed switchable asymmetric electrochemical functionalization of alkenes. Sci. Adv. 8, eadd7134 (2022).
Crossley, S. W. M., Barabé, F. & Shenvi, R. A. Simple, chemoselective, catalytic olefin isomerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 16788–16791 (2014).
Wang, S. et al. Cobalt-catalysed allylic fluoroalkylation of terpenes. Nat. Synth. 2, 1202–1210 (2023).
Wang, S. et al. Radical-triggered translocation of C–C double bond and functional group. Nat. Chem. 16, 1621–1629 (2024).
Jia, Z., Cheng, L., Zhang, L. & Luo, S. Asymmetric C–H dehydrogenative alkenylation via a photo-induced chiral α-imino radical intermediate. Nat. Commun. 15, 4044 (2024).
Francke, R. & Little, R. D. Redox catalysis in organic electrosynthesis: basic principles and recent developments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 2492–2521 (2014).
Feng, R., Smith, J. A. & Moeller, K. D. Anodic cyclization reactions and the mechanistic strategies that enable optimization. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 2346–2352 (2017).
Yan, M., Kawamata, Y. & Baran, P. S. Synthetic organic electrochemical methods since 2000: on the verge of a renaissance. Chem. Rev. 117, 13230–13319 (2017).
Jiang, Y., Xu, K. & Zeng, C. Use of electrochemistry in the synthesis of heterocyclic structures. Chem. Rev. 118, 4485–4540 (2018).
Kärkäs, M. D. Electrochemical strategies for C–H functionalization and C–N bond formation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 5786–5865 (2018).
Moeller, K. D. Using physical organic chemistry to shape the course of electrochemical reactions. Chem. Rev. 118, 4817–4833 (2018).
Möhle, S. et al. Modern electrochemical aspects for the synthesis of value-added organic products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 6018–6041 (2018).
Nutting, J. E., Rafiee, M. & Stahl, S. S. Tetramethylpiperidine N-oxyl (TEMPO), phthalimide N-oxyl (PINO), and related N-oxyl species: electrochemical properties and their use in electrocatalytic reactions. Chem. Rev. 118, 4834–4885 (2018).
Tang, S., Liu, Y. & Lei, A. Electrochemical oxidative cross-coupling with hydrogen evolution: a green and sustainable way for bond formation. Chem 4, 27–45 (2018).
Wiebe, A. et al. Electrifying organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 5594–5619 (2018).
Meyer, T. H., Choi, I., Tian, C. & Ackermann, L. Powering the future: how can electrochemistry make a difference in organic synthesis?. Chem 6, 2484–2496 (2020).
Zhang, J., Zhu, W., Chen, Z., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Dual-catalyzed stereodivergent electrooxidative homocoupling of benzoxazolyl acetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 1522–1531 (2024).
Huang, X., Zhang, Q., Lin, J., Harms, K. & Meggers, E. Electricity-driven asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis. Nat. Catal. 2, 34–40 (2019).
Zhang, Q., Chang, X., Peng, L. & Guo, C. Asymmetric Lewis acid catalyzed electrochemical alkylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 6999–7003 (2019).
Fu, N. et al. New bisoxazoline ligands enable enantioselective electrocatalytic cyanofunctionalization of vinylarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 14480–14485 (2019).
Xiong, P., Hemming, M., Ivlev, S. I. & Meggers, E. Electrochemical enantioselective nucleophilic α-C(sp3)–H alkenylation of 2-acyl imidazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 6964–6971 (2022).
Liang, K., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Enantioselective nickel-catalysed electrochemical cross-dehydrogenative amination. Nat. Synth. 2, 1184–1193 (2023).
Li, J. et al. Enantioselective nickel-electrocatalyzed cross-dehydrogenative α- and γ-nitroalkylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 34043–34052 (2024).
Wang, Q. et al. Enantioselective multicomponent electrochemical difunctionalization of terminal alkynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 8917–8927 (2024).
DeLano, T. J. & Reisman, S. E. Enantioselective electroreductive coupling of alkenyl and benzyl halides via nickel catalysis. ACS Catal 9, 6751–6754 (2019).
Li, L., Li, Y., Fu, N., Zhang, L. & Luo, S. Catalytic asymmetric electrochemical α-arylation of cyclic β-ketocarbonyls with anodic benzyne intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 14347–14351 (2020).
Dhawa, U. et al. Enantioselective pallada-electrocatalyzed C−H activation by transient directing groups: expedient access to helicenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 13451–13457 (2020).
Gao, P.-S. et al. CuII/TEMPO-catalyzed enantioselective C(sp3)–H alkynylation of tertiary cyclic amines through Shono-type oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 15254–15259 (2020).
Song, L. et al. Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes. Nat. Chem. 12, 747–754 (2020).
Wang, Z.-H. et al. TEMPO-enabled electrochemical enantioselective oxidative coupling of secondary acyclic amines with ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 15599–15605 (2021).
Ding, W., Li, M., Fan, J. & Cheng, X. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic 4-pyridinylation via electroreductive substitution reaction. Nat. Commun. 13, 5642 (2022).
Gao, S., Wang, C., Yang, J. & Zhang, J. Cobalt-catalyzed enantioselective intramolecular reductive cyclization via electrochemistry. Nat. Commun. 14, 1301 (2023).
Hu, X., Cheng-Sánchez, I., Cuesta-Galisteo, S. & Nevado, C. Nickel-catalyzed enantioselective electrochemical reductive cross-coupling of aryl aziridines with alkenyl bromides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 6270–6279 (2023).
Tan, X., Wang, Q. & Sun, J. Electricity-driven asymmetric bromocyclization enabled by chiral phosphate anion phase-transfer catalysis. Nat. Commun. 14, 357 (2023).
von Münchow, T., Dana, S., Xu, Y., Yuan, B. & Ackermann, L. Enantioselective electrochemical cobalt-catalyzed aryl C–H activation reactions. Science 379, 1036–1042 (2023).
Zhou, G. et al. Base-promoted electrochemical CoII-catalyzed enantioselective C−H oxygenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202302964 (2023).
Mazzarella, D. et al. Electrochemical asymmetric radical functionalization of aldehydes enabled by a redox shuttle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202401361 (2024).
Sibi, M. P., Ji, J., Wu, J. H., Gürtler, S. & Porter, N. A. Chiral Lewis acid catalysis in radical reactions: enantioselective conjugate radical additions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 9200–9201 (1996).
Sibi, M. P., Ji, J., Sausker, J. B. & Jasperse, C. P. Free radical-mediated intermolecular conjugate additions. Effect of the Lewis acid, chiral auxiliary, and additives on diastereoselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 7517–7526 (1999).
Sibi, M. P. & Chen, J. Enantioselective tandem radical reactions: vicinal difunctionalization in acyclic systems with control over relative and absolute stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 9472–9473 (2001).
Sibi, M. P., Zimmerman, J. & Rheault, T. Enantioselective conjugate radical addition to β-acyloxy acrylate acceptors: An approach to acetate Aldol-type products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 4521–4523 (2003).
Sibi, M. P., Petrovic, G. & Zimmerman, J. Enantioselective radical addition/trapping reactions with α,β-disubstituted unsaturated imides. Synthesis of anti-propionate Aldols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2390–2391 (2005).
Curtis, N. R. et al. Asymmetric fluorination approach to the scalable synthesis of a SYK Inhibitor. Org. Process Res. Dev. 19, 865–871 (2015).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the supercomputing center of USTC for providing computational resources and the Instruments Center for Physical Science of USTC. The authors acknowledge financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFA1506700, C.G.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21971227, 22222113, C.G.), CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research (YSBR-054, C.G.), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK9990000090, WK9990000111, C.G.), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK9990000133, C.G.). The project was supported by the Open Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no.2023M743373, 2024T170881, L.P.), and the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (GZB20230708, L.P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.G. conceived the project. T.X. performed the experiments and analyzed the data. M.L., J.Z., and L.P. synthesized the substrates and ligands. All authors discussed the results and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Zhongyi Zeng and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, T., Liu, M., Zhang, J. et al. Tunable enantioselective electrocatalytic functionalization of unactivated alkenes. Nat Commun 17, 1372 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-68123-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-68123-3